移植胚鼠弓状核细胞后对动脉粥样硬化形成的影响
作者:吴开云 高摄渊 熊俊平 李耀斌
单位:吴开云(江西医学院解剖学教研室);高摄渊(组织学与胚胎学教研室; 江西省南昌市 330006);熊俊平(江西医学院解剖学教研室);李耀斌(江西医学院解剖学教研室)
关键词:动脉粥样硬化;弓状核;移植;细胞悬液;大鼠
中国动脉硬化杂志000208[摘 要] 为进一步证实毁损弓状核可诱发动脉粥样硬化的早期变化这一作用,用毁损弓状核诱发动脉粥样硬化早期变化后,重新植入胚鼠弓状核细胞悬液来观察动脉壁的变化是否能得以恢复。实验用新生Wistar大鼠18只,按出生后1、3、5、7、9天皮下注射10%谷氨酸单钠4 g/kg体重,共注射5次,为毁损弓状核诱发动脉粥样硬化动物模型,存活30天后,取6只动物主动脉作为对照组Ⅰ,另12只动物分为实验组和对照组Ⅱ,实验组在弓状核区重新植入14天胚鼠弓状核细胞悬液 5 μL(细胞浓度为1×1015/L),对照组Ⅱ植入等量生理盐水继续存活30天后各取主动脉作电镜观察。结果发现:对照组Ⅰ动物主动脉壁内皮细胞腔面可见微绒毛样突起,内皮细胞核有些扭曲,不规则,内皮下层未见增厚;对照组Ⅱ动物内皮细胞变性、脱落,内皮下层明显增厚,出现许多大小不等的空泡和胶原纤维,有巨噬细胞和平滑肌细胞迁入内皮下层,这些变化是动脉粥样硬化发病的早期特征性病变;实验组动物内皮细胞核完整,内皮与内皮下层连接紧密,偶尔可见内皮细胞核扭曲。实验证明,在被毁损弓状核区重新植入胚鼠弓状核细胞后对动脉粥样硬化有明显恢复作用,从而证实下丘脑弓状核对动脉粥样硬化的形成具有重要调控作用。
, http://www.100md.com
[中图分类号] R363.2 [文献标识码] A
[文章编号] 1007-3949(2000)-02-0118-03
Influence of Transplanted Embryonic Arcuate Nucleus in Destroyed Nucleus on Atherosclerosis
WU Kai-Yun, GAO She-Yuan, XIONG Jun-Ping, and LI Yiao-Bin
(Department of Anatomy, Department of Histology and Embryology, Jiangxi Medical College, Nanchang 330006, China)
ABSTRACT Aim It has been proved in our previous work that destruction of arcuate nucleus could induce early atherosclerosis .In order to further research into the influence of hypothalamic arcuate nucleus on the development of atheroscerosis, this study was to investigated whether the transplantation of cell suspension of arcuate nucleus into the destroyed nucleus would act on the recovery of atherosclerosis. Methods Eighteen new born Wistar rats injected with monosodium glutamate(MSG)4 g/kg hypodermically once every other day for 5 d were used as induced atherosclerosis model. After surviving for 30 d, six animals sacrificed with their aorta taken serve as control group Ⅰ. The other 12 animals were equally divided into experiment group and control group Ⅱ. The experimental group were transplanted with 5 μL cell suspension (1×1015/L)of arcuate nucleus from 14 d embryo and control groupⅡ were given equal volume of normal saline. After surviving for another 30 d, the aorta of these animals were made ultrathin section and investigated under electromicroscope. Results In control group Ⅰ(arcuate nucleus damaged by MSG for 30 d), microvillous projections of endothelial cells were observed on the luminal surface and the nuclei of the endothelial cells became twisted and irregular, but without thickening of subendothelial tissue. In control group Ⅱ(arcuate nucleus damaged by MSG for 60 d), degeneration of endothelial cells could be seen and some endothelial cells had fallen off. The subendothelial tissue was evidently thickened with a few collagnous fibers, vesicles of various size and macrophage or smooth muscle cells migrated from blood and tunica media through the ruptured elastic intima, indicating characteristic changes of early atherosclerosis. In the experimental group (transplanted with embryonic arcuate nucleus), the endothelial cells remained intact, and connected tightly with subendothelial tissue, occasionally twisted nucleus could be seen. Conclusions This experiment indicate that transplanted arcuate nucleus in the destroyed nucleus has notably made the animal recovery from atherosclerosis and thereby confirms that hypothalamic arcuate nucleus has influence on development and/or control of atherosclerosis.
, 百拇医药
MeSH Atherosclerosis; Arcuate Nucleus; Transplant; Cell Suspension; Rat
对动脉粥样硬化(atherosclerosis,As)的研究已经历了一百多年,但对其发病机理仍未完全明了。以往对As发病机理的研究,基本上都有是围绕血管本身病变的过程而提出的,而对下丘脑血管中枢是否对As的形成具有调控作用很少有人提出过。70年代前苏联Zavodskaia 等[1]用电长期刺激家兔下丘脑可引起高脂血症和As形成;1983年王天保等[2]报道破坏下丘脑使冠状动脉粥样硬化加重;1997年日本Nishida等[3]报道在特发糖尿病大鼠内,通过损伤下丘脑可诱发As早期变化。在我们以前的研究工作中证实用不同方法毁损下丘脑弓状核后可诱发As早期病变[4,5],以及与As形成密切相关的物质(如总胆固醇、氧化型低密度脂蛋白、脂质过氧化物、一氧化氮等)都发生了明显改变[6,7]。为了进一步证实下丘脑弓状核对As形成的影响,本文用毁损弓状核诱发As早期病变后,重新植入胚鼠弓状核细胞悬液来观察As的变化是否得到恢复。力求为阐明下丘脑弓状核与As形成之间的关系提供有力证据。
, http://www.100md.com
1 材料与方法
选新生Wistar大鼠18只,按出生后第1、3、5、7、9天背部皮下注射10%谷氨酸单钠(monosodium glutamate, MSG)4 g/kg体重,共注射5次[4],为毁损弓状核诱发As动物模型,存活30天(喂饲大鼠普通饲料)后,取6只动物的主动脉作为对照组Ⅰ,另12只动物分为实验组和对照组Ⅱ,每组6只动物,实验组按照Pellegrino图谱A系统,固定于立体定位仪后,向下丘脑弓状核区(坐标为A 5.6, L和R 0.5,H 9.0)插入直径为0.1 mm绝缘针管(针管的末端是非绝缘的),植入14天胚鼠弓状核细胞5 μL(细胞浓度为1×1015/L),对照组Ⅱ注入等量生理盐水,两组动物在同一条件下继续存活30天(喂饲大鼠普通饲料)后各取主动脉作电镜观察。
2 结 果
对照组Ⅰ(注射MSG 后30 d),主动脉壁内皮细胞腔面可见微绒毛样突起,内皮细胞核有些扭曲,不规则,内皮下层未见增厚(图1,Figure 1);对照组Ⅱ(注射MSG 后60 d)动物血管壁内皮细胞变性、脱落,内皮下层明显增厚,出现许多大小不等的空泡和增生的胶原纤维,有巨噬细胞和平滑肌细胞迁入内皮下层,这些变化是As早期的特征性病变(图 2,Figure 2);实验组(注射MSG 30 d后植入胚鼠弓状核)动物血管壁内皮细胞核完整,内皮与内皮下层连接紧密,偶尔可见内皮细胞核扭曲(图 3,Figure 3)。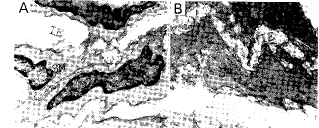
, 百拇医药
图1. 对照组Ⅰ动物注射谷氨酸单钠后30天的电镜观察
Figure 1. Electron micrograph (EM)of 30 d after arcuate nucleus being damaged by MSG. Short projections on the luminal surface of endothelial cells are present, the nuclei of the endothelial cells become twisted. A: × 6 000; B: ×6 000
图2. 对照组Ⅱ动物注射谷氨酸单钠60天后电镜观察
Figure 2. EM of 60 d after arcuate nucleus being damaged by MSG. Egeneration of endothelial cells could be seen and some as the endothelial cells had fallen off. The subendothelial tissue was evidently thickened with macrophges or smooth muscle cells migrated from blood and tunica media. A:× 9 000; B:× 4 800; C:× 3 000.
, 百拇医药
图3. 实验组动物注射谷氨酸单钠30天后植入胚鼠弓状核的电镜观察
Figure 3. EM of transplanted with embryonic arcuate nucleus after arcuate nucleus being damaged by MSG for 30 d. The endothelial cells remained intact, and connected tightly with subendothelial tissue,occasionally twisted nucleus could be seen. A:× 9 000; B: × 3 600.
3 讨 论
我室从1994 年开始对As发病的“中枢机理”进行了一些探索性研究,用不同方法毁损下丘脑弓状核后主动脉壁内皮细胞发生变性,细胞核肿胀,内皮下层增厚并出现空泡,可见有平滑肌细胞向内皮下层迁移,这些变化是As早期发病的特征性病变[4,5]。此外,血液中与As形成密切相关的物质也发生变化,如毁损弓状核后总胆固醇(TC)、氧化型低密度脂蛋白(ox-LDL)和脂过氧化物(LPO)均升高,而一氧化氮(NO)则下降,与用药物诱发As的变化极为相似[6,7]。从我们以前的研究结果来看,下丘脑弓状核对As形成可能具有重要影响。
, http://www.100md.com
如果这一结果进一步得到证实的话,对中枢发病机理的假说将提供重要证据。因此,为了进一步证实下丘脑弓状核对As的形成是否具有重要影响,本文用毁损弓状核诱发As早期病变后,重新植入胚鼠弓状核细胞悬液来观察As变化是否得到恢复。本文结果表明注射MSG 后30 d,对照组主动脉血管壁内皮细胞腔面可见微绒毛样突起,内皮细胞核有些扭曲,不规则,内皮下层未见明显增厚;注射MSG 后60 d对照组,内皮细胞变性、脱落,内皮下层明显增厚,出现许多大小不等的空泡和胶原纤维,有巨噬细胞和平滑肌细胞迁入内皮下层,这些变化 是As早期特征性病变;实验组(注射MSG 30d后植入胚鼠弓状核),内皮细胞核完整,内皮与内皮下层连接紧密,偶尔可见内皮细胞核扭曲。本文结果证明在被毁损弓状核区重新植入胚鼠弓状核对As有明显恢复作用,从而为证实下丘脑弓状核对As的形成具有重要调控作用提供了可靠证据,但其调控是通过何种物质来实现?其通路如何?需进一步深入研究。
[基金项目] 国家自然科学基金(39660031)及江西省自然科学基金资助项目
, http://www.100md.com
[作者简介] 吴开云,男,1954年11月出生,副教授,硕士研究生导师; 高摄渊,女,1927年11月出生,教授,硕士研究生导师。
参考文献
[1] Zavodskaia IS, Moreva EV, Sinitsyna TA, et al. Effect of electrostimulation of the supraoptic region of the hypothalamus on lipid metabolism and the development of atherosclerosis[J]. Biull Eksp Biol Med, 1978, 85(6): 661-664
[2] 王天保,周其善,唐秀梅,等. 破坏家兔下丘脑对实验性动脉粥样硬化的影响[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 1983, 11(2): 144-146
, http://www.100md.com
[3] Nishida M, Miyagawa JI, Tokunaga K, et al. Early morphologic changes of atherosclerosis induced by ventromedial hypothalamic lesion in the spontaneously diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rat [J]. J Lab Clin Med, 1997,129(2): 200-207
[4] 吴开云, 高摄渊. 毁损弓状核对动脉粥样硬化形成的影响[J]. 神经解剖学杂志, 1999, 15 (1): 79-81
[5] 吴开云, 熊俊平, 李耀斌, 等. 电解损弓状核对动脉粥样硬化形成的影响[J]. 中国学术期刊文摘, 1998, 4 (10): 1 254-255
[6] 吴开云,高摄渊.毁损弓状核对总胆固醇、高密度脂蛋白、氧化型低密度脂蛋白的影响[J]. 中国学术期刊文摘, 1998, 4 (10): 1 256-257
[7] 吴开云, 李耀斌, 熊俊平, 等. 毁损弓状核对一氧化氮和过氧化脂质的影响[J]. 中国学术期刊文摘, 1998, 4 (10): 1 257-258
1999-08-08收到
2000-04-26修回, http://www.100md.com
单位:吴开云(江西医学院解剖学教研室);高摄渊(组织学与胚胎学教研室; 江西省南昌市 330006);熊俊平(江西医学院解剖学教研室);李耀斌(江西医学院解剖学教研室)
关键词:动脉粥样硬化;弓状核;移植;细胞悬液;大鼠
中国动脉硬化杂志000208[摘 要] 为进一步证实毁损弓状核可诱发动脉粥样硬化的早期变化这一作用,用毁损弓状核诱发动脉粥样硬化早期变化后,重新植入胚鼠弓状核细胞悬液来观察动脉壁的变化是否能得以恢复。实验用新生Wistar大鼠18只,按出生后1、3、5、7、9天皮下注射10%谷氨酸单钠4 g/kg体重,共注射5次,为毁损弓状核诱发动脉粥样硬化动物模型,存活30天后,取6只动物主动脉作为对照组Ⅰ,另12只动物分为实验组和对照组Ⅱ,实验组在弓状核区重新植入14天胚鼠弓状核细胞悬液 5 μL(细胞浓度为1×1015/L),对照组Ⅱ植入等量生理盐水继续存活30天后各取主动脉作电镜观察。结果发现:对照组Ⅰ动物主动脉壁内皮细胞腔面可见微绒毛样突起,内皮细胞核有些扭曲,不规则,内皮下层未见增厚;对照组Ⅱ动物内皮细胞变性、脱落,内皮下层明显增厚,出现许多大小不等的空泡和胶原纤维,有巨噬细胞和平滑肌细胞迁入内皮下层,这些变化是动脉粥样硬化发病的早期特征性病变;实验组动物内皮细胞核完整,内皮与内皮下层连接紧密,偶尔可见内皮细胞核扭曲。实验证明,在被毁损弓状核区重新植入胚鼠弓状核细胞后对动脉粥样硬化有明显恢复作用,从而证实下丘脑弓状核对动脉粥样硬化的形成具有重要调控作用。
, http://www.100md.com
[中图分类号] R363.2 [文献标识码] A
[文章编号] 1007-3949(2000)-02-0118-03
Influence of Transplanted Embryonic Arcuate Nucleus in Destroyed Nucleus on Atherosclerosis
WU Kai-Yun, GAO She-Yuan, XIONG Jun-Ping, and LI Yiao-Bin
(Department of Anatomy, Department of Histology and Embryology, Jiangxi Medical College, Nanchang 330006, China)
ABSTRACT Aim It has been proved in our previous work that destruction of arcuate nucleus could induce early atherosclerosis .In order to further research into the influence of hypothalamic arcuate nucleus on the development of atheroscerosis, this study was to investigated whether the transplantation of cell suspension of arcuate nucleus into the destroyed nucleus would act on the recovery of atherosclerosis. Methods Eighteen new born Wistar rats injected with monosodium glutamate(MSG)4 g/kg hypodermically once every other day for 5 d were used as induced atherosclerosis model. After surviving for 30 d, six animals sacrificed with their aorta taken serve as control group Ⅰ. The other 12 animals were equally divided into experiment group and control group Ⅱ. The experimental group were transplanted with 5 μL cell suspension (1×1015/L)of arcuate nucleus from 14 d embryo and control groupⅡ were given equal volume of normal saline. After surviving for another 30 d, the aorta of these animals were made ultrathin section and investigated under electromicroscope. Results In control group Ⅰ(arcuate nucleus damaged by MSG for 30 d), microvillous projections of endothelial cells were observed on the luminal surface and the nuclei of the endothelial cells became twisted and irregular, but without thickening of subendothelial tissue. In control group Ⅱ(arcuate nucleus damaged by MSG for 60 d), degeneration of endothelial cells could be seen and some endothelial cells had fallen off. The subendothelial tissue was evidently thickened with a few collagnous fibers, vesicles of various size and macrophage or smooth muscle cells migrated from blood and tunica media through the ruptured elastic intima, indicating characteristic changes of early atherosclerosis. In the experimental group (transplanted with embryonic arcuate nucleus), the endothelial cells remained intact, and connected tightly with subendothelial tissue, occasionally twisted nucleus could be seen. Conclusions This experiment indicate that transplanted arcuate nucleus in the destroyed nucleus has notably made the animal recovery from atherosclerosis and thereby confirms that hypothalamic arcuate nucleus has influence on development and/or control of atherosclerosis.
, 百拇医药
MeSH Atherosclerosis; Arcuate Nucleus; Transplant; Cell Suspension; Rat
对动脉粥样硬化(atherosclerosis,As)的研究已经历了一百多年,但对其发病机理仍未完全明了。以往对As发病机理的研究,基本上都有是围绕血管本身病变的过程而提出的,而对下丘脑血管中枢是否对As的形成具有调控作用很少有人提出过。70年代前苏联Zavodskaia 等[1]用电长期刺激家兔下丘脑可引起高脂血症和As形成;1983年王天保等[2]报道破坏下丘脑使冠状动脉粥样硬化加重;1997年日本Nishida等[3]报道在特发糖尿病大鼠内,通过损伤下丘脑可诱发As早期变化。在我们以前的研究工作中证实用不同方法毁损下丘脑弓状核后可诱发As早期病变[4,5],以及与As形成密切相关的物质(如总胆固醇、氧化型低密度脂蛋白、脂质过氧化物、一氧化氮等)都发生了明显改变[6,7]。为了进一步证实下丘脑弓状核对As形成的影响,本文用毁损弓状核诱发As早期病变后,重新植入胚鼠弓状核细胞悬液来观察As的变化是否得到恢复。力求为阐明下丘脑弓状核与As形成之间的关系提供有力证据。
, http://www.100md.com
1 材料与方法
选新生Wistar大鼠18只,按出生后第1、3、5、7、9天背部皮下注射10%谷氨酸单钠(monosodium glutamate, MSG)4 g/kg体重,共注射5次[4],为毁损弓状核诱发As动物模型,存活30天(喂饲大鼠普通饲料)后,取6只动物的主动脉作为对照组Ⅰ,另12只动物分为实验组和对照组Ⅱ,每组6只动物,实验组按照Pellegrino图谱A系统,固定于立体定位仪后,向下丘脑弓状核区(坐标为A 5.6, L和R 0.5,H 9.0)插入直径为0.1 mm绝缘针管(针管的末端是非绝缘的),植入14天胚鼠弓状核细胞5 μL(细胞浓度为1×1015/L),对照组Ⅱ注入等量生理盐水,两组动物在同一条件下继续存活30天(喂饲大鼠普通饲料)后各取主动脉作电镜观察。
2 结 果
对照组Ⅰ(注射MSG 后30 d),主动脉壁内皮细胞腔面可见微绒毛样突起,内皮细胞核有些扭曲,不规则,内皮下层未见增厚(图1,Figure 1);对照组Ⅱ(注射MSG 后60 d)动物血管壁内皮细胞变性、脱落,内皮下层明显增厚,出现许多大小不等的空泡和增生的胶原纤维,有巨噬细胞和平滑肌细胞迁入内皮下层,这些变化是As早期的特征性病变(图 2,Figure 2);实验组(注射MSG 30 d后植入胚鼠弓状核)动物血管壁内皮细胞核完整,内皮与内皮下层连接紧密,偶尔可见内皮细胞核扭曲(图 3,Figure 3)。

, 百拇医药
图1. 对照组Ⅰ动物注射谷氨酸单钠后30天的电镜观察
Figure 1. Electron micrograph (EM)of 30 d after arcuate nucleus being damaged by MSG. Short projections on the luminal surface of endothelial cells are present, the nuclei of the endothelial cells become twisted. A: × 6 000; B: ×6 000

图2. 对照组Ⅱ动物注射谷氨酸单钠60天后电镜观察
Figure 2. EM of 60 d after arcuate nucleus being damaged by MSG. Egeneration of endothelial cells could be seen and some as the endothelial cells had fallen off. The subendothelial tissue was evidently thickened with macrophges or smooth muscle cells migrated from blood and tunica media. A:× 9 000; B:× 4 800; C:× 3 000.

, 百拇医药
图3. 实验组动物注射谷氨酸单钠30天后植入胚鼠弓状核的电镜观察
Figure 3. EM of transplanted with embryonic arcuate nucleus after arcuate nucleus being damaged by MSG for 30 d. The endothelial cells remained intact, and connected tightly with subendothelial tissue,occasionally twisted nucleus could be seen. A:× 9 000; B: × 3 600.
3 讨 论
我室从1994 年开始对As发病的“中枢机理”进行了一些探索性研究,用不同方法毁损下丘脑弓状核后主动脉壁内皮细胞发生变性,细胞核肿胀,内皮下层增厚并出现空泡,可见有平滑肌细胞向内皮下层迁移,这些变化是As早期发病的特征性病变[4,5]。此外,血液中与As形成密切相关的物质也发生变化,如毁损弓状核后总胆固醇(TC)、氧化型低密度脂蛋白(ox-LDL)和脂过氧化物(LPO)均升高,而一氧化氮(NO)则下降,与用药物诱发As的变化极为相似[6,7]。从我们以前的研究结果来看,下丘脑弓状核对As形成可能具有重要影响。
, http://www.100md.com
如果这一结果进一步得到证实的话,对中枢发病机理的假说将提供重要证据。因此,为了进一步证实下丘脑弓状核对As的形成是否具有重要影响,本文用毁损弓状核诱发As早期病变后,重新植入胚鼠弓状核细胞悬液来观察As变化是否得到恢复。本文结果表明注射MSG 后30 d,对照组主动脉血管壁内皮细胞腔面可见微绒毛样突起,内皮细胞核有些扭曲,不规则,内皮下层未见明显增厚;注射MSG 后60 d对照组,内皮细胞变性、脱落,内皮下层明显增厚,出现许多大小不等的空泡和胶原纤维,有巨噬细胞和平滑肌细胞迁入内皮下层,这些变化 是As早期特征性病变;实验组(注射MSG 30d后植入胚鼠弓状核),内皮细胞核完整,内皮与内皮下层连接紧密,偶尔可见内皮细胞核扭曲。本文结果证明在被毁损弓状核区重新植入胚鼠弓状核对As有明显恢复作用,从而为证实下丘脑弓状核对As的形成具有重要调控作用提供了可靠证据,但其调控是通过何种物质来实现?其通路如何?需进一步深入研究。
[基金项目] 国家自然科学基金(39660031)及江西省自然科学基金资助项目
, http://www.100md.com
[作者简介] 吴开云,男,1954年11月出生,副教授,硕士研究生导师; 高摄渊,女,1927年11月出生,教授,硕士研究生导师。
参考文献
[1] Zavodskaia IS, Moreva EV, Sinitsyna TA, et al. Effect of electrostimulation of the supraoptic region of the hypothalamus on lipid metabolism and the development of atherosclerosis[J]. Biull Eksp Biol Med, 1978, 85(6): 661-664
[2] 王天保,周其善,唐秀梅,等. 破坏家兔下丘脑对实验性动脉粥样硬化的影响[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 1983, 11(2): 144-146
, http://www.100md.com
[3] Nishida M, Miyagawa JI, Tokunaga K, et al. Early morphologic changes of atherosclerosis induced by ventromedial hypothalamic lesion in the spontaneously diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rat [J]. J Lab Clin Med, 1997,129(2): 200-207
[4] 吴开云, 高摄渊. 毁损弓状核对动脉粥样硬化形成的影响[J]. 神经解剖学杂志, 1999, 15 (1): 79-81
[5] 吴开云, 熊俊平, 李耀斌, 等. 电解损弓状核对动脉粥样硬化形成的影响[J]. 中国学术期刊文摘, 1998, 4 (10): 1 254-255
[6] 吴开云,高摄渊.毁损弓状核对总胆固醇、高密度脂蛋白、氧化型低密度脂蛋白的影响[J]. 中国学术期刊文摘, 1998, 4 (10): 1 256-257
[7] 吴开云, 李耀斌, 熊俊平, 等. 毁损弓状核对一氧化氮和过氧化脂质的影响[J]. 中国学术期刊文摘, 1998, 4 (10): 1 257-258
1999-08-08收到
2000-04-26修回, http://www.100md.com