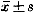 |
关键词:颅脑损伤;髓鞘碱性蛋白;酶联免疫吸附测定
摘要 目的:研究颅脑损伤后血清、脑脊液髓鞘碱性蛋白(MBP)的动态变化与颅脑损伤的预后之间的关系。方法:用ELISA法测定76例急性颅脑损伤患者伤后不同时间血清和脑脊液MBP含量,结合预后分级进行分析。结果:死亡、重残组病人在伤后24小时内血清MBP就显著增高,并持续至伤后9~10日;而轻残组则在伤后3~5日才增高,9~10日恢复正常;脑脊液测定结果与血清检测结果呈正相关。结论:在颅脑损伤的预后判断上,血清MBP测定具有简便快捷的优点,脑脊液MBP测定具有准确可靠的优点,二者结合使判断更具科学性。
The relationship between the change of myelin basic protein and the prognosis ofhead injured patients Wang Yutian, Zhao Jiannong, Wan Haifeng, et al.Department of Neurosurgery, People's Hospital of Hainan Province, Haikou 570311
Abstract Objective: To study the relationship between the changeof myelin basic protein (MBP) and the prognosis of head injured patients. Methods: Serumand CSF levels of MBP. were measured in 76 patients at the different time after acute headinjury by ELISA. Results: Mean serum and CSF concentraions of MBP. in patients withoutcome of death or severe disability were significantly raised at the time of admissionand remained high for 10 days after injury compared with those in controls(P<0.01).Inpatients with moderate disability the mean MBP. concentraions only raised during 3~5days(P<0.01) and declined at 9~10 days (P>0.05) after injury. Conclusion: At theprediction of outcome in patients after head injury. serum MBP. may be easy and rapid andCSF MBP. is accurate and reliable.
......
您现在查看是摘要页,全文长 11248 字符。