吗啡长时程作用对SH-SY5Y细胞cAMP系统及c-Fos磷酸化的影响△
作者:方芳 曹清 宋福津 刘景生
单位:中国医学科学院 中国协和医科大学 基础医学研究所药理室,北京 100005
关键词:吗啡;依赖;蛋白激酶A;c-Fos;磷酸化
中国医学科学院学报990405 摘要 目的 探讨吗啡长时作用下分化的人成神经瘤SH-SY5Y细胞中cAMP系统变化以及PKA对转录因子c-Fos的磷酸化调节。方法 采用蛋白竞争结合法、酶活性测定法及同位素掺入法分别观察cAMP、PKA及c-Fos的变化。结果 (1) 100 μmol/L吗啡作用2 min~36 h可使SH-SY5Y细胞cAMP水平呈双相变化:短时作用下cAMP水平降低,随着吗啡作用时间的延长,cAMP水平逐渐回升,至36 h时明显高于对照,这时加入100 μmol/L纳洛酮可诱发cAMP水平的反弹性超高现象。表明吗啡作用36 h可使分化的SH-SY5Y细胞产生类吗啡依赖样变化;(2) 吗啡长时作用下,胞质可溶相PKA活性也呈双相变化,而膜相PKA活性未见明显变化;(3) 吗啡作用36 h时,细胞c-Fos磷酸化水平显著降低,PKA抑制剂可抑制此作用;(4) 纳洛酮可抑制上述PKA活性及c-Fos磷酸化水平的改变。结论 SH-SY5Y细胞cAMP-PKA系统的上调可能与吗啡依赖的形成有关,而且在吗啡依赖样细胞中PKA可能通过磷酸酶而使细胞c-Fos发生去磷酸化,从而激活某些基因的转录,这可能是吗啡依赖时细胞产生适应性变化的重要机制之一。
, 百拇医药
中图号 R96
Effects of Long-Term Morphine Exposure on the cAMP System
and c-Fos Phosphorylation in Differentiated SH-SY5Y Cells
and c-Fos Phosphorylation in Differentiated SH-SY5Y Cells
Fang Fang Cao Qing Song Fujin Liu Jingsheng#
(Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, CAMS and PUMC, Beijing 100005)
, 百拇医药
Objective To further understand the effects of long-term morphine exposure on the cAMP system and c-Fos phosphorylation in differentiated SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Methods Cellular changes of cAMP, PKA and c-Fos were detected by protein competitive conjunction, enzyme activity and isotope incorporation methods respectively.Results (1) Long-term exposure (2 min~36 h) to morphine (100 μmol/L) could induce the biphasic changes in cAMP contents. Treament for 2 min to 1 h, morphine caused rapid and siginificant decrease of the cAMP level and then gradully recovered and apparently increased at 36 h. At that time, naloxone added to the incubation media caused an overshoot of cellular cAMP; (2) Long-term exposure to morphine could also induce the biphasic changes in cytosolic PKA activity. This is consistent with the changes of cAMP during the chronic treatment of cells with morphine. But no changes were observed in membrane PKA activity; (3) In morphine dependent-like cells decreased c-Fos phosphorylation level was observed. PKA inhibitor could significantly inhibit this change; (4) Concomitant administration of naloxone could block the changes in PKA activity and c-Fos phosphorylation described above.Conclusions The up-regulation of cAMP system in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells may be involved in the development of morphine dependent and in morphine dependent-like SH-SY5Y cells and PKA was suggested to regulate c-Fos dephosphorylation through activating phosphatase and then activate some genes transcription, which might be one of the important mechanism regardingas cellular adaptive responses underlying dependence to opioid drugs.
, 百拇医药
Key words morphine; dependence; protein kinase A; c-Fos; phosphorylation
以往对于阿片类物质耐受和依赖机制的研究主要集中在阿片受体的变化上,如受体的数目和亲和力等,但是关于阿片类药物耐受和依赖的形成机制至今尚不清楚。近年来人们的注意力逐渐转向了阿片作用的受体后机制,其中细胞G蛋白活性、胞内第二信使和蛋白磷酸化过程的改变尤其引人注目。研究发现,胞内腺苷酸环化酶(AC)活性及cAMP水平随着吗啡作用时间的延长而呈双相变化[1、2]。Collier等[3]人认为,AC/cAMP水平的改变可能是产生吗啡耐受和依赖的生化基础。为进一步探讨产生吗啡依赖的机制,本研究观察了吗啡长时作用于分化的SH-SY5Y细胞过程中cAMP水平、cAMP所调节的PKA活性的动态变化、PKA对转录因子c-Fos的磷酸化调节。
1 材料和方法
, 百拇医药
细胞 SH-SY5Y细胞由美国旧金山加州大学细胞培养中心Ibrahim Tuet惠赠。
主要试剂 硫酸吗啡(morphine sulfate, Mor.),为Puninsula公司产品;盐酸纳洛酮(naloxone hydrochloride, NAl.)、Histone ⅡA、ATP、cAMP,为Sigma公司产品;c-Fos兔IgG抗体(为c-Fos p62特异性抗体,与FosB、Fra-1或Fra-2无交叉反应),为Santa Cruz公司产品。[γ-32P]-ATP(18.5×1014 Bq/(mmol.L),为北京市亚辉生物医学工程公司产品。32P-磷酸盐(无载体,3.33×108 Bq/ml),为北京原子能研究所提供。
SH-SY5Y细胞类吗啡依赖样模型的建立 SH-SY5Y细胞用RPMI-1640培养基按文献[4]的方法培养,以4×105个/ml细胞接种于6孔板或培养瓶,24 h后加入分化剂(RA)并使其浓度达到20 μmol/L。RA作用6 d后,换培养液,加入100 μmol/L吗啡,作用2 min~36 h,或PKA抑制剂(protein kinase A inhibitor fragment 6~22 amide) 50 μg/ml 作用36 h。收集细胞前加入10 μmol/L腺苷酸环化酶刺激剂(forskolin)作用15 min及磷酸二脂酶抑制剂(IBMX)1 mmol/L作用5 min,其中一组吗啡作用36 h后加入100 μmol/L纳洛酮作用10 min。药物作用完毕后,迅速弃去培养液,加入6%TCA 1 ml,用细胞刮棒刮下细胞移入试管,并用0.5 ml 2% TCA洗一次,合并两次TCA,超声进一步破碎细胞,4℃离心(3000 r/min, 15 min)。上清液采用竞争性蛋白结合分析法测定cAMP的水平。
, 百拇医药
细胞蛋白激酶粗提物制备:药物作用完毕,将细胞迅速置于冰浴中,加入预冷的缓冲液[25 mmol/L Tris、2 mmol/L EDTA、0.5 mmol/L DTT、 0.1 mmol/L 蛋白酶抑制剂(leupeptin)、0.5 mmol/L 蛋白酶抑制剂(PMSF)、 50 mmol/L 巯基乙醇、0.25 mol/L蔗糖,pH7.4]。刮下细胞,超声破碎后于4℃以800 r/min离心10 min。再取上清离心60 min(4℃,100 000×g),上清液用于测定可溶相蛋白激酶活性,沉淀加入含0.3%Triton X-100的匀浆缓冲液(与初次缓冲液体积相同),冰浴中溶解后,于4℃离心(100 000×g 60 min),收集上清液用于测定膜相蛋白激酶活性。
细胞PKA活性测定 按文献[5]方法进行。
细胞c-Fos磷酸化测定 参照文献[6,7]的方法加以改良。最后从样品中取20 μl上清进行SDS-PAGE分析(5%积层胶,10%分离胶)。电泳结束后,进行染色、脱色及干燥,-70℃曝光2~3 d。以电泳带的黑度(经密度仪扫描测定)表示磷酸化的强度。
, 百拇医药
数据处理:数据以均值±标准误(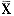 ±
± )表示,采用单因素方差分析,组间差异比较用t检验。
)表示,采用单因素方差分析,组间差异比较用t检验。
2 结果
SH-SY5Y细胞类吗啡依赖样模型建立 人成神经瘤细胞SH-SY5Y在含分化剂RA的培养液培养6 d后分化,轴突明显增多,成为具有神经细胞特征的细胞。以100 μmol/L吗啡分别作用于分化的SH-SY5Y细胞2、10、30 min及 36 h时,胞浆cAMP呈现双相变化,再加入100 μmol/L纳洛酮后,胞浆cAMP水平出现反弹性超高(overshoot)现象(图1)。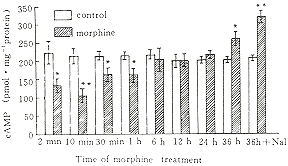
图 1 吗啡在不同作用时间对forskolin 刺激SH-SY5Y细胞引起胞浆内cAMP升高的影响及纳洛酮引起cAMP的反弹现象
, http://www.100md.com
Fig 1 Time-course of effects of 100 μmol/L morphine on forskolin stimulated cAMP accumulation in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells, and naloxone induced cAMP overshoot. ( ±
± , n=4)
, n=4)
P<0.05, P<0.01 compared to control at the same time
SH-SY5Y细胞形成阿片依赖样过程中PKA活性的变化 在吗啡作用2 min~1 h过程中,胞浆可溶相PKA活性呈双相变化,但膜相PKA活性与对照组相未见明显变化(图2)。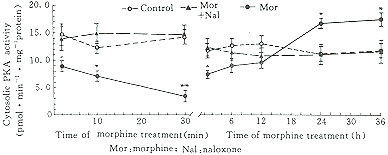
, 百拇医药
图 2 吗啡在不同作用时间对SH-SY5Y细胞胞浆内PKA活性的影响
Fig 2 Time-course of effects of 100 μmol/L morphine on PKA activity of cytosol fraction of differentiated SH-SY5Y cells (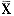 ±
± ,n=4)
,n=4)
P<0.05,P<0.01 compared to control at the same time
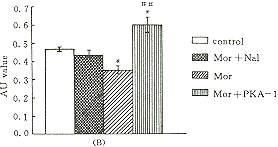
PKA对吗啡依赖样SH-SY5Y细胞c-Fos磷酸化的调节 用32P-磷酸盐孵育细胞,作胞内磷酸化测定结果显示,吗啡依赖样细胞c-Fos磷酸化水平比对照组明显降低,加PKA抑制剂组c-Fos磷酸化状态明显增强。纳洛酮给药组c-Fos磷酸化未见明显变化(图3)。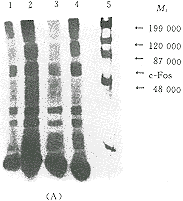
, http://www.100md.com
图 3 吗啡及PKA抑制剂长时间作用于SH-SY5Y对c-Fos磷酸化的影响
Fig 3 Effects of long-term morphine exposure and protein kinase A inhibitors on c-Fos phosphorylation in cultured SH-SY5Y cells
(A) Lane 1: control; Lane 2: Mor+Nal;Lane 3: Mor; Lane 4:Mor+PKA-I; Lane 5: molecular weight standards. (B) The band corresponding to Mr62 000 c-Fos on autoradiograms was analyzed by scanning densitometry. Results from three separate experiments are presented (as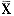 ±
± ); P<0.05,P<0.01 compared to control; ## P<0.01 compared to morphine group; AU: absorption unit;Mor:morphine; Nal:naloxone;PKA: protein kinase A inhibitors
); P<0.05,P<0.01 compared to control; ## P<0.01 compared to morphine group; AU: absorption unit;Mor:morphine; Nal:naloxone;PKA: protein kinase A inhibitors
, http://www.100md.com
3 讨论
本实验显示,分化的SH-SY5Y细胞,在吗啡长时作用过程中细胞cAMP水平呈双相变化。这与Yu[4]和Carter[7]的研究结果类似,表明吗啡长时作用于富含μ阿片受体的SH-SY5Y细胞也可产生类似于吗啡作用于整体动物所产生的依赖、戒断时cAMP水平的变化。本研究首次报道在吗啡长时作用的SH-SY5Y细胞中cAMP调节的PKA活性的变化,发现胞质可溶相PKA活性与cAMP水平的变化相似,在吗啡长时作用过程中也呈双相变化。即吗啡短时作用下胞质可溶相PKA活性受到抑制,吗啡长时作用下PKA活性明显升高;而膜相PKA活性未见明显变化。表明在吗啡长时作用的SH-SY5Y细胞中,cAMP水平的变化可能主要是调节可溶相而非膜相PKA活性。以上结果提示,阿片长时作用不仅可引起AC活性及cAMP水平的上调,还可导致AC/cAMP系统的其他环节如PKA活性的上调;从而进一步证实AC/cAMP系统的上调与“超高”代表了一种与阿片依赖和戒断有关的变化。AC/cAMP-PKA系统的增强可能与维持或上调以及使神经元处于过度激活状态有关,因此可能是形成和维持吗啡耐受依赖状态的一个重要机制。
, http://www.100md.com
蛋白质的可逆磷酸化是细胞信息传递的公共通路,是使细胞对信号作出持续反应的一种调节方式,因而蛋白质的磷酸化调节在吗啡耐受依赖形成中的作用也越来越受到重视。Guitar和Nestler等[8]。曾在吗啡耐受依赖大鼠蓝斑核及其他脑区检出吗啡和cAMP调节的磷蛋白(morphine and cAMP-regulated phosphoproteins),但当时并不清楚这些蛋白质的性质。由于阿片类物质耐受依赖是一长时效应,受体后效应系统的变化必然会影响某些基因的表达,从而引起神经元功能的改变。转录因子的量及其活性的改变可以影响基因表达水平。蛋白磷酸化作用是调节转录因子活性的重要方式,推测吗啡长时作用下AC/cAMP系统的上调也可能是通过激活PKA而调节某些转录因子的磷酸化水平,从而改变某些基因的表达。c-Fos是即刻早期基因编码的转录因子,脱磷酸化状态的c-Fos与c-Jun组成二聚体形成AP-1,可作为转录激活物发挥作用。本研究发现,吗啡依赖样SH-SY5Y细胞c-Fos磷酸化水平明显降低而PKA抑制剂可使c-Fos磷酸化水平明显增高,提示吗啡长时作用可通过c-Fos的去磷酸化而激活某些基因的转录,从而影响神经元的功能。因此推测,吗啡依赖样SH-SY5Y细胞中AC/cAMP系统的上调激活了PKA,而活化的PKA可能通过激活磷酸酶使c-Fos发生去磷酸化,影响某些基因的表达,从而使细胞产生依赖状态时的适应性变化。
, 百拇医药
△国家自然科学基金(39770852,39470803)资助;*北京协和医院病理科 100730;#通讯作者
参考文献
1 Sharma SK, Klee WA, Nirenberg M. Dual regulation of adenylate cyclase accounts for narcotic dependence and tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1975, 72:3092~3096
2 Musacchio JM, Greenspan DL. The adenylate cyclase rebound response to naloxone in the NG 108-15 cells:effects of etorphine and other opiates. Neuropharmacology, 1986, 25:833~837
, 百拇医药
3 Collier HO. Cellular site of opiate dependence. Nature, 1980, 283:625~629
4 Yu VC, Eiger S, Duan DS, et al. Regulation of cyclic cAMP by the μ-opioid receptor in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. J Neurochem, 1990, 55:1390~1396
5 方 芳,陈轶琨,王小明,等.吗啡长时程作用对小鼠脑组织蛋白激酶A及C活性的影响.基础医学与临床,1997,17:115~120
6 Sambrook J ,Fritsch EF, Maniatis T. Molecular cloning, A laboratory manual. 2nd ed. New York:Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989
, 百拇医药
7 Carter BD, Medzihradsky F. Receptor mechanisms of opioid tolerance in SH-SY5Y human neural cells. Mol Pharmacol, 1992, 43:465~473
8 Guitart X, Nestler EJ. Identification of morphineand cyclic AMP-regulated phospoprotein (MMRPPS) in the locus coerulas and other regions of rat brain: regulation by acute and chronic morphine. J Neurosci, 1989, 9:4371~4387
(1998-01-24 收稿), 百拇医药
单位:中国医学科学院 中国协和医科大学 基础医学研究所药理室,北京 100005
关键词:吗啡;依赖;蛋白激酶A;c-Fos;磷酸化
中国医学科学院学报990405 摘要 目的 探讨吗啡长时作用下分化的人成神经瘤SH-SY5Y细胞中cAMP系统变化以及PKA对转录因子c-Fos的磷酸化调节。方法 采用蛋白竞争结合法、酶活性测定法及同位素掺入法分别观察cAMP、PKA及c-Fos的变化。结果 (1) 100 μmol/L吗啡作用2 min~36 h可使SH-SY5Y细胞cAMP水平呈双相变化:短时作用下cAMP水平降低,随着吗啡作用时间的延长,cAMP水平逐渐回升,至36 h时明显高于对照,这时加入100 μmol/L纳洛酮可诱发cAMP水平的反弹性超高现象。表明吗啡作用36 h可使分化的SH-SY5Y细胞产生类吗啡依赖样变化;(2) 吗啡长时作用下,胞质可溶相PKA活性也呈双相变化,而膜相PKA活性未见明显变化;(3) 吗啡作用36 h时,细胞c-Fos磷酸化水平显著降低,PKA抑制剂可抑制此作用;(4) 纳洛酮可抑制上述PKA活性及c-Fos磷酸化水平的改变。结论 SH-SY5Y细胞cAMP-PKA系统的上调可能与吗啡依赖的形成有关,而且在吗啡依赖样细胞中PKA可能通过磷酸酶而使细胞c-Fos发生去磷酸化,从而激活某些基因的转录,这可能是吗啡依赖时细胞产生适应性变化的重要机制之一。
, 百拇医药
中图号 R96
Effects of Long-Term Morphine Exposure on the cAMP System
and c-Fos Phosphorylation in Differentiated SH-SY5Y Cells
and c-Fos Phosphorylation in Differentiated SH-SY5Y Cells
Fang Fang Cao Qing Song Fujin Liu Jingsheng#
(Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, CAMS and PUMC, Beijing 100005)
, 百拇医药
Objective To further understand the effects of long-term morphine exposure on the cAMP system and c-Fos phosphorylation in differentiated SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Methods Cellular changes of cAMP, PKA and c-Fos were detected by protein competitive conjunction, enzyme activity and isotope incorporation methods respectively.Results (1) Long-term exposure (2 min~36 h) to morphine (100 μmol/L) could induce the biphasic changes in cAMP contents. Treament for 2 min to 1 h, morphine caused rapid and siginificant decrease of the cAMP level and then gradully recovered and apparently increased at 36 h. At that time, naloxone added to the incubation media caused an overshoot of cellular cAMP; (2) Long-term exposure to morphine could also induce the biphasic changes in cytosolic PKA activity. This is consistent with the changes of cAMP during the chronic treatment of cells with morphine. But no changes were observed in membrane PKA activity; (3) In morphine dependent-like cells decreased c-Fos phosphorylation level was observed. PKA inhibitor could significantly inhibit this change; (4) Concomitant administration of naloxone could block the changes in PKA activity and c-Fos phosphorylation described above.Conclusions The up-regulation of cAMP system in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells may be involved in the development of morphine dependent and in morphine dependent-like SH-SY5Y cells and PKA was suggested to regulate c-Fos dephosphorylation through activating phosphatase and then activate some genes transcription, which might be one of the important mechanism regardingas cellular adaptive responses underlying dependence to opioid drugs.
, 百拇医药
Key words morphine; dependence; protein kinase A; c-Fos; phosphorylation
以往对于阿片类物质耐受和依赖机制的研究主要集中在阿片受体的变化上,如受体的数目和亲和力等,但是关于阿片类药物耐受和依赖的形成机制至今尚不清楚。近年来人们的注意力逐渐转向了阿片作用的受体后机制,其中细胞G蛋白活性、胞内第二信使和蛋白磷酸化过程的改变尤其引人注目。研究发现,胞内腺苷酸环化酶(AC)活性及cAMP水平随着吗啡作用时间的延长而呈双相变化[1、2]。Collier等[3]人认为,AC/cAMP水平的改变可能是产生吗啡耐受和依赖的生化基础。为进一步探讨产生吗啡依赖的机制,本研究观察了吗啡长时作用于分化的SH-SY5Y细胞过程中cAMP水平、cAMP所调节的PKA活性的动态变化、PKA对转录因子c-Fos的磷酸化调节。
1 材料和方法
, 百拇医药
细胞 SH-SY5Y细胞由美国旧金山加州大学细胞培养中心Ibrahim Tuet惠赠。
主要试剂 硫酸吗啡(morphine sulfate, Mor.),为Puninsula公司产品;盐酸纳洛酮(naloxone hydrochloride, NAl.)、Histone ⅡA、ATP、cAMP,为Sigma公司产品;c-Fos兔IgG抗体(为c-Fos p62特异性抗体,与FosB、Fra-1或Fra-2无交叉反应),为Santa Cruz公司产品。[γ-32P]-ATP(18.5×1014 Bq/(mmol.L),为北京市亚辉生物医学工程公司产品。32P-磷酸盐(无载体,3.33×108 Bq/ml),为北京原子能研究所提供。
SH-SY5Y细胞类吗啡依赖样模型的建立 SH-SY5Y细胞用RPMI-1640培养基按文献[4]的方法培养,以4×105个/ml细胞接种于6孔板或培养瓶,24 h后加入分化剂(RA)并使其浓度达到20 μmol/L。RA作用6 d后,换培养液,加入100 μmol/L吗啡,作用2 min~36 h,或PKA抑制剂(protein kinase A inhibitor fragment 6~22 amide) 50 μg/ml 作用36 h。收集细胞前加入10 μmol/L腺苷酸环化酶刺激剂(forskolin)作用15 min及磷酸二脂酶抑制剂(IBMX)1 mmol/L作用5 min,其中一组吗啡作用36 h后加入100 μmol/L纳洛酮作用10 min。药物作用完毕后,迅速弃去培养液,加入6%TCA 1 ml,用细胞刮棒刮下细胞移入试管,并用0.5 ml 2% TCA洗一次,合并两次TCA,超声进一步破碎细胞,4℃离心(3000 r/min, 15 min)。上清液采用竞争性蛋白结合分析法测定cAMP的水平。
, 百拇医药
细胞蛋白激酶粗提物制备:药物作用完毕,将细胞迅速置于冰浴中,加入预冷的缓冲液[25 mmol/L Tris、2 mmol/L EDTA、0.5 mmol/L DTT、 0.1 mmol/L 蛋白酶抑制剂(leupeptin)、0.5 mmol/L 蛋白酶抑制剂(PMSF)、 50 mmol/L 巯基乙醇、0.25 mol/L蔗糖,pH7.4]。刮下细胞,超声破碎后于4℃以800 r/min离心10 min。再取上清离心60 min(4℃,100 000×g),上清液用于测定可溶相蛋白激酶活性,沉淀加入含0.3%Triton X-100的匀浆缓冲液(与初次缓冲液体积相同),冰浴中溶解后,于4℃离心(100 000×g 60 min),收集上清液用于测定膜相蛋白激酶活性。
细胞PKA活性测定 按文献[5]方法进行。
细胞c-Fos磷酸化测定 参照文献[6,7]的方法加以改良。最后从样品中取20 μl上清进行SDS-PAGE分析(5%积层胶,10%分离胶)。电泳结束后,进行染色、脱色及干燥,-70℃曝光2~3 d。以电泳带的黑度(经密度仪扫描测定)表示磷酸化的强度。
, 百拇医药
数据处理:数据以均值±标准误(
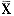 ±
± )表示,采用单因素方差分析,组间差异比较用t检验。
)表示,采用单因素方差分析,组间差异比较用t检验。2 结果
SH-SY5Y细胞类吗啡依赖样模型建立 人成神经瘤细胞SH-SY5Y在含分化剂RA的培养液培养6 d后分化,轴突明显增多,成为具有神经细胞特征的细胞。以100 μmol/L吗啡分别作用于分化的SH-SY5Y细胞2、10、30 min及 36 h时,胞浆cAMP呈现双相变化,再加入100 μmol/L纳洛酮后,胞浆cAMP水平出现反弹性超高(overshoot)现象(图1)。

图 1 吗啡在不同作用时间对forskolin 刺激SH-SY5Y细胞引起胞浆内cAMP升高的影响及纳洛酮引起cAMP的反弹现象
, http://www.100md.com
Fig 1 Time-course of effects of 100 μmol/L morphine on forskolin stimulated cAMP accumulation in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells, and naloxone induced cAMP overshoot. (
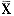 ±
± , n=4)
, n=4)P<0.05, P<0.01 compared to control at the same time
SH-SY5Y细胞形成阿片依赖样过程中PKA活性的变化 在吗啡作用2 min~1 h过程中,胞浆可溶相PKA活性呈双相变化,但膜相PKA活性与对照组相未见明显变化(图2)。

, 百拇医药
图 2 吗啡在不同作用时间对SH-SY5Y细胞胞浆内PKA活性的影响
Fig 2 Time-course of effects of 100 μmol/L morphine on PKA activity of cytosol fraction of differentiated SH-SY5Y cells (
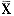 ±
± ,n=4)
,n=4)P<0.05,P<0.01 compared to control at the same time
PKA对吗啡依赖样SH-SY5Y细胞c-Fos磷酸化的调节 用32P-磷酸盐孵育细胞,作胞内磷酸化测定结果显示,吗啡依赖样细胞c-Fos磷酸化水平比对照组明显降低,加PKA抑制剂组c-Fos磷酸化状态明显增强。纳洛酮给药组c-Fos磷酸化未见明显变化(图3)。
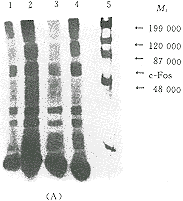

, http://www.100md.com
图 3 吗啡及PKA抑制剂长时间作用于SH-SY5Y对c-Fos磷酸化的影响
Fig 3 Effects of long-term morphine exposure and protein kinase A inhibitors on c-Fos phosphorylation in cultured SH-SY5Y cells
(A) Lane 1: control; Lane 2: Mor+Nal;Lane 3: Mor; Lane 4:Mor+PKA-I; Lane 5: molecular weight standards. (B) The band corresponding to Mr62 000 c-Fos on autoradiograms was analyzed by scanning densitometry. Results from three separate experiments are presented (as
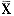 ±
± ); P<0.05,P<0.01 compared to control; ## P<0.01 compared to morphine group; AU: absorption unit;Mor:morphine; Nal:naloxone;PKA: protein kinase A inhibitors
); P<0.05,P<0.01 compared to control; ## P<0.01 compared to morphine group; AU: absorption unit;Mor:morphine; Nal:naloxone;PKA: protein kinase A inhibitors, http://www.100md.com
3 讨论
本实验显示,分化的SH-SY5Y细胞,在吗啡长时作用过程中细胞cAMP水平呈双相变化。这与Yu[4]和Carter[7]的研究结果类似,表明吗啡长时作用于富含μ阿片受体的SH-SY5Y细胞也可产生类似于吗啡作用于整体动物所产生的依赖、戒断时cAMP水平的变化。本研究首次报道在吗啡长时作用的SH-SY5Y细胞中cAMP调节的PKA活性的变化,发现胞质可溶相PKA活性与cAMP水平的变化相似,在吗啡长时作用过程中也呈双相变化。即吗啡短时作用下胞质可溶相PKA活性受到抑制,吗啡长时作用下PKA活性明显升高;而膜相PKA活性未见明显变化。表明在吗啡长时作用的SH-SY5Y细胞中,cAMP水平的变化可能主要是调节可溶相而非膜相PKA活性。以上结果提示,阿片长时作用不仅可引起AC活性及cAMP水平的上调,还可导致AC/cAMP系统的其他环节如PKA活性的上调;从而进一步证实AC/cAMP系统的上调与“超高”代表了一种与阿片依赖和戒断有关的变化。AC/cAMP-PKA系统的增强可能与维持或上调以及使神经元处于过度激活状态有关,因此可能是形成和维持吗啡耐受依赖状态的一个重要机制。
, http://www.100md.com
蛋白质的可逆磷酸化是细胞信息传递的公共通路,是使细胞对信号作出持续反应的一种调节方式,因而蛋白质的磷酸化调节在吗啡耐受依赖形成中的作用也越来越受到重视。Guitar和Nestler等[8]。曾在吗啡耐受依赖大鼠蓝斑核及其他脑区检出吗啡和cAMP调节的磷蛋白(morphine and cAMP-regulated phosphoproteins),但当时并不清楚这些蛋白质的性质。由于阿片类物质耐受依赖是一长时效应,受体后效应系统的变化必然会影响某些基因的表达,从而引起神经元功能的改变。转录因子的量及其活性的改变可以影响基因表达水平。蛋白磷酸化作用是调节转录因子活性的重要方式,推测吗啡长时作用下AC/cAMP系统的上调也可能是通过激活PKA而调节某些转录因子的磷酸化水平,从而改变某些基因的表达。c-Fos是即刻早期基因编码的转录因子,脱磷酸化状态的c-Fos与c-Jun组成二聚体形成AP-1,可作为转录激活物发挥作用。本研究发现,吗啡依赖样SH-SY5Y细胞c-Fos磷酸化水平明显降低而PKA抑制剂可使c-Fos磷酸化水平明显增高,提示吗啡长时作用可通过c-Fos的去磷酸化而激活某些基因的转录,从而影响神经元的功能。因此推测,吗啡依赖样SH-SY5Y细胞中AC/cAMP系统的上调激活了PKA,而活化的PKA可能通过激活磷酸酶使c-Fos发生去磷酸化,影响某些基因的表达,从而使细胞产生依赖状态时的适应性变化。
, 百拇医药
△国家自然科学基金(39770852,39470803)资助;*北京协和医院病理科 100730;#通讯作者
参考文献
1 Sharma SK, Klee WA, Nirenberg M. Dual regulation of adenylate cyclase accounts for narcotic dependence and tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1975, 72:3092~3096
2 Musacchio JM, Greenspan DL. The adenylate cyclase rebound response to naloxone in the NG 108-15 cells:effects of etorphine and other opiates. Neuropharmacology, 1986, 25:833~837
, 百拇医药
3 Collier HO. Cellular site of opiate dependence. Nature, 1980, 283:625~629
4 Yu VC, Eiger S, Duan DS, et al. Regulation of cyclic cAMP by the μ-opioid receptor in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. J Neurochem, 1990, 55:1390~1396
5 方 芳,陈轶琨,王小明,等.吗啡长时程作用对小鼠脑组织蛋白激酶A及C活性的影响.基础医学与临床,1997,17:115~120
6 Sambrook J ,Fritsch EF, Maniatis T. Molecular cloning, A laboratory manual. 2nd ed. New York:Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989
, 百拇医药
7 Carter BD, Medzihradsky F. Receptor mechanisms of opioid tolerance in SH-SY5Y human neural cells. Mol Pharmacol, 1992, 43:465~473
8 Guitart X, Nestler EJ. Identification of morphineand cyclic AMP-regulated phospoprotein (MMRPPS) in the locus coerulas and other regions of rat brain: regulation by acute and chronic morphine. J Neurosci, 1989, 9:4371~4387
(1998-01-24 收稿), 百拇医药