 |
关键词:膀胱肿瘤;癌;微卫星
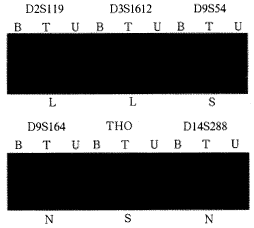
摘要 目的 探讨微卫星不稳定性(MSI)检测在膀胱移行细胞癌(TCC)诊断中的价值。 方法 采用PCR扩增、聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳、银染等技术。选用了20种微卫星标记物对50例TCC进行分析(每例均包括血、尿及肿瘤组织3种标本)。 结果 50例尿标本中47例发生MSI,阳性率为94%,每例患者尿中微卫星改变均与原发肿瘤标本一致。 结论 尿沉渣MSI检测技术是诊断膀胱肿瘤敏感有效的、无损伤的方法之一。
Microsatellite analysis ofurine in the detection of transitional cell carcinoma of bladder
FU Yaowen,SONG Yue,YUAN Chunhui,et al.
Department of Urology,The Third Clinical College,Norman Bethune University of MedicalSciences,Changchun 130031
Abstract Objective To investigate therole of MSI in urine in TCC of bladder. Methods MSI assay was carried out forblood,urine and tumor samples of 50 cases of TCC of bladder using PCR with 20microsatellite loci. Results MSI was positive in urine samples of 47 of 50 patients(94%) and the genetic change in urine DNA was identical to that in the primary tumor inall. Conclusions Microsatellite analysis of urine sediment is a sensitive,effectiveand nontraumatic means for the early detection of bladder cancer.
......
您现在查看是摘要页,全文长 9989 字符。