第四节 免疫细胞化学技术的某些新进展
免疫细胞化学技术在继续改进和完善中,新的技术方法不断出现。除目前国内已开始应用的免疫金技术和免疫金银技术外,80年代,新的免疫细胞化学技术还有半抗原交联抗体法和令人瞩目的分子杂交免疫细胞化学技术。免疫金银技术和分子杂交免疫细胞化学技术将分别以专章 叙述,本节 仅就半抗原交联抗体法作一简要介绍。
【半抗原交联抗体法(Hapten –Coupled techniques)】
近年来,为提高敏感性和减低非特异性染色,有些学者(Cammisuli 1976; Jassani 1981; Falini 1983) 在常规免疫细胞化学技术的基础上,发展了半抗原交联抗体法,可作免疫荧光或免疫酶染色。本法的基本原理是应用半抗原标记第一抗体。常用的半抗原有阿散酸,即对氨基苯砷酸(Arsanilic acid, ARS),对氨基苯酰甘氨酸(P—aminobenzoyl glycine),亚对氨苯酰甘氨酸(N—P—aminobonozyl glutamic acid)和二硝基苯氨基丙睛亚胺酸脂(dinitrophenyl aminopropionitrile imido ester, DNP)。通过酰胺化反应把半抗原结合到抗体分子上。在间接法(二步法)中,先以半抗原标记的特异性抗体(第一抗体)孵育切片,然后加入半抗原的标记抗体,(标记物可为荧光素或酶)(图6-4)。在PAP染色(三步法)中,先用半抗原标记的第一抗体孵育切片,再加未标记的抗半抗原特异性抗体作为桥抗体,第三步加半抗原交联的PAP与之反应,并作酶的呈色反应(图6-5)。第一和第三抗体分别为半抗原标记的特异性抗体和以半抗原标记的抗酶抗体制备的含半抗原的PAP复合物。本法具有许多优点,主要是:①敏感性高。由于本法是通过酰胺化反应标记半抗原,对抗体活性损失极小,抗体保留较高的活性,能结合较大量的半抗原,平均每个球蛋白分子可同时结合20个半抗原分子,每个半抗原又可用抗半抗原抗体相结合,特异免疫反应明显放大,其敏感性明显高于常规的免疫酶和免疫荧光染色技术,特别有助于发现滴度低的同种抗血清和含抗原量较少的组织。②可用于双重免疫染色。利用两种交叉反应的半抗原如阿散酸和对氨基苯酰甘氨酸分别标记来自同一种动物的两种特异性(第一抗体)血清,应用两步法或三步法,即可在同一张切片内同时显示两种不同的抗原。③由于特异性强、敏感性高,因此背景染色低。

图6-4 半抗原标记抗体酶技术—两步法
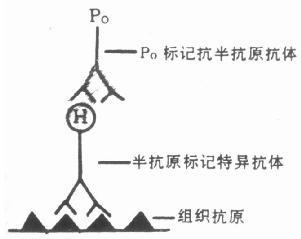
图6-5 半抗原标记抗体酶技术—PAP法
参考文献
1.Bayer EA, et al . Affinity Cytochemistry: The localization of lectin and antibody receptors on erythrocytes iva avidin—biotin complex. FEBS Letters, 1975;68:240
2.Brabec RK, et al . Differential lectin binding to cellular membranes in the epithelium of the new born rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1987;77:477
3.Falini B. New development in immunoperoxidase techniques and their application. Arch Pathl Lab Med, 1983;107:105
4.Jasani B. Et al. Use of monoclonal antihapten antibodies of immno—Iocalization of tissue antigens. J Clin Pathol, 1981;34:100
5.Kivela T and Tarkanen A. A lectin cytochemical study of glycoconjugates in the human retina. Cell Tissue Res, 1987;249:277
6.Newman RA, et al . Binding of peanut lectin to breast epithelium, human carcinoma and cultured rat mammary stem cells:Use of the lectin as a marker of mammary differentiation. J Natl Cancer Inst, 1979;63:1339
7.Ponder BAJ, et al . Lectin histochemistry. (Immunocyto—chemistry Eds. JM Polak and SV Noorden )Wright PSG Bristol London Boston 1983;129
8.Rose ML, et al . Peanut lectin binding properties of germinal centres of mouse lymphoid tissue. Nature, 1980;284:364
9.Streit WJ and Kreutzberg GW. Lectin binding by resting and reactive microglia. Neurocytology, 1987;16:249
10. Virtanen AL, et al . Fluorochrome – coupled lectins reveal distinct ceullar domains in human epidermis. J Histochem Cytochem, 1986;34(3):307
11.Watanalte M, et al. Discrete distribution of binding sites for Dolichos biflrous agglutinin and for peanut agglutinin (PNA)in mouse organ tissues. J Histochem Cytochem, 1981; 29:779
12. 王益寿.葡萄球菌蛋白A的性质和应用.国外医学(生物制品分册),1980;4:145
13. 张华忠,等. 凝集素在人体正常组织的定位.中华医学杂志,1985;65:144~147
14. 沈铭昌,等.应用DBA标记胃粘膜上皮化生与胃癌的关系.肿瘤,1987;7:55~57
15.Ueda T, et al. Lectin histochemistry of maligant fibrohistocyte tumors. Am J Surg Pathol, 1987;11(4):257
16. Ree HJ. Lectin disfinction of benign from malignant histocyts. Cancer, 1985;56(8):2046
(蔡文琴)
校对:2000/05/17 杨丽华
, 百拇医药