吸烟与慢性阻塞性肺疾病发病率的关系
吸烟|肺疾病,阻塞性,关键词:
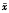 |
关键词:吸烟;肺疾病,阻塞性
【摘要】 目的
调查吸烟指数与慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD)发病率间的关系,促使吸烟者戒烟。方法 1992年春对北京市房山区、湖北省潜江地区及辽宁省沈阳市郊区(县)在册的102230名村民中≥15岁人群进行入户调查、问卷、体检及肺功能测定,分析吸烟与COPD的关系。结果 筛选出由单纯吸烟引起的COPD患者一秒钟用力呼气容积/用力肺活量(FEV1 /FVC)<70%822人,占吸烟人数的24.6%,由吸烟及慢性气道炎症史引起COPD者624例,占该组被调查人数的40.4%。分析两组COPD患者与吸烟指数(每日平均吸烟支数×吸烟年数)的关系。COPD患者与吸烟有关者为71.6%(1 446/2 020),吸烟指数愈大,COPD发生率愈高(40%以上),肺功能损害也愈严重。结论 国人吸烟者中COPD发生率高于国外报道,在长期吸烟者中COPD的发生率不是恒定不变的,而是随吸烟量的增多,患COPD的机会也逐渐增多。戒烟不能存在侥幸心理。The relationship betweensmoking and the incidence of COPD
CHENG Xiansheng , LI Jingzhou, ZHANG Zhenxiang, et al. Fuwai Cardiovascular Hospital, CAMS & PUMC, Beijing100037
【Abstract】 Objective
To study the relationship between smokingindex and the incidence of COPD to persuade smokers quit smoking. Methods COPDwas diagnosed based on family inquiring, questionnaire and pulmonary function test. Thesmoking index was calculated by the average cigarettes a day times the years of smoking.Results 822 cases(account for 24.6% of investigated subjects) of COPD due tosmoking were identified, and 624 cases were found (account for 40.4% of investegatedsubjects) to have a history of both smoking and chronic airway inflammation. The higherthe smoking index, the higher the incidence of COPD (above 40%), and the more severe theirlung function imparement. The smoking was 71.6% of the cause in COPD patients.Conclusions The incidence of COPD associated with smoking is higher in Chinathan that in the Western countries. The incidence of COPD in population with long smokinghistory is not invariable, while it is gradually rising with increasing smoking index.......
您现在查看是摘要页,全文长 20470 字符。