胫骨后倾角解剖与放射学测量评价
作者:张树栋 曲广运 张光辉 杨林海
单位:张树栋(264001烟台市烟台山医院骨科);张光辉 杨林海(CT室);曲广运(香港大学骨科学系)
关键词:膝关节;人工;放射学;解剖学;局部
中华骨科杂志000405
【摘要】目的测量国人胫骨后倾角,为全膝关节置换及翻修术提供确切的胫骨后倾角数值。方法25具尸体(50个胫骨标本),切除胫骨平台表面软组织及半月板,测量胫骨平台内、外侧后倾角度;并摄X线片,模拟手术方法测量髓内、髓外胫骨后倾角度。结果胫骨平台内侧后倾角为15.02°±4.20°,外侧后倾角为11.74°±3.80°。胫骨X线片髓内定位胫骨后倾角为11.55°±3.60°,髓外定位胫骨后倾角为14.67°±3.68°,退变关节的胫骨后倾角增大。结论无论正常或退变关节的胫骨平台后倾角,内侧大于外侧;胫骨X线片髓内定位胫骨后倾角小于髓外定位胫骨后倾角,后者与实际解剖测量胫骨平台内侧后倾角值的差异无显著性意义(P>0.05)。建议将胫骨平台内侧后倾角的数值作为全膝关节置换术的参考指数。
, 百拇医药
Evaluation of posterior slope of tibial plateau in Chinese
ZHANG Shudong, QU Guangyun, ZHANG Guanghui, et al.
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yantai Shan Hospital,Yantai 264001, China
【 Abstract】 Objective To determine the posterior slope angle of tibial plateau in Chinese for providing an actual value of the posterior slope of the tibia, an indispensable value during total knee arthoplasty. Methods Twenty five Chinese cadaveric tibia specimens were used for the measurement of the posterior slope of tibial plateau. The articular cartilage and the discs were removed and the lateral and medial posterior slope of the tibia were measured. Radiographs were then taken. To mimic the operative procedures, the intramedullary and extramedullary tibial slopes were measured. Results The values of posterior slope were 15.02° ± 4.20° at the medial plateau and 11.74° ± 3.80° at the lateral side by direct measurement. The intramedullary and extramedullary posterior slope angles were 11.55° ± 3.60° and 14.67° ± 3.68° by radiographic measurement. The posterior slope was increased in the degenerative cadaveric knees. Conclusion The posterior slope at medial plateau was greater than that at lateral one whether in normal or in degenerative knees. Intramedullary posterior tibial slope was smaller than extramedullary one, and the latter was similar to the medial plateau by direct measurement. It is suggested that the medial posterior slope of tibial plateau should be a reference index during total knee arthroplasty.
, 百拇医药
【 Key words】 Knee prosthesis; Radiology; Anatomy,regional
在人工全膝关节置换及翻修术中,一个理想的胫骨后倾角是术后恢复膝关节伸屈功能,保持膝关节稳定性及延长假体使用寿命的基本前提。为此,我们对25具尸体的胫骨后倾角进行了实体及放射学髓内、髓外(模拟手术定位)等方面的测量。
材料与方法
一、材料
25具国人尸体,男20具,女5具,共50个胫骨标本。年龄17~94岁,平均68.3岁。将胫、腓骨附着的软组织切除,同时将胫骨平台表面的软组织和半月板切除。分别编号,并对胫骨平台有退行性变(边缘唇样增生、内翻隆起、向两侧倾斜)的15个标本登记注明。
二、方法
, 百拇医药
(一)X线投照:将胫骨依次固定于支架上,统一定位,放置一标准X线刻度尺,球管距离100cm,摄侧位片备用(图1)。
图1X线片髓内、髓外测量图
(二)胫骨拍摄:将胫骨放置于固定架上,在内侧平台中1/2处水平放置一枚长20cm的梅花形髓内钉,并与胫骨嵴方向平行(图2),用数码电子照相机在距胫骨120cm处,垂直于胫骨中上1/3且与髓内钉平行的方向摄片。同法用于胫骨平台外侧的摄片。依次摄片并打印出纸片备用。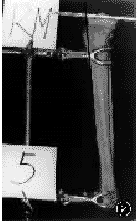
图2实体测量角度
三、胫骨后倾角的测量
(一)X线片髓内测量:模拟手术的髓内定位法,测量胫骨平台前后缘连线与髁间棘前缘和髓腔最狭窄处中1/2连线的角度(图1)。
, 百拇医药
(二)X线片髓外测量:测量胫骨平台前后缘连线与胫骨结节上方和胫骨前缘骨皮质连线的角度(图1)。
(三)数码电子照相机纸片:测量胫骨平台上髓内钉延长线与胫骨结节上方和胫骨前缘骨皮质连线的角度(图2)。不符合标准的4张X线片及1张纸片废除,不参加统计学处理。测定数值用SPSS统计软件处理。
结果
测得胫骨平台内侧胫骨后倾角15.02°±4.20°,外侧胫骨后倾角11.74°±3.80°,内侧>外侧。X线片髓外定位测量胫骨后倾角14.67°±3.68°,髓内定位测量胫骨后倾角11.55°±3.60°,髓外>髓内。胫骨平台内侧胫骨后倾角与髓外定位测量胫骨后倾角相近,差异无显著性意义(P>0.05)。15个退行性变关节的胫骨后倾角增大(表1,2)。
表1有/无退变的关节胫骨后倾角比较(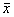 ±s) 测量方法
±s) 测量方法
, 百拇医药
退变关节(例)
无退变关节(例)
t值
P值
胫骨平台内侧
16.16°±4.56°(15)
14.51°±3.95°(34)
1.359
>0.05
胫骨平台外侧
13.56°±3.42°(15)
10.94°±3.75°(34)
, 百拇医药
2.327
<0.05
X线片-髓内
13.10°±3.39°(15)
10.81°±3.51°(31)
2.098
<0.05
X线片-髓外
16.70°±3.53°(15)
13.69°±3.39°(31)
2.783
<0.05
, 百拇医药
表2不同测量方法胫骨后倾角比较(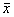 ±s) 分组
±s) 分组
比较项目
例数
胫骨后倾角
t值
P值
1
胫骨平台内侧
49
15.02°±4.20°
4.177
, 百拇医药
<0.01
胫骨平台外侧
49
11.74°±3.80°
2
X线片髓内测量
46
11.55°±3.60°
4.106
<0.01
X线片髓外测量
46
14.67°±3.68°
, 百拇医药
3
胫骨平台内侧
49
15.02°±4.20°
0.440
>0.05
X线片髓外测量
46
14.67°±3.68°
讨论
文献报告的胫骨平台后倾角大约为10°,多为放射学测量结果,也并未见提及胫骨平台内、外侧的后倾角是否一致[1-3]。本研究对国人胫骨后倾角进行实体与放射学测量,结果表明:(1)无论正常或有退变关节的胫骨后倾角,其内侧均较外侧为大(P<0.01,表2)。故我们认为手术确定截骨水平的胫骨后倾角应以内侧为主,以防失误。有膝外翻退变者可例外。(2)X线片髓内定位胫骨后倾角小于髓外定位,后者与实际测量的胫骨平台内侧后倾角数值相近,差异无显著性意义(P>0.05,表2)。胫骨后倾角往往不引起人们重视,术中只注意矫正胫骨的内、外翻畸形,而忽视对胫骨后倾角的观测。我们认为用髓外定位确定胫骨截骨平面、胫骨后倾角及力线是可靠的,若用髓内定位则应注意胫骨后倾角较髓外定位小3°左右。如果胫骨后倾角过大,易出现膝关节伸直障碍;过小易出现屈膝受限或膝伸直时不稳。(3)退行性变的膝关节胫骨平台内、外侧的胫骨后倾角,X线片髓内、髓外测量的胫骨后倾角均较正常关节增大(因标本数量不足,有待于进一步证实)。进行全膝关节置换术时,如果胫骨平台后倾角度不够,截骨位置偏高或正常易导致后方截骨不完全;如截骨位置偏低,膝关节伸屈活动不受限,但越远离关节面,松质骨越疏松,势必加速假体的下沉或松动。
, http://www.100md.com
参考文献
1,Jiang CC, Yip KM, Liu TK. Posterior slope angle of the medial tibial plateau. J Formos Med Assoc, 1994, 93: 509- 512.
2,Julliard R, Genin P, Weil G, et al. The median functional slope of the tibia. Principle. Technique of measurement. Value. Interest. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot, 1993, 79: 625- 634.
3,Brazier J, Migaud H, Gougeon F, et al. Evaluation of methods for radiographic measurement of the tibial slope: a study of 83 healthy knees. Rev Chir Orhtop Reparatrice Appar Mot, 1996, 82: 195- 200.
(收稿日期:1999-04-12), 百拇医药
单位:张树栋(264001烟台市烟台山医院骨科);张光辉 杨林海(CT室);曲广运(香港大学骨科学系)
关键词:膝关节;人工;放射学;解剖学;局部
中华骨科杂志000405
【摘要】目的测量国人胫骨后倾角,为全膝关节置换及翻修术提供确切的胫骨后倾角数值。方法25具尸体(50个胫骨标本),切除胫骨平台表面软组织及半月板,测量胫骨平台内、外侧后倾角度;并摄X线片,模拟手术方法测量髓内、髓外胫骨后倾角度。结果胫骨平台内侧后倾角为15.02°±4.20°,外侧后倾角为11.74°±3.80°。胫骨X线片髓内定位胫骨后倾角为11.55°±3.60°,髓外定位胫骨后倾角为14.67°±3.68°,退变关节的胫骨后倾角增大。结论无论正常或退变关节的胫骨平台后倾角,内侧大于外侧;胫骨X线片髓内定位胫骨后倾角小于髓外定位胫骨后倾角,后者与实际解剖测量胫骨平台内侧后倾角值的差异无显著性意义(P>0.05)。建议将胫骨平台内侧后倾角的数值作为全膝关节置换术的参考指数。
, 百拇医药
Evaluation of posterior slope of tibial plateau in Chinese
ZHANG Shudong, QU Guangyun, ZHANG Guanghui, et al.
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yantai Shan Hospital,Yantai 264001, China
【 Abstract】 Objective To determine the posterior slope angle of tibial plateau in Chinese for providing an actual value of the posterior slope of the tibia, an indispensable value during total knee arthoplasty. Methods Twenty five Chinese cadaveric tibia specimens were used for the measurement of the posterior slope of tibial plateau. The articular cartilage and the discs were removed and the lateral and medial posterior slope of the tibia were measured. Radiographs were then taken. To mimic the operative procedures, the intramedullary and extramedullary tibial slopes were measured. Results The values of posterior slope were 15.02° ± 4.20° at the medial plateau and 11.74° ± 3.80° at the lateral side by direct measurement. The intramedullary and extramedullary posterior slope angles were 11.55° ± 3.60° and 14.67° ± 3.68° by radiographic measurement. The posterior slope was increased in the degenerative cadaveric knees. Conclusion The posterior slope at medial plateau was greater than that at lateral one whether in normal or in degenerative knees. Intramedullary posterior tibial slope was smaller than extramedullary one, and the latter was similar to the medial plateau by direct measurement. It is suggested that the medial posterior slope of tibial plateau should be a reference index during total knee arthroplasty.
, 百拇医药
【 Key words】 Knee prosthesis; Radiology; Anatomy,regional
在人工全膝关节置换及翻修术中,一个理想的胫骨后倾角是术后恢复膝关节伸屈功能,保持膝关节稳定性及延长假体使用寿命的基本前提。为此,我们对25具尸体的胫骨后倾角进行了实体及放射学髓内、髓外(模拟手术定位)等方面的测量。
材料与方法
一、材料
25具国人尸体,男20具,女5具,共50个胫骨标本。年龄17~94岁,平均68.3岁。将胫、腓骨附着的软组织切除,同时将胫骨平台表面的软组织和半月板切除。分别编号,并对胫骨平台有退行性变(边缘唇样增生、内翻隆起、向两侧倾斜)的15个标本登记注明。
二、方法
, 百拇医药
(一)X线投照:将胫骨依次固定于支架上,统一定位,放置一标准X线刻度尺,球管距离100cm,摄侧位片备用(图1)。

图1X线片髓内、髓外测量图
(二)胫骨拍摄:将胫骨放置于固定架上,在内侧平台中1/2处水平放置一枚长20cm的梅花形髓内钉,并与胫骨嵴方向平行(图2),用数码电子照相机在距胫骨120cm处,垂直于胫骨中上1/3且与髓内钉平行的方向摄片。同法用于胫骨平台外侧的摄片。依次摄片并打印出纸片备用。

图2实体测量角度
三、胫骨后倾角的测量
(一)X线片髓内测量:模拟手术的髓内定位法,测量胫骨平台前后缘连线与髁间棘前缘和髓腔最狭窄处中1/2连线的角度(图1)。
, 百拇医药
(二)X线片髓外测量:测量胫骨平台前后缘连线与胫骨结节上方和胫骨前缘骨皮质连线的角度(图1)。
(三)数码电子照相机纸片:测量胫骨平台上髓内钉延长线与胫骨结节上方和胫骨前缘骨皮质连线的角度(图2)。不符合标准的4张X线片及1张纸片废除,不参加统计学处理。测定数值用SPSS统计软件处理。
结果
测得胫骨平台内侧胫骨后倾角15.02°±4.20°,外侧胫骨后倾角11.74°±3.80°,内侧>外侧。X线片髓外定位测量胫骨后倾角14.67°±3.68°,髓内定位测量胫骨后倾角11.55°±3.60°,髓外>髓内。胫骨平台内侧胫骨后倾角与髓外定位测量胫骨后倾角相近,差异无显著性意义(P>0.05)。15个退行性变关节的胫骨后倾角增大(表1,2)。
表1有/无退变的关节胫骨后倾角比较(
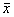 ±s) 测量方法
±s) 测量方法, 百拇医药
退变关节(例)
无退变关节(例)
t值
P值
胫骨平台内侧
16.16°±4.56°(15)
14.51°±3.95°(34)
1.359
>0.05
胫骨平台外侧
13.56°±3.42°(15)
10.94°±3.75°(34)
, 百拇医药
2.327
<0.05
X线片-髓内
13.10°±3.39°(15)
10.81°±3.51°(31)
2.098
<0.05
X线片-髓外
16.70°±3.53°(15)
13.69°±3.39°(31)
2.783
<0.05
, 百拇医药
表2不同测量方法胫骨后倾角比较(
 ±s) 分组
±s) 分组比较项目
例数
胫骨后倾角
t值
P值
1
胫骨平台内侧
49
15.02°±4.20°
4.177
, 百拇医药
<0.01
胫骨平台外侧
49
11.74°±3.80°
2
X线片髓内测量
46
11.55°±3.60°
4.106
<0.01
X线片髓外测量
46
14.67°±3.68°
, 百拇医药
3
胫骨平台内侧
49
15.02°±4.20°
0.440
>0.05
X线片髓外测量
46
14.67°±3.68°
讨论
文献报告的胫骨平台后倾角大约为10°,多为放射学测量结果,也并未见提及胫骨平台内、外侧的后倾角是否一致[1-3]。本研究对国人胫骨后倾角进行实体与放射学测量,结果表明:(1)无论正常或有退变关节的胫骨后倾角,其内侧均较外侧为大(P<0.01,表2)。故我们认为手术确定截骨水平的胫骨后倾角应以内侧为主,以防失误。有膝外翻退变者可例外。(2)X线片髓内定位胫骨后倾角小于髓外定位,后者与实际测量的胫骨平台内侧后倾角数值相近,差异无显著性意义(P>0.05,表2)。胫骨后倾角往往不引起人们重视,术中只注意矫正胫骨的内、外翻畸形,而忽视对胫骨后倾角的观测。我们认为用髓外定位确定胫骨截骨平面、胫骨后倾角及力线是可靠的,若用髓内定位则应注意胫骨后倾角较髓外定位小3°左右。如果胫骨后倾角过大,易出现膝关节伸直障碍;过小易出现屈膝受限或膝伸直时不稳。(3)退行性变的膝关节胫骨平台内、外侧的胫骨后倾角,X线片髓内、髓外测量的胫骨后倾角均较正常关节增大(因标本数量不足,有待于进一步证实)。进行全膝关节置换术时,如果胫骨平台后倾角度不够,截骨位置偏高或正常易导致后方截骨不完全;如截骨位置偏低,膝关节伸屈活动不受限,但越远离关节面,松质骨越疏松,势必加速假体的下沉或松动。
, http://www.100md.com
参考文献
1,Jiang CC, Yip KM, Liu TK. Posterior slope angle of the medial tibial plateau. J Formos Med Assoc, 1994, 93: 509- 512.
2,Julliard R, Genin P, Weil G, et al. The median functional slope of the tibia. Principle. Technique of measurement. Value. Interest. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot, 1993, 79: 625- 634.
3,Brazier J, Migaud H, Gougeon F, et al. Evaluation of methods for radiographic measurement of the tibial slope: a study of 83 healthy knees. Rev Chir Orhtop Reparatrice Appar Mot, 1996, 82: 195- 200.
(收稿日期:1999-04-12), 百拇医药