5-氨基酮戊酸光动力学疗法体外杀伤人喉癌细胞株HEP-2的研究
作者:万新区 王楚平 程凯 李玲莉 徐世正 李常胜 杨占秋
单位:万新区(同济医科大学附属梨园医院皮肤科,武汉市,430077);王楚平(同济医科大学黄石中心医院教学医院);程凯(同济医科大学附属梨园医院皮肤科,武汉市,430077);李玲莉(湖北医科大学附属第一医院皮肤科);徐世正(湖北医科大学附属第一医院皮肤科);李常胜(湖北医科大学基础医学院);杨占秋(湖北医科大学基础医学院)
关键词:氨基酮戊酸;光化学疗法;肿瘤细胞,培养的
中华激光医学杂志000210
摘要 目的 探讨5-氨基酮戊酸光动力学疗法(ALA-PDT)体外伤杀肿瘤细胞的最佳照光时机和最佳照光能量。方法 用ALA诱导人喉癌细胞株HEP-2产生内源性的原卟啉Ⅸ,以功率密度为30 mW/cm2的He-Ne激光,分别照射与ALA共同培养1、4、8、12、48 h的HEP-2细胞,并对与ALA共同培养8 h的HEP-2细胞,以同样功率密度的He-Ne激光,分别照射0.5、1.0、2.0、3.0、4.0 min,能量密度分别为0.9、1.8、3.6、7.2、14.4 J/cm2。用MTT法测定照光后HEP-2细胞的死亡率。
, 百拇医药
结果 (1)光照时机选择在ALA与HEP-2细胞培养8 h时杀伤效应最强;(2)ALA-PDT对HEP-2细胞的杀伤效应与照光能量呈正相关(r=0.88,P<0.05)。
结论 ALA-PDT能有效地杀伤体外培养的肿瘤细胞,其杀伤最佳效果与照光时机和照光能量有关。
中图分类号: TN249;R730.58 文献标识码: A
文章编号: 1003-9430(2000)02-0102-03
Study on the Killing Effect of in Vitro Photodynamic Thorapy Using
Delta-aminolevulinic Acid on HEP-2 Cells
, 百拇医药
WAN Xinqu, CHENG Kai
(Department of Dermatology, Liyuan Hospital, Tongji Medical University, Wuhan 430077, China)
WANG Chuping
(Teaching Hospital of Huangshi Central Hospital, Tongji Medical University)
LI Lingli, XU Shizheng
(Department of Dermatology, First Affiliated Hospital, Hubei Medical University)
, http://www.100md.com
LI Changsheng, YANG Zhanqiu
(School of Basic Medical Sciences, Hubei Medical University)
ABSTRACT Objective To study the optimal irradiation time and power density in photodynamic therapy with delta-aminolevulinic acid(ALA-PDT) for tumor cells photoinactivation in vitro.Methods Endogenous protoporthyrin Ⅸ (PPⅨ) was induced by ALA in HEP-2 cell line. The He-Ne laser with a power density of 30mW/cm2 was used to irradiate the HEP-2 cells co-cultured with ALA for 1, 4, 8, 12 and 48 h respectively. The HEP-2 cells co-cultured with ALA for 8 h were harvested and were subjected to the irradiation with the same power density for 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0 min respectively, and with the energy density being 0.9, 1.8, 3.6, 7.2 and 14.4 J/cm2, respectively. The cell mortality following the irradiation was measured by using MTT assay.Results The strongest photoinactivation effect occured in the HEP-2 cells co-cultured with 1 mmol/L ALA for 8 h. The killing activity of ALA-PDT to the HEP-2 cells was positively correlated with the power density of the irradiation (r=0.88, P<0.05).Conclusions ALA-PDT can effectively kill the cultured HEP-2 cells in vitro. The optimal killing activity was related to the time and the power density of the laser irradiation.
, 百拇医药
Key words Aminolevulinic acid; Photochemotherapy; Tumor cells, cultured
光动力学疗法(photodynamic therapy, PDT)近年来已广泛应用于治疗各种体表肿瘤。以血卟啉衍生物作为光敏剂的PDT取得一定效果,但存在用药后患者需避光4~6周等令人难以接受的缺点[1]。90年代,国外试用5-氨基酮戊酸(delta-aminolevulinic acid, ALA)-PDT治疗肿瘤,即以ALA诱导肿瘤细胞产生具有光敏作用的原卟啉Ⅸ(PPⅨ)后,再进行PDT,取得一定效果[2]。为探讨该疗法在国内的临床应用,我们观察了ALA-PDT对人喉癌细胞株HEP-2的体外杀伤效应,并探讨了ALA-PDT体外杀肿瘤细胞的最佳时机和最佳光能量。
材料和方法
一、材料
, 百拇医药
HEP-2细胞购于湖北医科大学病毒研究所。ALA购于Sigma公司,四甲基偶氮唑盐(MTT)购于上海华美公司。
二、方法
1.照光时机的选择对ALA-PDT杀伤效应的影响 将HEP-2细胞按105个/孔接种96孔细胞培养板,培养24 h,去培养液,按培养1、4、8、12、48 h的要求,顺序加入终浓度为1 mmol/L的ALA,继续培养至规定的设置时间。取出细胞用PBS液洗2次。实验细胞分组:(1)对照组(细胞+ALA+遮光);(2)ALA-PDT组(细胞+ALA+He-Ne激光照射)。Ne-He激光波长630 nm,功率密度30 mW/cm2,有效光斑直径1.0~1.3 cm,照射3 min,能量密度为7.2 J/cm2。照射后,继续培养24 h,取出细胞,采用MTT分析法[3]测定细胞死亡率。MTT法原理是活细胞特别是增殖期的细胞,可通过线粒体能量代谢过程中的琥珀酸脱氢酶的作用使淡黄色的MTT还原为蓝黑色的甲 ,甲
,甲 的量与细胞增殖程度成正比,与细胞死亡率成反比。
的量与细胞增殖程度成正比,与细胞死亡率成反比。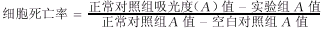
, http://www.100md.com
2.照光能量的选择对ALA-PDT杀伤效应的影响 将HEP-2细胞按105个/孔接种96孔培养板培养24 h,去培养液,加入终浓度为1 mmol/L的ALA,再培养8 h。取出细胞用PBS洗2次。按上述方法分组,然后用30 mW/cm2的He-Ne激光分别照射0.5、1.0、2.0、3.0、4.0 min,能量密度分别为0.9、1.8、3.6、7.2、14.4 J/cm2,照射后继续培养24 h,按上述方法计算细胞死亡率。
3.统计学处理 各组之间细胞死亡率的比较,采用配伍组设计多个样本均数两两比较的Newman-Keuls q检验[4]。照光时机和能量选择对ALA-PDT杀伤效应的影响,采用两因素关系的相关性与回归分析。
结 果
一、照光时机对ALA-PDT杀伤效应的影响
, http://www.100md.com
实验结果见表1。ALA与HEP-2细胞共同培养1 h后照光,对HEP-2细胞即有杀伤效应,以培养8 h后照光杀伤效应最强。
表1 ALA与HEP-2细胞共同培养不同时间后照光对HEP-2细胞的杀伤效应( ±s)
±s)
Tab.1 The photodynamic killing activity to the HEP-2 cells co-cultured with ALA for 1,4,8,12 and 48 h( ±s) 组别
±s) 组别
, http://www.100md.com
Groups
样本数
Samples
HEP-2细胞
死亡率
HEP-2 cell
mortality
q值*
q value*
对照组 Control group
8
0.080±0.004
, http://www.100md.com
A
ALA-PTD组 ALA-PDT group
培养1 h co-cultured 1 h
8
0.232±0.005
B
培养4 h co-cultured 4 h
8
0.674±0.038
C
培养8 h co-cultured 8 h
, 百拇医药
8
0.973±0.063
D
培养12 h co-cultured 12 h
8
0.697±0.047
C
培养48 h co-cultured 48 h
8
0.075±0.035
A
* q值项的字母相同 The same alphabets of q term,P>0.05,q值项字母不同 Different alphabets of q term,P<0.05
, http://www.100md.com
二、照光能量对ALA-PDT杀伤效应的影响
实验结果见表2。HEP-2细胞与ALA共同培养8 h后接受不同能量密度的激光照射,细胞死亡率随照光能量的增加而升高,在0.9、1.8、3.6、7.2 J/cm24组间,细胞死亡率与照光剂量呈正相关(r=0.88, P<0.05);当照光能量增至7.2 J/cm2后,细胞死亡率不再有明显升高。
表2 照光能量对ALA-PDT杀伤HEP-2细胞效应的影响( ±s)
±s)
Tab.2 The influence on killing activity of ALA-PDT to HEP-2 cells with an energy density of 0.9,1.8,3.6,7.2 or 14.4 J/cm2( ±s) 激光能量密度
±s) 激光能量密度
, 百拇医药
Laser energy density
(J/cm2)
样本数
Samples
HEP-2细胞死亡率
HEP-2 cell mortality
q值*
q value*
0.9
8
0.321±0.02
, 百拇医药
D
1.8
8
0.633±0.006
C
3.6
8
0.820±0.004
B
7.2
8
0.943±0.004
A
, 百拇医药
14.4
8
0.958±0.003
A
* q值项字母相同 The same alphabets of q term,P>0.05,q值项字母不同 Different alphabets of q term,P<0.05讨 论
ALA是血红素前体物,由甘氨酸、琥珀酸、辅酶A在ALA合成酶作用下合成,之后在ALA脱水酶等一系列酶作用下生成原卟啉,其中具有强光敏作用的PPⅨ是主体[5,6]。在正常情况下,这种合成途径受机体负反馈机制调节,因此机体内并未有过剩的PPⅨ。当给予外源性ALA后,这种调节机制被打乱,机体某些增殖较快的组织或者某些肿瘤细胞即可产生过量的PPⅨ,并聚积在相应的组织内[5,7-9]。
, http://www.100md.com
ALA诱导肿瘤细胞产生PPⅨ,细胞内PPⅨ的量随着ALA与细胞作用时间变化而变化,只有当细胞内PPⅨ达到最大时给予激光照射,才会产生最大杀伤效应。本实验结果显示,当照光时机选择在ALA与细胞共同培养8 h时,细胞死亡率最高,这与我们以前的实验结果[9]相吻合。该实验结果表明,细胞与ALA共同孵育8 h时,细胞内PPⅨ量最大。
ALA-PDT杀伤细胞作用不仅与细胞内PPⅨ含量有关,而且与照光能量有关。能量太小,达不到最大治疗效果;能量太大,又会产生光漂白作用。本实验结果表明,在一定范围内,增加照光能量可显著提高PDT杀伤能力,但超过某一范围,照光能量与细胞死亡率就不再呈正相关关系,这与Ratcliffe等[10]的结论基本一致。
作者简介:万新区(1963-),男,湖北广水人,同济医科大学附属梨园医院皮肤科主治医师,医学硕士,主要从事皮肤肿瘤的光动力学研究,以及银屑病、系统性红斑狼疮的中西医结合治疗。
, 百拇医药
参考文献
[1] Dougherty T, Cooper MT, Mang TS, et al. Cutaneous phototoxic occurrences in patients receiving photofin[J]. Lasers Surg Med, 1990, 10:485-488.
[2] Kennedy JC, Pottier KH. Photodynamic therapy with endogenous protoporphyrin IX: basic principles and present clinical experience[J]. J Photothem Photobiol B, 1990, 6:143-148.
[3] 温汉平,王小宁,孙华蕴,等. 肿瘤细胞体外药敏试验MTT分解法[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志,1993,16:470-471.
, 百拇医药
[4] 杨树勤,主编. 卫生统计学[M]. 第3版. 北京:人民卫生出版社,1993. 48-49.
[5] Shizheng Xu, Menon IA, Becker MAC, et al. Endogenous porphyrins in murine skin and transplanted PAM-212 squamous cell carcinoma tissues affter injections of δ-aminolevulinic acid[J]. Chin Med J, 1995, 108:286-290.
[6] Fijan S, Dough R. Photodynamic therapy of epithelial skin tumor using delta-aminolaevulinic acid and desferrioxamine[J]. Br J Dematol, 1995, 132:282-288.
, 百拇医药
[7] Svanberg K, Anderson T, Killander D, et al. Photodynamic therapy of non-melanoma malignant tumous of the skin using topical δ-aminolaevulinic acid sensitization and laser irradiation[J]. Br J Dematol, 1994, 130:743-751.
[8] Regula J, Mackobert A, Gorchein A, et al. Photosensitiastion and photodynamic therapy of oesophageal, duodenal and colorectal tumors using δ-animolaevulinic acid induced protoprophyrin Ⅸ: a pilot study[J]. Gut, 1995, 36:67-75.
, http://www.100md.com
[9] 万新区,程凯,李常胜,等. δ-氨基酮戊酸体外诱异HEP-2细胞产生内源性原卟啉Ⅸ的动力学研究[J]. 中华理疗杂志,1998,6:349.
[10] Ratcliffe SL, Mattews EK. Modification of the photodynamic action of δ-animolaevulinic acid(ALA) on rat pancreatoma cells by mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptor ligands[J]. Br J Cancer, 1995, 71:300-305.
(收稿日期:1999-01-15), 百拇医药
单位:万新区(同济医科大学附属梨园医院皮肤科,武汉市,430077);王楚平(同济医科大学黄石中心医院教学医院);程凯(同济医科大学附属梨园医院皮肤科,武汉市,430077);李玲莉(湖北医科大学附属第一医院皮肤科);徐世正(湖北医科大学附属第一医院皮肤科);李常胜(湖北医科大学基础医学院);杨占秋(湖北医科大学基础医学院)
关键词:氨基酮戊酸;光化学疗法;肿瘤细胞,培养的
中华激光医学杂志000210
摘要 目的 探讨5-氨基酮戊酸光动力学疗法(ALA-PDT)体外伤杀肿瘤细胞的最佳照光时机和最佳照光能量。方法 用ALA诱导人喉癌细胞株HEP-2产生内源性的原卟啉Ⅸ,以功率密度为30 mW/cm2的He-Ne激光,分别照射与ALA共同培养1、4、8、12、48 h的HEP-2细胞,并对与ALA共同培养8 h的HEP-2细胞,以同样功率密度的He-Ne激光,分别照射0.5、1.0、2.0、3.0、4.0 min,能量密度分别为0.9、1.8、3.6、7.2、14.4 J/cm2。用MTT法测定照光后HEP-2细胞的死亡率。
, 百拇医药
结果 (1)光照时机选择在ALA与HEP-2细胞培养8 h时杀伤效应最强;(2)ALA-PDT对HEP-2细胞的杀伤效应与照光能量呈正相关(r=0.88,P<0.05)。
结论 ALA-PDT能有效地杀伤体外培养的肿瘤细胞,其杀伤最佳效果与照光时机和照光能量有关。
中图分类号: TN249;R730.58 文献标识码: A
文章编号: 1003-9430(2000)02-0102-03
Study on the Killing Effect of in Vitro Photodynamic Thorapy Using
Delta-aminolevulinic Acid on HEP-2 Cells
, 百拇医药
WAN Xinqu, CHENG Kai
(Department of Dermatology, Liyuan Hospital, Tongji Medical University, Wuhan 430077, China)
WANG Chuping
(Teaching Hospital of Huangshi Central Hospital, Tongji Medical University)
LI Lingli, XU Shizheng
(Department of Dermatology, First Affiliated Hospital, Hubei Medical University)
, http://www.100md.com
LI Changsheng, YANG Zhanqiu
(School of Basic Medical Sciences, Hubei Medical University)
ABSTRACT Objective To study the optimal irradiation time and power density in photodynamic therapy with delta-aminolevulinic acid(ALA-PDT) for tumor cells photoinactivation in vitro.Methods Endogenous protoporthyrin Ⅸ (PPⅨ) was induced by ALA in HEP-2 cell line. The He-Ne laser with a power density of 30mW/cm2 was used to irradiate the HEP-2 cells co-cultured with ALA for 1, 4, 8, 12 and 48 h respectively. The HEP-2 cells co-cultured with ALA for 8 h were harvested and were subjected to the irradiation with the same power density for 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0 min respectively, and with the energy density being 0.9, 1.8, 3.6, 7.2 and 14.4 J/cm2, respectively. The cell mortality following the irradiation was measured by using MTT assay.Results The strongest photoinactivation effect occured in the HEP-2 cells co-cultured with 1 mmol/L ALA for 8 h. The killing activity of ALA-PDT to the HEP-2 cells was positively correlated with the power density of the irradiation (r=0.88, P<0.05).Conclusions ALA-PDT can effectively kill the cultured HEP-2 cells in vitro. The optimal killing activity was related to the time and the power density of the laser irradiation.
, 百拇医药
Key words Aminolevulinic acid; Photochemotherapy; Tumor cells, cultured
光动力学疗法(photodynamic therapy, PDT)近年来已广泛应用于治疗各种体表肿瘤。以血卟啉衍生物作为光敏剂的PDT取得一定效果,但存在用药后患者需避光4~6周等令人难以接受的缺点[1]。90年代,国外试用5-氨基酮戊酸(delta-aminolevulinic acid, ALA)-PDT治疗肿瘤,即以ALA诱导肿瘤细胞产生具有光敏作用的原卟啉Ⅸ(PPⅨ)后,再进行PDT,取得一定效果[2]。为探讨该疗法在国内的临床应用,我们观察了ALA-PDT对人喉癌细胞株HEP-2的体外杀伤效应,并探讨了ALA-PDT体外杀肿瘤细胞的最佳时机和最佳光能量。
材料和方法
一、材料
, 百拇医药
HEP-2细胞购于湖北医科大学病毒研究所。ALA购于Sigma公司,四甲基偶氮唑盐(MTT)购于上海华美公司。
二、方法
1.照光时机的选择对ALA-PDT杀伤效应的影响 将HEP-2细胞按105个/孔接种96孔细胞培养板,培养24 h,去培养液,按培养1、4、8、12、48 h的要求,顺序加入终浓度为1 mmol/L的ALA,继续培养至规定的设置时间。取出细胞用PBS液洗2次。实验细胞分组:(1)对照组(细胞+ALA+遮光);(2)ALA-PDT组(细胞+ALA+He-Ne激光照射)。Ne-He激光波长630 nm,功率密度30 mW/cm2,有效光斑直径1.0~1.3 cm,照射3 min,能量密度为7.2 J/cm2。照射后,继续培养24 h,取出细胞,采用MTT分析法[3]测定细胞死亡率。MTT法原理是活细胞特别是增殖期的细胞,可通过线粒体能量代谢过程中的琥珀酸脱氢酶的作用使淡黄色的MTT还原为蓝黑色的甲
, http://www.100md.com
2.照光能量的选择对ALA-PDT杀伤效应的影响 将HEP-2细胞按105个/孔接种96孔培养板培养24 h,去培养液,加入终浓度为1 mmol/L的ALA,再培养8 h。取出细胞用PBS洗2次。按上述方法分组,然后用30 mW/cm2的He-Ne激光分别照射0.5、1.0、2.0、3.0、4.0 min,能量密度分别为0.9、1.8、3.6、7.2、14.4 J/cm2,照射后继续培养24 h,按上述方法计算细胞死亡率。
3.统计学处理 各组之间细胞死亡率的比较,采用配伍组设计多个样本均数两两比较的Newman-Keuls q检验[4]。照光时机和能量选择对ALA-PDT杀伤效应的影响,采用两因素关系的相关性与回归分析。
结 果
一、照光时机对ALA-PDT杀伤效应的影响
, http://www.100md.com
实验结果见表1。ALA与HEP-2细胞共同培养1 h后照光,对HEP-2细胞即有杀伤效应,以培养8 h后照光杀伤效应最强。
表1 ALA与HEP-2细胞共同培养不同时间后照光对HEP-2细胞的杀伤效应(
Tab.1 The photodynamic killing activity to the HEP-2 cells co-cultured with ALA for 1,4,8,12 and 48 h(
, http://www.100md.com
Groups
样本数
Samples
HEP-2细胞
死亡率
HEP-2 cell
mortality
q值*
q value*
对照组 Control group
8
0.080±0.004
, http://www.100md.com
A
ALA-PTD组 ALA-PDT group
培养1 h co-cultured 1 h
8
0.232±0.005
B
培养4 h co-cultured 4 h
8
0.674±0.038
C
培养8 h co-cultured 8 h
, 百拇医药
8
0.973±0.063
D
培养12 h co-cultured 12 h
8
0.697±0.047
C
培养48 h co-cultured 48 h
8
0.075±0.035
A
* q值项的字母相同 The same alphabets of q term,P>0.05,q值项字母不同 Different alphabets of q term,P<0.05
, http://www.100md.com
二、照光能量对ALA-PDT杀伤效应的影响
实验结果见表2。HEP-2细胞与ALA共同培养8 h后接受不同能量密度的激光照射,细胞死亡率随照光能量的增加而升高,在0.9、1.8、3.6、7.2 J/cm24组间,细胞死亡率与照光剂量呈正相关(r=0.88, P<0.05);当照光能量增至7.2 J/cm2后,细胞死亡率不再有明显升高。
表2 照光能量对ALA-PDT杀伤HEP-2细胞效应的影响(
Tab.2 The influence on killing activity of ALA-PDT to HEP-2 cells with an energy density of 0.9,1.8,3.6,7.2 or 14.4 J/cm2(
, 百拇医药
Laser energy density
(J/cm2)
样本数
Samples
HEP-2细胞死亡率
HEP-2 cell mortality
q值*
q value*
0.9
8
0.321±0.02
, 百拇医药
D
1.8
8
0.633±0.006
C
3.6
8
0.820±0.004
B
7.2
8
0.943±0.004
A
, 百拇医药
14.4
8
0.958±0.003
A
* q值项字母相同 The same alphabets of q term,P>0.05,q值项字母不同 Different alphabets of q term,P<0.05讨 论
ALA是血红素前体物,由甘氨酸、琥珀酸、辅酶A在ALA合成酶作用下合成,之后在ALA脱水酶等一系列酶作用下生成原卟啉,其中具有强光敏作用的PPⅨ是主体[5,6]。在正常情况下,这种合成途径受机体负反馈机制调节,因此机体内并未有过剩的PPⅨ。当给予外源性ALA后,这种调节机制被打乱,机体某些增殖较快的组织或者某些肿瘤细胞即可产生过量的PPⅨ,并聚积在相应的组织内[5,7-9]。
, http://www.100md.com
ALA诱导肿瘤细胞产生PPⅨ,细胞内PPⅨ的量随着ALA与细胞作用时间变化而变化,只有当细胞内PPⅨ达到最大时给予激光照射,才会产生最大杀伤效应。本实验结果显示,当照光时机选择在ALA与细胞共同培养8 h时,细胞死亡率最高,这与我们以前的实验结果[9]相吻合。该实验结果表明,细胞与ALA共同孵育8 h时,细胞内PPⅨ量最大。
ALA-PDT杀伤细胞作用不仅与细胞内PPⅨ含量有关,而且与照光能量有关。能量太小,达不到最大治疗效果;能量太大,又会产生光漂白作用。本实验结果表明,在一定范围内,增加照光能量可显著提高PDT杀伤能力,但超过某一范围,照光能量与细胞死亡率就不再呈正相关关系,这与Ratcliffe等[10]的结论基本一致。
作者简介:万新区(1963-),男,湖北广水人,同济医科大学附属梨园医院皮肤科主治医师,医学硕士,主要从事皮肤肿瘤的光动力学研究,以及银屑病、系统性红斑狼疮的中西医结合治疗。
, 百拇医药
参考文献
[1] Dougherty T, Cooper MT, Mang TS, et al. Cutaneous phototoxic occurrences in patients receiving photofin[J]. Lasers Surg Med, 1990, 10:485-488.
[2] Kennedy JC, Pottier KH. Photodynamic therapy with endogenous protoporphyrin IX: basic principles and present clinical experience[J]. J Photothem Photobiol B, 1990, 6:143-148.
[3] 温汉平,王小宁,孙华蕴,等. 肿瘤细胞体外药敏试验MTT分解法[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志,1993,16:470-471.
, 百拇医药
[4] 杨树勤,主编. 卫生统计学[M]. 第3版. 北京:人民卫生出版社,1993. 48-49.
[5] Shizheng Xu, Menon IA, Becker MAC, et al. Endogenous porphyrins in murine skin and transplanted PAM-212 squamous cell carcinoma tissues affter injections of δ-aminolevulinic acid[J]. Chin Med J, 1995, 108:286-290.
[6] Fijan S, Dough R. Photodynamic therapy of epithelial skin tumor using delta-aminolaevulinic acid and desferrioxamine[J]. Br J Dematol, 1995, 132:282-288.
, 百拇医药
[7] Svanberg K, Anderson T, Killander D, et al. Photodynamic therapy of non-melanoma malignant tumous of the skin using topical δ-aminolaevulinic acid sensitization and laser irradiation[J]. Br J Dematol, 1994, 130:743-751.
[8] Regula J, Mackobert A, Gorchein A, et al. Photosensitiastion and photodynamic therapy of oesophageal, duodenal and colorectal tumors using δ-animolaevulinic acid induced protoprophyrin Ⅸ: a pilot study[J]. Gut, 1995, 36:67-75.
, http://www.100md.com
[9] 万新区,程凯,李常胜,等. δ-氨基酮戊酸体外诱异HEP-2细胞产生内源性原卟啉Ⅸ的动力学研究[J]. 中华理疗杂志,1998,6:349.
[10] Ratcliffe SL, Mattews EK. Modification of the photodynamic action of δ-animolaevulinic acid(ALA) on rat pancreatoma cells by mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptor ligands[J]. Br J Cancer, 1995, 71:300-305.
(收稿日期:1999-01-15), 百拇医药