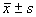 |
关键词:
【摘要 】 目的 探讨体育运动对高血压病患者血胰岛素的影响。方法 将109例轻度原发性高血压病患者随机分配到运动组(53例)和对照组(56例)。两组均接受尼群地平降压治疗,同时对运动组进行为期3个月的中等强度运动干预。测量两组入选时和3个月后血压、空腹血糖、血胰岛素、血脂及口服葡萄糖负荷后1、2小时血糖及胰岛素。结果 经过3个月规则运动,运动组空腹及糖负荷后1、2小时胰岛素水平低于对照组(P值均<0.05),其空腹胰岛素下降程度与运动量呈正相关(r=0.61,P<0.05),血胆固醇、甘油三酯及低密度脂蛋白水平低于对照组(P<0.05)。结论 长期中等强度的体育运动能降低高血压病患者空腹及糖负荷后血胰岛素水平,并有利于纠正血脂代谢紊乱。
The effects of physical exercise on serum insulin levels in patients with mild essential hypertension Wu Yuetao* , Wang Juesheng, Chen Ganren, et al. * The Second Affiliated Hospital of Hunan Medical University, Changsha 410011
【 Abstract 】 Objective To determine the effects of physical exercise on serum insulin levels in hypertensives. Methods One hundred and nine patients with mild essential hypertension were randomly assigned to exercise group (n=53) or control group (n=56). Both groups were under nitrendipine regimen, but the intervention group underwent extra physical exercise of moderate intensity. The blood pressure, fasting serum lipids, blood glucose and insulin levels before and 1 hour and 2 hours after oral glucose loading were taken from each subject at entry and three months after the observation. Results There were significant decrease in insulin concentration at fasting, 1 hour and 2 hours after glucose loading in the exercise group (P<0.05) after 3 months of exercise. The magnitude of decrease in fasting insulin levels correlated with the increase in amount of exercise (r=0.61, P<0.01). In addition, exercise group experienced significant decrease in serum cholesterol, triglyceride, low density lipoprotein cholesterol (P<0.05) as compared with the control group. Conclusion Regular physical exercise can decrease the insulin levels at fasting and after glucose loading and facilitate the control of dyslipidemia in essential hypertension.
【 Key words 】 Sports Hypertension Insulin
近年来许多研究表明高血压病患者同时合并胰岛素抵抗(IR)、糖和脂质代谢紊乱 ......
您现在查看是摘要页,全文长 29132 字符。