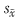 |
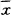 |
关键词:老年人;戒烟者;肺功能;随访研究
【摘要】 目的 观察健康老年人戒烟10年后肺功能的10年变化。方法 51名戒烟10年以上的健康老年人为研究对象,并挑选条件相同的从不吸烟健康老年人12名作为随访对照,肺功能检查按常规方法进行。结果 戒烟10年后健康老年人在随访的10年中肺功能与从不吸烟健康老年人肺功能相比,肺活量(VC)、用力肺活量(FVC)、一秒钟用力呼气容积(FEV1 )年下降值差异有显著性(P<0.01);呼气峰流速(PEF)年下降值差异有显著性(P<0.05);残气量(RV)、残气量/肺总量(RV/TLC)的年增加值差异有显著性(P<0.01)。一秒钟用力呼气容积与用力肺活量比值(FEV1 /FVC)、最大通气量(MVV)、最大呼气中期流量(MMEF)、功能残气量(FRC)、肺总量(TLC)也有一定的改变,但变化值未达到统计学意义。结论 通过随访研究发现即使戒烟后曾吸烟对肺功能仍然存在一定影响,可能与研究对象吸烟时间长,吸烟量大所形成某些不可逆病理变化有关,并建议吸烟者应尽早戒烟。
Follow-up study of lung function changes for 10 years in healthy elder of ex-smokers
LIU Changting,WANG Delong.
Dept. of Respiratory Diseases, General Hospital of PLA, Beijing 100853
【Abstract】 Objective To observe changes of lung function for 10 years in healthy elderly ex-smokers who have quitted smoking for more than 10 years. Methods 51 healthy elderly ex-smokers were selected and routine lung function tests were performed, 12 subjects, who have never smoked and all other criteria were similar, were chosen as controls. Their routine lung function tests have also been followed up for 10 years. Results The decrease of VC, FVC, FEV1 and PEF of ex-smokers were significantly lower than non-smokers, the increase of RV and RV/TLC were significantly higher than non-smokers. FEV1 /FVC, MVV, MMEF, FRC and TLC were also different, however, the difference has not reached statistically significant. Conclusions The influence of smoking could be prolonged, even the subject has stopped smoking for years, so we suggested to stop smoking the early the better.
......
您现在查看是摘要页,全文长 13718 字符。