关键词:U50488;心律失常;心肌细胞;磷酯酶C;细胞内钙
【摘要】 观察选择性Kappa(κ)阿片受体激动剂U50488对大鼠离体心心律及心肌细胞内游离钙([Ca2+ ]i)的作用。结果显示:U50488可诱发心律失常并增加静息心肌细胞[Ca2+ ]i,U50488诱发心律失常及增加心肌细胞[Ca2+ ]i的作用可被选择性κ阿片受体拮抗剂Nor-binaltorphimine(Nor-BNI)及选择性磷酯酶C抑制剂U73122、新霉素及链霉素所阻断。表明心脏κ阿片受体激活所致的心律失常是由于磷酸肌醇信号传导通路激活引起心肌细胞[Ca2+ ]i增多所致。
The effect of U50448 on the cardiac rhythm and intracellular calcium in the rat heart
1. Zhang Weimin, Respiratory Department, Liu Hua Qiao Hospital, Guangzhou 510010; 2. Wong Tak-Ming.
Department of Physiology, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong
【Abstract】 The effect of U50448, a selective κ-opioid receptor agonist, on cardiac rhythm in the isolated perused rat heart and intracellular calcium ([Ca2+ ]i) in the single ventricular rat myocyte were studied. The results showed that U50488 can induce arrhythmias dose-dependently in the isolated perfused rat heart and increase [Ca2+ ]i in the single ventricular rat myocyte. The effect of U50488 can be blocked by a selective κ-receptor antagonist, nor-binaltorphimine. The arrhythmogenic effects and the increase of [Ca2+ ]i induced by U50488 were blocked by U73122, neomycin and streptomycin, selective phospholipase C inhibitors, not by U73433, the inactive structural analog of U73122. These results demonstrated that the arrhythmogenic effect of cardiac κ-receptor is due to activation of phosphoinositol/Ca2+ pathway.
【Key words】 κ-opioid receptor Arrhythmias Isolated rat heart Phospholipase C Intracellular Ca2+
业已证实心肌细胞膜上存在大量Kappa(κ)亚型阿片受体[1] 。整体动物及离体工作心脏灌流实验表明:心脏κ阿片受体与心律失常的发生关系密切[2,3] 。鉴于心肌细胞内游离钙离子([Ca2+ ]i)在心律失常发生中起重要作用[4] ,本实验同时观察特异性κ阿片受体激动剂U50448对大鼠离体工作心心律及单个心肌细胞[Ca2+ ]i的变化。结果显示:心肌细胞磷酸肌醇传导途径激活所致的[Ca2+ ]i升高是心脏κ阿片受体诱发心律失常的主要机制。
材料与方法
一、材料:
200~250 g的SD大鼠由香港大学纯种动物室提供。U50448、Nor-binaltorphimine (Nor-BNI)、U73122、胶原酶Ⅰ型、新霉素、链霉素及荧光染料Fura-2/AM均为Sigma公司产品。
二、方法:
1.离体工作心脏模型:
腹腔注射肝素钠500u/kg,断头后立刻开胸取出心脏,放入4℃冰盐水预冷,迅速经主动脉逆插管悬挂于Langen-dorff装置上,应用95% O2 和5%CO2 平衡的Krebs-Ringer液以60mmHg恒压、35℃恒温经主动脉灌流。
心律失常评价:以注射选择性κ阿片受体激动剂U50488(5×10-6 M)后30min内出现的心律失常记分评价,记分标准见文献[2] 。
2.心肌单细胞分离及细胞内游离Ca2+ 的测定:
心肌单细胞分离方法见文献[5] 。
细胞内游离Ca2+ 测定:取少量的细胞与溶于DMSO中的Fura-2/AM(最终浓度为10μM)共同孵育30min,在荧光倒置显微镜(Nikon)下以双波长(340nm,380nm)的紫外光(Photo Technical International)激发单个心肌细胞,二个波长的荧光信号比例(340/380)用以代表细胞内钙变化。
3.实验分组:
(1)对照组:Krebs-Ringer液灌流60min。
(2)U50448组:Krebs-Ringer液灌流30min后给U50488(10min)。
(3)U73122、新霉素及链霉素干预组:Krebs-Ringer液灌流30min,应用含U73122、新霉素或链霉素的Krebs-Ringer液灌流10min后给U50488。
结 果
一、U73122、新霉素及链霉素对U50488所致离体心心律的影响:
如表1所示:选择性κ阿片受体激动剂U50488诱发大鼠离体心心律失常,作用呈剂量效应关系。U50448诱发的心律失常可被选择性κ阿片受体拮抗剂Nor-BNI阻断。磷酯酶C的选择性抑制剂U73122、新霉素及链霉素显著减少U50488诱导的心律失常,作用呈剂量效应关系。U73122的无活性同分异构体U73433对U50488诱发的心律失常无明显抑制作用。
表1 U73122、新霉素及链霉素对U50488所致离体心心律的影响
| 例数 | 心律失常发生数 | 心律失常 | 心律失常记分(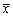 ±s) ±s) | ||||
| 偶发房早 | 频发房早 | 偶发室早 | 频发室早 | ||||
| 对照组 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| U50488组 | |||||||
| 80 nmol | 8 | 4* | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1.13±0.45 |
| 400 nmol | 11 | 10* | 6* | 5* | 3* | 1 | 2.64±0.32 |
| 800 nmol | 11 | 10* | 4 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 3.55±0.39 |
| 预处理后用U50448(400 nmol)组 | |||||||
| Nor-BNI | |||||||
| 100 nmol | 6 | 0## | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 新霉素 | |||||||
| 0.01 mM | 9 | 9 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 2.67±0.35 |
| 0.1 mM | 10 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0.90±0.28# |
| 1.0 mM | 9 | 3# | 3 | 0# | 0# | 0 | 0.33±0.16## |
| 链霉素 | |||||||
| 0.01 mM | 9 | 9 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 2.33±0.22 |
| 0.1 mM | 9 | 6 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1.78±0.47# |
| 1.0 mM | 10 | 3# | 1 | 2 | 0# | 0 | 0.50±0.26## |
| U73122 | |||||||
| 0.1 μM | 8 | 8 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 2.33±0.63 |
| 1.0 μM | 9 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1.78±0.40# |
| 10 μM | 10 | 2# | 2 | 0# | 0# | 0 | 0.20±0.13## |
| U73433 | |||||||
| 0.1 μM | 8 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 3.63±0.39 |
| 1.0 μM | 9 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3.11±0.55 |
| 10 μM | 10 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2.60±0.64 |
二、U73122、新霉素及链霉素对U50488所致心肌细胞内钙变化的影响:如图1所示,选择性κ阿片受体激动剂U50488能诱发心肌细胞内游离钙离子浓度升高,作用呈剂量效应关系。U50488诱发心肌细胞内游离钙离子浓度升高的作用可被选择性κ阿片受体拮抗剂Nor-BNI阻断(图2,3)(n=6,P<0.01)。磷酯酶C的选择性抑制剂U73122(10μM)、新霉素(1mM)及链霉素(1mM)能完全阻断U50488(30μm)诱导的心肌细胞内钙升高(图2,3)(n=6,P<0.01)。U73122的无活性同分异构体U73433(10μm)对U50488诱发的心肌细胞内钙升高无明显抑制作用(n=6,P>0.05)(图2,3)。
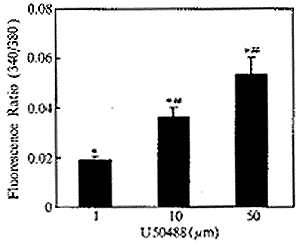
图1 U50488对大鼠心室肌细胞内游离钙的影响
*:与对照正常组比P<0.05。#:与低浓度组比P<0.05。

图2 磷酯酶C抑制剂对U50488
诱导的心肌[Ca2+ ]i影响
讨 论
受体放射配基结合实验、生理学及分子生物学研究显示心肌细胞含丰富κ阿片受体[1,2,6] 。心脏组织发现属于κ阿片受体激动剂的强啡肽及其类多肽及强啡肽原的mRNA[7] ,提示心脏本身就能产生内源性阿片物质,并可经心脏κ阿片受体调节心功能。既往的实验显示:κ阿片受体拮抗剂Mr2266能拮抗整体动物因心脏缺血再灌流所致的心律失常,且Mr2266抗心律失常作用明显强于非特异性阿片受体拮抗剂纳络酮[8] ,提示心脏κ阿片受体与心律失常发生关系密切。本实验结果显示:特异性κ受体激动剂U50488在离体工作心脏引起心律失常的作用可被选择性κ阿片受体拮抗剂Nor-BNI阻断,说明U50448致心律失常是特异性通过心脏κ阿片受体起作用。
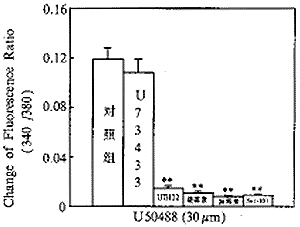
图3 磷酯酶C抑制剂对U50488
诱导的心肌[Ca2+ ]i影响
采用荧光指示剂Fura-2,我们观察了U50488对单个心室肌细胞[Ca2+ ]i的影响。与Ventura等的发现相一致[9] ,5~200μm的U50488浓度依赖性地升高心肌细胞[Ca2+ ]i,其作用可被Nor-BNI所阻断,说明该作用是通过激活心肌细胞膜上的κ阿片受体。
最近的研究显示:刺激心肌细胞κ阿片受体能经G蛋白激活磷酯酶C(PLC),使三磷酸肌醇(IP3 )生成增多,继尔增加细胞内钙从钙池释放引起心肌细胞[Ca2+ ]i增多[5] 。既往的研究证实,心肌细胞[Ca2+ ]i增多是心律失常发生的重要因素[4] 。本实验用特异性PLC抑制剂U73122及氨基糖甙类抗菌素抑制IP2 向IP3 转化[10,11] 后U50488引起心律失常及升高[Ca2+ ]i的作用同时消失,实验结果表明:心肌细胞PLC/IP3 /Ca2+ 信号传导途径的激活是心脏κ阿片受体引起心律失常的细胞学机制。
参考文献
1 W. M. Zhang, W. Q. Jin, T.M. Wong. Multiplicity of kappa opiolid receptor binding in the rat cardiac sarcolemma. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 1996, 28: 1547~1554
2 T. M. Wong, A. Y. S. Lee, K. K Tai. Effects of drugs interacting with opioid receptors during normal perfusion or ischaemia and reperfusion in the isolated rat heart-an attempt to identify cardiac opioid receptor subtype(s) involved in arrhythmogenesis. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 1990, 22:1167~1175
3 Q. Xia, J. Z. Sheng, K. K. Tai, T.M. Wong. Effects of chronic U50488H treatment on binding and mechanical responses of the rat hearts. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 1994, 268:930~934
4 F. T. Thandroyen, A. C.Morris, H.K. Hagler, et al. Intracellular calcium transients and arrhythmia in isolated heart cells. Circ Res, 1991, 69:810~819
5 J. Z. Sheng,T. M. Wong. Chronic U50488H abolishes inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and intracellular Ca2+ elevations evoked by κ-opioid receptor in rat myocytes. Eur J Pharmacol, 1996, 307:323~329
6 G. Wittert, P. Hope,D. Pyle. Tissue distribution of opioid receptor gene expression in the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 1996,218: 877~881
7 S. Spampinato, M.Canossa, C. Ventura, et al. Heterogeneity of immunoreactive dynorphin B-like material in human, rat, rabbit and guinea-pig heart. Life Sci, 1991, 48:551~559
8 J. E. Mackenzie, J. R. Parratt and R. Sitsapesan. The effects of drugs interacting with opioid receptors on ischaemic arrhythmias in anaesthetised rats. Br J Pharmacol, 1986,89: 614P
9 C. Ventura, H. Spurgeon, E G. Lakatta, et al. κ and δ opioid receptor stimulation affects cardiac myocyte function and Ca2+ release from an intracellular poll in myocytes and neurons. Cir Res, 1992,70:66~81
10 L. S. Ramsammy, C. Josepovitz, G. J. Kaloyanides. Gentamycin inhibits agonist stimulation of the phosphatidylinositol cascade in primary culotures of rabbit proximal tubular cells and in rat renal cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 1988, 247; 989~996
11 E. Gabev, J. Kasianowicz, T. Abbott, et al. Binding of neomycin to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2 ). Biochem Biophys Actas, 1989, 979:105~112
, http://www.100md.com