人体颞下颌关节盘后组织生物力学研究
作者:康宏 易新竹 陈孟诗 包广洁
单位:康宏 易新竹(华西医科大学 口腔医学院,成都 610041);陈孟诗(四川大学 土木工程与应用力学系,成都 610065);包广洁(兰州医学院 口腔系,兰州 73000)
关键词:盘后组织;颞下颌关节;生物力学
生物医学工程学杂志000207 摘要 确定了颞下颌关节盘后组织的生物力学性质,研究其功能机制。对取自8个新鲜关节标本的13个盘后组织试件进行了软组织单向拉伸应力松弛和破坏实验,结合Fung YC拟线性粘弹性理论对实验结果进行了分析。结果表明:盘后组织的生理二相区在20%~30%应变范围内。盘后组织拉伸强度和刚度较小但破坏应变较大;外侧组织的屈服能量高于内侧而拉伸强度和刚度无差异。在低应变水平,可以用拟线性粘弹性模型描述盘后组织的流变学特性。结论是盘后组织具有较低的强度安全储备,组织被动变形很有可能是关节盘前移的潜在因素。
, 百拇医药
A Biomechanical Study on the Retrodiscal Tissue of Human Temporomandibular Joint
Kang Hong Yi Xinzhu
(College of Stomatology,West China University of Medical Sciences,Chengdu 610041)
Chen Mengshi
(Department of Civil Engineering and Applied Mechanics, Sichuan University,Chengdu 610065)
Bao Guangjie
, 百拇医药
(Department of stomatology,Lanzhou Medical College,Lanzhou 73000)
Abstract In order to investigate the biomechanical properties and functional mechanism of the retrodiscal tissue (RT) of human temporomandibular joint (TMJ), we conducted a uniaxial tensile test on thirteen RT specimens taken from eight fresh TMJs of the human cadavers aged between 8-15 years (m=11.8yrs).The experimental data were analyzed in conjunction with the Quasi-Linear Viscoelastic Theory as proposed by Fung YC to characterize the time-dependent behaviour and the constitutive relationship of the RT.The results showed that the physiological biphasic zone of stress-strain curve lied within 20%-30% strain levels.The elastic modulus (MPa),tensile strength(MPa) and strain to failure(%) were high.There were significant differences in strain to yielding and energy resorption (N*mm) between lateral and medial RT.There was a good agreement between theoretical prediction value and experimental result within 6% strain level. These data suggest that there would be a higher passive deformation and lower safety storage of strength in the RT which could be related to anterior displacement of the TMJ disc and that Fung's Theory can adequately describe the stress-time behaviour and the constitutive relationship of the RT within lower strain rate.
, http://www.100md.com
Key words Temporomandibular joint(TMJ) Retrodiscal tissue Biomechanics
1 引 言
盘后组织是指前与关节盘后带相连,向后延伸附着于颅骨和髁突的具有高度顺应性的疏松结缔组织,在颞下颌关节功能运动中,其形态和体积随髁突位置的改变而变化,对滑液的产生与运输,盘突复合体功能的精细调节,以及生理和病理状态下的软组织改建与修复起重要作用[1]。本研究旨在用生物力学的方法获取盘后组织的材料参数及适宜的本构方程,从生物力学角度初步探讨其生理功能和病理机制。
2 材料与方法
2.1 标本收集与试件制备
收集4具新鲜尸体标本,年龄8~15岁,死后6 h内完整取下双侧颞下颌关节,仔细分离暴露关节上腔,肉眼及体视镜观察,盘后组织应无明显渗血、增生或断裂情况。从鳞鼓裂和关节盘后带冠状方向切取骨—盘后组织—关节盘后带标本,纵向切取内、外侧试件。试件用塑料袋密封4 ℃冰箱保存,一周内完成试验。
, 百拇医药
2.2 方法[2]
2.2.1 实验仪器及条件 实验在软组织单向拉伸及应力松弛试验仪(Revere Co USA,UMPI-005-A)上进行,X-Y函数记录仪同步记录应力-时间及应力-应变关系,实验中用林格液滴注,保持试件湿润。实验在室温下(8℃~14℃)进行。
2.2.2 实验步骤 (1)预调:游标尺测试件初始长度,以0.02 mm/s的应变速度拉伸至6%的应变长,同速卸载休息10 min,预调3次即可;(2)使试件在0~0.25 s内产生2%,4%,5%,6%阶跃应变,保持100 s,分别记录应力-时间关系曲线;(3)以0.05 mm/s的速度将试件拉伸破坏,记录应力-应变关系曲线;(4)用Fung YC拟线性粘弹性理论对实验值进行拟合分析。
3 结 果
3.1 盘后组织的应力-时间关系
, 百拇医药
图1为不同应变下的应力松弛实验曲线,应力松弛在最初5 s内十分明显,而归一化松弛函数G(t)对应变水平不敏感,但组织的瞬时弹性响应对应变水平较为敏感,呈高度非线性,随应变水平增加,弹性响应急剧增大(见表1)。
图1 盘后组织不同阶段应变下的应力松弛曲线
G(t)为归一化松弛函数
Fig 1 Relaxation curve of the retrodiscal tissue of the TMJ at different strain rates
G(t):the normalized relaxation function
表1 盘后组织的瞬时弹性响应
, http://www.100md.com
Table 1 The simultaneous elastic response of the retrodiscal tissue of the TMJ Strain(%)
Elastic response(MPa)
2
0.0203±0.0084
4
0.0358±0.0036
5
0.0469±0.0053
6
0.0597±0.0054
, 百拇医药
3.2 盘后组织的应力-应变关系
表2为盘后组织的材料参数;图2为盘后组织应力-应变关系实验曲线。表2 盘后组织拉伸屈服和破坏时的材料参数
Table 2 The material parameters of the retrodiscal tissue of the TMJ in tensile yielding and fracture Material parameter
Yielding
Fracture
Stress(MPa)
1.46± 0.97
1.76± 1.01
, 百拇医药
Strain(%)
48.75±23.23
95.25±33.19
Energy resorption(N*mm)
4.95± 2.99
19.29±13.21
Tensile modulus(MPa)
4.35± 3.27
图2 盘后组织的应力-应变曲线,初始段在20%~30%应变内
, http://www.100md.com
Fig 2 Stress-strain curve of the retrodiscal tissue of the TMJ.The initial stage(strain)was within 20%-30%
3.3 盘后组织不同区域的应力-应变关系
图3为盘后组织内外侧应力-应变关系实验曲线,表3为盘后组织不同区域屈服时的材料参数比较。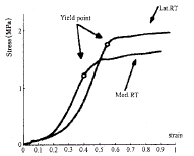
图3 盘后组织内、外侧部分的应力-应变实验曲线内侧部分初始段和拟线性段左移,屈服段低于外侧
Fig 3 Stress-strain experimental curve of the retrodiscal tissue in lateral and medial parts
, 百拇医药
表3 内外侧盘后组织屈服时各材料参数比较
Table 3 Comparison of the mechanical parameters of the retrodiscal tissue between medial and lateral parts Parameter
Lateral part(n=7)
Medial part(n=6)
Stress(MPa)
1.78±1.31
1.24±0.57
Strain(%)
55.74±22.83
, http://www.100md.com
41.72±26.09
Energy resorption (N*mm)
8.04±8.62
5.01±4.66
Tensile modulus(MPa)
4.51±4.26
4.313±2.41
4 理论分析
用Fung YC[3]拟线性粘弹性理论对实验数据进行分析,得出描述盘后组织应力松弛特性和应力应变关系的二个本构方程式:G(t)=0.8497-0.0242lnt
, 百拇医药
σ=0.2238[exp(3.8046ε)-1]
5 讨 论
5.1 盘后组织的应力-时间特性
盘后组织有一定拉伸应力松弛,同其他生物软组织一样也具有明显的粘弹性效应。由于应力松弛的程度主要取决于固体基质和液体的相对流动,盘后组织在拉伸载荷作用下,产生一定应变,随着液体流出及固相基质变形,组织内的应力将随时间而减弱并趋于平衡[4]。在该过程中,水的流动可使应力扩散,水在组织中流动的相对速度取决于水通过固体孔隙的渗透性的大小,组织对水的渗透性不同,应力松弛效应也不同。瞬时弹性响应对应变的非线性也反映出这一点,说明应力松弛方式在盘后组织分散机械应力过程中起重要作用。
5.2 盘后组织的应力-应变特性
生物软组织在力学上可看成是由胶原、弹力纤维和蛋白糖基质构成的复合材料。一般认为,小变形时弹性纤维承受较大应力,当变形增大直至破坏,应力主要由胶原纤维承受,蛋白多糖对组织的强度影响较小但影响组织受力后的变形历程[5]。有研究认为盘后区主要由疏松的Ⅰ型胶原,散在的弹力纤维网,大量静脉窦,小动脉,淋巴及结缔组织小梁构成,富含低分子量的硫酸肤质[6]。由于固体基质多呈分散状态,只在某一区域有纤维的定向排列,在受到外来载荷作用时,使更多的纤维排列一致,以承受更大的拉伸应力。一旦胶原排列与受力方向一致,拉伸刚度则急剧增大以防止组织继续变形产生损伤。在应力-应变曲线上,初始段代表了组织的生理应变范围,反映出盘后组织对生物应变具有较高的适应能力。由于盘后组织的屈服和断裂强度、拉伸模量较低而破坏应变大,组织抗拉伸和抗变形的能力有限,强度安全储备较低,而组织被动变形很大,从生物力学角度考虑,盘后组织牵引关节盘后移的能力有限,组织变形较大有可能是关节盘前移位的潜在因素。
, http://www.100md.com
盘后组织外侧拉伸应力和拉伸模量略高于内侧,其生物力学机制可能与对抗关节盘前内侧翼外肌上头的牵拉作用有关。Kino[7]、Yang等[8]对组织学的研究也表明盘后组织内侧富含弹性纤维,而外侧纤维以胶原成分为主,可能是内外侧力学行为不一致的重要因素。
理论分析表明,在较低应变水平,用拟线性粘弹性理论导出的本构方程可以很好地表征盘后组织的流变学特性,为颞下颌关节生物力学的进一步研究提供必要的实验数据。
本课题为甘肃省中青年科学基金部分资助项目(ZS981-A23-60Y)
参考文献
1,Scapino RP.The Posterior Attachment:Its structure,function,and appearance in TMJ imaging studies.Part1,2.J Craniomandib Disord Facial Oral Pain,1991;5∶83,155
, 百拇医药
2,Shengyi T,Yinghua X,Mengshi C et al.Biomechanical properties and collagen fiber orientatin of the TMJ discs in dogs.Part2 Tensile mechanical proerties of the disc.J Craniomandib Disord Facial Oral Pain,1991;5∶107
3,Fung YC.Biomecharics:mechanical properties of living tissue,Springer-Verlag,New York,1981;202
4,Mow VC,Kuei SC,Lai WM et al.Biphasic Creep and Stress Relaxation of Articular Cartilage in Comressin:Theory and Experiments.ASME J Biomech Engng,1980;102∶73
, http://www.100md.com
5,李晋唐著.骨及软组织流变学概论.成都:成都科技大学出版社.1989:113
6,Mills DK,Fiandaca UJ,Scapino RP.Morphologic,Microscopic,and Immunohistochemical Investigations into the Function of the rimate TMJ Disc.J Orfac Pain,1994;8∶137
7,Kino K,Ohmura Y,Amagasa T.Recnsideration of the bilaminar zone in the retrodiscal area of the temtoro mandibular joint.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol,1993;75∶410
8,Yang L,Wang H,Wang M et al.Development of collagen fibers and vasculature of the fetal TMJ.Okajimas-folia-Anat-Jpn,1992;69∶145
(收稿:1998-10-30 修回:1999-06-09), http://www.100md.com
单位:康宏 易新竹(华西医科大学 口腔医学院,成都 610041);陈孟诗(四川大学 土木工程与应用力学系,成都 610065);包广洁(兰州医学院 口腔系,兰州 73000)
关键词:盘后组织;颞下颌关节;生物力学
生物医学工程学杂志000207 摘要 确定了颞下颌关节盘后组织的生物力学性质,研究其功能机制。对取自8个新鲜关节标本的13个盘后组织试件进行了软组织单向拉伸应力松弛和破坏实验,结合Fung YC拟线性粘弹性理论对实验结果进行了分析。结果表明:盘后组织的生理二相区在20%~30%应变范围内。盘后组织拉伸强度和刚度较小但破坏应变较大;外侧组织的屈服能量高于内侧而拉伸强度和刚度无差异。在低应变水平,可以用拟线性粘弹性模型描述盘后组织的流变学特性。结论是盘后组织具有较低的强度安全储备,组织被动变形很有可能是关节盘前移的潜在因素。
, 百拇医药
A Biomechanical Study on the Retrodiscal Tissue of Human Temporomandibular Joint
Kang Hong Yi Xinzhu
(College of Stomatology,West China University of Medical Sciences,Chengdu 610041)
Chen Mengshi
(Department of Civil Engineering and Applied Mechanics, Sichuan University,Chengdu 610065)
Bao Guangjie
, 百拇医药
(Department of stomatology,Lanzhou Medical College,Lanzhou 73000)
Abstract In order to investigate the biomechanical properties and functional mechanism of the retrodiscal tissue (RT) of human temporomandibular joint (TMJ), we conducted a uniaxial tensile test on thirteen RT specimens taken from eight fresh TMJs of the human cadavers aged between 8-15 years (m=11.8yrs).The experimental data were analyzed in conjunction with the Quasi-Linear Viscoelastic Theory as proposed by Fung YC to characterize the time-dependent behaviour and the constitutive relationship of the RT.The results showed that the physiological biphasic zone of stress-strain curve lied within 20%-30% strain levels.The elastic modulus (MPa),tensile strength(MPa) and strain to failure(%) were high.There were significant differences in strain to yielding and energy resorption (N*mm) between lateral and medial RT.There was a good agreement between theoretical prediction value and experimental result within 6% strain level. These data suggest that there would be a higher passive deformation and lower safety storage of strength in the RT which could be related to anterior displacement of the TMJ disc and that Fung's Theory can adequately describe the stress-time behaviour and the constitutive relationship of the RT within lower strain rate.
, http://www.100md.com
Key words Temporomandibular joint(TMJ) Retrodiscal tissue Biomechanics
1 引 言
盘后组织是指前与关节盘后带相连,向后延伸附着于颅骨和髁突的具有高度顺应性的疏松结缔组织,在颞下颌关节功能运动中,其形态和体积随髁突位置的改变而变化,对滑液的产生与运输,盘突复合体功能的精细调节,以及生理和病理状态下的软组织改建与修复起重要作用[1]。本研究旨在用生物力学的方法获取盘后组织的材料参数及适宜的本构方程,从生物力学角度初步探讨其生理功能和病理机制。
2 材料与方法
2.1 标本收集与试件制备
收集4具新鲜尸体标本,年龄8~15岁,死后6 h内完整取下双侧颞下颌关节,仔细分离暴露关节上腔,肉眼及体视镜观察,盘后组织应无明显渗血、增生或断裂情况。从鳞鼓裂和关节盘后带冠状方向切取骨—盘后组织—关节盘后带标本,纵向切取内、外侧试件。试件用塑料袋密封4 ℃冰箱保存,一周内完成试验。
, 百拇医药
2.2 方法[2]
2.2.1 实验仪器及条件 实验在软组织单向拉伸及应力松弛试验仪(Revere Co USA,UMPI-005-A)上进行,X-Y函数记录仪同步记录应力-时间及应力-应变关系,实验中用林格液滴注,保持试件湿润。实验在室温下(8℃~14℃)进行。
2.2.2 实验步骤 (1)预调:游标尺测试件初始长度,以0.02 mm/s的应变速度拉伸至6%的应变长,同速卸载休息10 min,预调3次即可;(2)使试件在0~0.25 s内产生2%,4%,5%,6%阶跃应变,保持100 s,分别记录应力-时间关系曲线;(3)以0.05 mm/s的速度将试件拉伸破坏,记录应力-应变关系曲线;(4)用Fung YC拟线性粘弹性理论对实验值进行拟合分析。
3 结 果
3.1 盘后组织的应力-时间关系
, 百拇医药
图1为不同应变下的应力松弛实验曲线,应力松弛在最初5 s内十分明显,而归一化松弛函数G(t)对应变水平不敏感,但组织的瞬时弹性响应对应变水平较为敏感,呈高度非线性,随应变水平增加,弹性响应急剧增大(见表1)。

图1 盘后组织不同阶段应变下的应力松弛曲线
G(t)为归一化松弛函数
Fig 1 Relaxation curve of the retrodiscal tissue of the TMJ at different strain rates
G(t):the normalized relaxation function
表1 盘后组织的瞬时弹性响应
, http://www.100md.com
Table 1 The simultaneous elastic response of the retrodiscal tissue of the TMJ Strain(%)
Elastic response(MPa)
2
0.0203±0.0084
4
0.0358±0.0036
5
0.0469±0.0053
6
0.0597±0.0054
, 百拇医药
3.2 盘后组织的应力-应变关系
表2为盘后组织的材料参数;图2为盘后组织应力-应变关系实验曲线。表2 盘后组织拉伸屈服和破坏时的材料参数
Table 2 The material parameters of the retrodiscal tissue of the TMJ in tensile yielding and fracture Material parameter
Yielding
Fracture
Stress(MPa)
1.46± 0.97
1.76± 1.01
, 百拇医药
Strain(%)
48.75±23.23
95.25±33.19
Energy resorption(N*mm)
4.95± 2.99
19.29±13.21
Tensile modulus(MPa)
4.35± 3.27

图2 盘后组织的应力-应变曲线,初始段在20%~30%应变内
, http://www.100md.com
Fig 2 Stress-strain curve of the retrodiscal tissue of the TMJ.The initial stage(strain)was within 20%-30%
3.3 盘后组织不同区域的应力-应变关系
图3为盘后组织内外侧应力-应变关系实验曲线,表3为盘后组织不同区域屈服时的材料参数比较。

图3 盘后组织内、外侧部分的应力-应变实验曲线内侧部分初始段和拟线性段左移,屈服段低于外侧
Fig 3 Stress-strain experimental curve of the retrodiscal tissue in lateral and medial parts
, 百拇医药
表3 内外侧盘后组织屈服时各材料参数比较
Table 3 Comparison of the mechanical parameters of the retrodiscal tissue between medial and lateral parts Parameter
Lateral part(n=7)
Medial part(n=6)
Stress(MPa)
1.78±1.31
1.24±0.57
Strain(%)
55.74±22.83
, http://www.100md.com
41.72±26.09
Energy resorption (N*mm)
8.04±8.62
5.01±4.66
Tensile modulus(MPa)
4.51±4.26
4.313±2.41
4 理论分析
用Fung YC[3]拟线性粘弹性理论对实验数据进行分析,得出描述盘后组织应力松弛特性和应力应变关系的二个本构方程式:G(t)=0.8497-0.0242lnt
, 百拇医药
σ=0.2238[exp(3.8046ε)-1]
5 讨 论
5.1 盘后组织的应力-时间特性
盘后组织有一定拉伸应力松弛,同其他生物软组织一样也具有明显的粘弹性效应。由于应力松弛的程度主要取决于固体基质和液体的相对流动,盘后组织在拉伸载荷作用下,产生一定应变,随着液体流出及固相基质变形,组织内的应力将随时间而减弱并趋于平衡[4]。在该过程中,水的流动可使应力扩散,水在组织中流动的相对速度取决于水通过固体孔隙的渗透性的大小,组织对水的渗透性不同,应力松弛效应也不同。瞬时弹性响应对应变的非线性也反映出这一点,说明应力松弛方式在盘后组织分散机械应力过程中起重要作用。
5.2 盘后组织的应力-应变特性
生物软组织在力学上可看成是由胶原、弹力纤维和蛋白糖基质构成的复合材料。一般认为,小变形时弹性纤维承受较大应力,当变形增大直至破坏,应力主要由胶原纤维承受,蛋白多糖对组织的强度影响较小但影响组织受力后的变形历程[5]。有研究认为盘后区主要由疏松的Ⅰ型胶原,散在的弹力纤维网,大量静脉窦,小动脉,淋巴及结缔组织小梁构成,富含低分子量的硫酸肤质[6]。由于固体基质多呈分散状态,只在某一区域有纤维的定向排列,在受到外来载荷作用时,使更多的纤维排列一致,以承受更大的拉伸应力。一旦胶原排列与受力方向一致,拉伸刚度则急剧增大以防止组织继续变形产生损伤。在应力-应变曲线上,初始段代表了组织的生理应变范围,反映出盘后组织对生物应变具有较高的适应能力。由于盘后组织的屈服和断裂强度、拉伸模量较低而破坏应变大,组织抗拉伸和抗变形的能力有限,强度安全储备较低,而组织被动变形很大,从生物力学角度考虑,盘后组织牵引关节盘后移的能力有限,组织变形较大有可能是关节盘前移位的潜在因素。
, http://www.100md.com
盘后组织外侧拉伸应力和拉伸模量略高于内侧,其生物力学机制可能与对抗关节盘前内侧翼外肌上头的牵拉作用有关。Kino[7]、Yang等[8]对组织学的研究也表明盘后组织内侧富含弹性纤维,而外侧纤维以胶原成分为主,可能是内外侧力学行为不一致的重要因素。
理论分析表明,在较低应变水平,用拟线性粘弹性理论导出的本构方程可以很好地表征盘后组织的流变学特性,为颞下颌关节生物力学的进一步研究提供必要的实验数据。
本课题为甘肃省中青年科学基金部分资助项目(ZS981-A23-60Y)
参考文献
1,Scapino RP.The Posterior Attachment:Its structure,function,and appearance in TMJ imaging studies.Part1,2.J Craniomandib Disord Facial Oral Pain,1991;5∶83,155
, 百拇医药
2,Shengyi T,Yinghua X,Mengshi C et al.Biomechanical properties and collagen fiber orientatin of the TMJ discs in dogs.Part2 Tensile mechanical proerties of the disc.J Craniomandib Disord Facial Oral Pain,1991;5∶107
3,Fung YC.Biomecharics:mechanical properties of living tissue,Springer-Verlag,New York,1981;202
4,Mow VC,Kuei SC,Lai WM et al.Biphasic Creep and Stress Relaxation of Articular Cartilage in Comressin:Theory and Experiments.ASME J Biomech Engng,1980;102∶73
, http://www.100md.com
5,李晋唐著.骨及软组织流变学概论.成都:成都科技大学出版社.1989:113
6,Mills DK,Fiandaca UJ,Scapino RP.Morphologic,Microscopic,and Immunohistochemical Investigations into the Function of the rimate TMJ Disc.J Orfac Pain,1994;8∶137
7,Kino K,Ohmura Y,Amagasa T.Recnsideration of the bilaminar zone in the retrodiscal area of the temtoro mandibular joint.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol,1993;75∶410
8,Yang L,Wang H,Wang M et al.Development of collagen fibers and vasculature of the fetal TMJ.Okajimas-folia-Anat-Jpn,1992;69∶145
(收稿:1998-10-30 修回:1999-06-09), http://www.100md.com