 |
 |
关键词:幽门螺杆菌;抗生素类;毒力
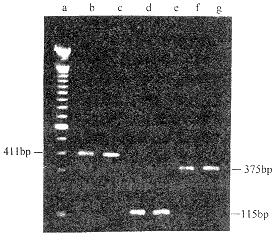
【摘要】 目的 揭示抗生素诱变的球形幽门螺杆菌(Hp)与定居有关毒力的变异情况。方法 采用亚抑菌浓度抗生素作用,使5株Hp发生球形变异,检测球形Hp的尿素酶活性及其对Hep-2细胞(喉癌上皮细胞)的粘附性,并用PCR法检测其尿素酶A,尿素酶B及粘附素基因。结果 球形Hp尿素酶活性降低,对Hep-2细胞的粘附性降低,电镜下可见球形Hp侵入细胞内。球形Hp的411bp尿素酶A,115bp尿素酶B及375bp粘附素基因的PCR均阳性。结论 抗生素诱变的球形Hp与定居相关的毒力减弱,但其有关毒力基因片段未缺失。
Study on the Colonizational virulence of coccoid Helicobacter Pylori induced by antibiotics SHE Feifei, SU Donghui, ZHU Ping, et al. Dept. of Microbiology, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350005
【Abstract】 Objective To show the virulence related to the colonization of antibiotic-induced coccoid Helicobacter pylori mutant.Methods Five strains of coccoid H. pylori, which were transformed from bacillary by exposure to antibiotics in subinhibitory concentrations, were examined by their activities of urease and their adherance to Hep-2 cell, the gene variety of urease A, urease B and hpaA were analysed by PCR.Results Both activity of urease and adherance to Hep-2 cell of coccoid H. pylori were decreased, and the invasion of coccoid H.pylori into hep-2 cell could be seen under etectromicroscope, moreover, 411bp Ure A, 115bp UreB and 375bp hpaA in coccoid H.pylori were all shown to be positive as by PCR.Conclusion Virulence related to colonization in antibiotic induced coccoid H.pylori decreases, yet there is no deletion in virulence-related gene fragments.
......
您现在查看是摘要页,全文长 12871 字符。