抗恶性疟HRP-11单链抗体的筛选和鉴定
作者:徐伟文 董文其 李明 毕惠祥 陈白虹 王萍
单位:徐伟文(第一军医大学热带病研究室,广东 广州 510515);董文其(第一军医大学热带病研究室,广东 广州 510515);李明(第一军医大学热带病研究室,广东 广州 510515);毕惠祥(第一军医大学热带病研究室,广东 广州 510515);陈白虹(第一军医大学热带病研究室,广东 广州 510515);王萍(第一军医大学热带病研究室,广东 广州 510515)
关键词:噬菌体抗体库;单链抗体;富组胺酸蛋白(HRP-11);恶性疟
细胞与分子免疫学杂志000301 摘要:目的研究开发简便、快速和有效的疟疾诊断技术。方法利用噬菌体抗体库技术,在构建抗恶性疟原虫红内期噬菌体抗体库的基础上,经3轮“吸附-洗脱-扩增”的富集反应后,筛选抗HRP-II阳性克隆株并进行可溶性诱导表达,最后用ELISA和Western blot等进行鉴定。结果筛选 出6株抗HRP-II阳性克隆株,表达的单链抗体Mr为31000左右,能与HRP-II抗原起特异性结合反应。结论本研究为研制疟疾快速诊断试剂盒奠定了基础。
, http://www.100md.com
中图号:R72.3+1 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1007-8738(2000)03-0185-04
Screening and identification of anti-HRPII single chain Fv antibodies of Plasmodium falciparum
XU Wei-wen DONG Wen-qi LI Ming BI Hui-xiang CHEN Bai-hong WANG Ping
(Institute of Tropical Diseases, 1st Military Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China)
Abstract: To develop simple, rapid, and efficacious diagnostic methods for malaria is one of the remaining key tasks for malaria control. Previously, we have created a phage-displayed antibody library against Plasmodium falciparum. Six clones of antibody with good reactivity to HRP II in ELISA were isolated from the library after 3 rounds of enrichment. Soluble ScFvs were produced and the characteristics were determined. The results of Western blot showed that they could bind to HRP II specifically and had a relative molecular mass(Mr) about 31 000. The work provided a solid fund for diagnostic kit development for malaria.
, 百拇医药
Keywords: phage-display antibody library; single-chain Fv antibody; histidine-rich protein II▲
Malaria remains one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in the tropic〔1, 2〕 . Early rapid and accurate diagnostic method is one of the key measures for malaria control, remaining to be improved urgently and becomes to be a main task according to roll back malaria〔3〕 . Recently, a new tool called phagedispla-yed antibody library, based on the phage display biotechnology and PCR, has shown great power on screening and panning because it united not only the genotype and phonotype but also the ability of antigen recognition and amplification together〔4〕 .We have constructed an anti-Plasimodium falciparum(P.f) phage-displayed antibody library previously〔5〕 . In this study, the recombinant histidine-rich protein II (HRP II) were used as a target antigen for screening of anti-HRP II single chain Fv antibodies from the library. HRP II as an immunological target for diagnosis of malaria was confirmed〔6〕 and it was well engineered and ready for use in our laboratory. Additionally, the ParaSightTM F and ICT Malaria P.f.TM based on the monoclonal antibody(mAb) against HRP II of P.f for detecting of plasmodium parasites were accepted by WHO and the products were proved to have a promising future as a rapid diagnostic technique. The objective of this study is to develop anti-HRP II ScFv antibodies for malaria diagnosis.
, http://www.100md.com
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Panning and enrichment of anti-HRPII recombinant phage antibodies
For panning and enrichment, rescue was firstly performed for the initial recombinant phage antibody library incubated for 1 hour at 37℃ with shaking at 250 r/min, and helper phage M13KO7 was added and incubated for another hour at 37℃ with shaking at 250 r/min. It was spinned at 1000 g in a clinical centrifuge for 10 minutes to sediment the cells. Then the entire sample gently was resuspended in 10 mL of 2× YT-AK medium. After an overnight incubation at 37℃ with shaking at 250 r/min, it was spined at 1 000 g for 20 minutes and the supernatant which contained the recombinant phages was collected. Then 2 mL of PEG/NaCl was added to the 10 mL of supernatant containing phage antibodies and placed on ice for 45 minutes for precipitation first. It was spinned at 10 000 g for 20 minutes at 4℃ and the pellet resuspended in 16 mL of 2× YT medium diluted with 14 ml of blocking buffer containing 0.1 g/L sodium azide and incubated at room temperature for 15 minutes. Then 20 mL of the diluted recombinant phage was added to the flask which was coated overnight with 10 g/L HRP II antigen in PBS and well blocked. The flask was incubated for 2 hours at 37℃ , washed for 10 times with PBS and another 10 times with PBS containing 1 mL/L Tween -20.10 mL of log-phase TG1 cells were added to the flask and incubated with shaking at 37℃ for 1 hour for reinfection. After three rounds of panning, reinfected TG1 cells with bound phages directly in the panning flask were plated for colony isolation.
, 百拇医药
Screening for anti-HRPII recombinant phages
Recombinant phages were rescued from individual clones and screened for HRP II binding by ELISA. In brief, microtiter wells were coated with recombinant HRP II-β -galactosidase fusion protein and β -galactos-idase overnight at 4° C, respectively. Bound phages were detected by incubation with a 1∶ 5 000 dilution of conjugate (Pharmacia Biotech). And the detection was achieved by addition of ABTS substrate. Clones reacted to HRP II-β -galactosidase only were selected as positives. And the positive phages were trans-infected into E.coli HB2151 cells, which recognize the amber stop codon between the ScFv and the gene III fragment and this led to the production of a soluble form of the ScFv antibody fragments.
, http://www.100md.com
Production and identification of soluble ScFv antibodies
Overnight induction of 5 mL of E.coli HB2151 cells containing phagemid DNA with 1 mmoL/L isopropyl β -D-thiogalactopyanoside(IPTG) led the ScFvs to secret to the periplasm. Cells were pelleted by centrifugation, and supernatants(containing any extracellular soluble ScFvs)were collected too.To prepare periplasmic extracts, osmotic shock method was used. The soluble ScFvs were detected and identified by ELISA,dot-ELISA, and Western-blot〔7, 8〕 .
, http://www.100md.com
RESULTS
Panning Phagemid-containing bacterial colonies were infected with M13KO7 helper phages to yield recombinant phages which display ScFv antibodies. Recombinant HRP II protein was used as a target antigen for panning and screening. After three rounds of rescue and panning, phage antibody library against P.f was generated and the interested phages were obviously enriched. The titer was increased from 6.0× 107cfu/L at the first round to 1.6× 1010 cfu/L at the second round and 4.1× 108 cfu/L at the third round. The titer reducing at the end of the third round may be due to the 20 more washes we added.
, http://www.100md.com
Screening Using ELISA assay, we yielded six strains of positive clones which had a good reaction with HRP II(Table 1).
Tab 1 ELISA results of screening from phage-displayed antibody library No.
+
-
PF7
PF13
PF22
PF112
PF180
, 百拇医药
PF184
A405
0.65
0.10
0.20
0.20
0.27
0.21
0.24
0.34
“ + ” :Positive control; “ -” :Negative control.
Detection and identification Following identification of antigen-positive clones, all six positive clones were used to infect E.coli HB2151 nonsupressor strain for the purpose of large-scale production of soluble antibodies. The expressed soluble antibodies were detected by ELISA and the results were showed in table 2. Two of them(PF22, PF184) were chosen for further research such as Dot-ELISA and Western-blot to identify their binding specificity to target antigen HRP II and relative molecular mass(Mr)and the cell compartment(s) in which they were concentrated. The results were showed in figure 1,2,3 and 4. And it indicated that both of the two positive clones could bind to HRP II specifically. The Mr of expressed antibody was about 31 000. And it was the supernatant that the soluble antibody concentrated.
, http://www.100md.com
Tab 2 ELISA results of ScFvs from different cell compartments ( A450)
Supernatant
Periplasmic extract
Whole cell extract
PF22
0.493
0.487
0.412
PF184
0.460
, http://www.100md.com
0.458
0.408
+
1.904
-
-
-
0.078
-
-
“ + ” : Positive control; “ -” : Negative control.
, 百拇医药
Fig 1 Dot-ELISA of soluble ScFv using anti-tag E
1:Positive control; 2:Soluble antibody in supernatant of PF22; 3: Periplasmic soluble antibody of PF22; 4: Intracellular soluble antibody of PF22; 5: Soluble antibody in supernatant of PF184; 6: Periplasmic soluble antibody of PF184; 7: Intracellular soluble antibody of PF184; 8:Negative control; 9:Blank control.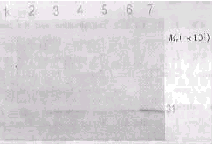
Fig 2 Analysis of soluble ScFvs from different sites by Western blot using anti-tag E 1:E.coli HB2151; 2:Intracellular soluble antibody of PF184;3: Periplasmic soluble antibody of PF184; 4: Soluble antibody in supernatant of PF184; 5:Intracellular soluble antibody of PF22; 6: Periplasmic soluble antibody of PF22; 7: Soluble antibody in supernatant of PF22.
, 百拇医药
Fig 3 SDS-PAGE analysis of anti-HRPII(ScFvs) on 120 g/L gel
1:E. coli HB2151; 2:Soluble antibody in supernatant of PF22;3: Periplasmic soluble antibody of PF22; 4: Intracellular soluble antibody of PF22; 5: Soluble antibody in supernatant of PF184; 6: Periplasmic soluble antibody of PF184; 7: Intracellular soluble antibody of PF184.
Fig 4 Specificity of ScFv binding to HRP II by Western blot
, http://www.100md.com
1: Vector self-ligated clone used as a negative; 2: PF184 ScFv;3:PF22 ScFv; 4:anti-HRPII mAb(3A3); 5:anti-β -galactosidase mAb;6: HRP II SDS-PAGE gel;7:β -galactosidase SDS-PAGE gel. HRP II-β -galacto-sidase; b: β -galactosidase.
DISCUSSION
Malaria remains one of the important infectious diseases in tropic and sub-tropic area. A rapid and convenient method for early diagnosis of malaria contributes a lot to malaria control. In recent years, antigen-capture with monoclonal antibody(mAb) has been proved to be very useful in immunologic diagnosis. The techniques based on it such as dipstick have the virtue as rapid, simple and accurate. The ParaSightTM F and ICT Malaria P.f.TM, based on the mAb against histidine-rich protein II(HRP II) of P.f, one of the best confirmed immunological targets for diagnosis of malaria, have been proved to have a promising future for detecting plasmodium parasites and accepted by WHO〔7,8〕 . Regretfully, there are still some obstacles hinge its wide use (e.g. the products are very expensive, stable large-scale production of the mAbs has some difficulty). The power of recombinant phage antibodies, coupled with the ease and versatility of recombinant DNA methodology, offer an improved route for the production of high specific antibodies quickly in bacterial cultures.
, 百拇医药
For those reasons, we have constructed a phage-displayed antibody library against Plasmodium falciparum using this new bio-technique. After three rounds of panning with recombinant HRP II, an enrichment of sub-library against HRP II with content about 4.1× 108cfu/L was generated. Consequently, six clones expressing antibodies against HRP II were isolated from the library. Two of them(PF22 and PF184) were chosen for further research. ScFvs were produced by inducing with IPTG and their characteristics as anti-HRP II ScFvs were determined by ELISA and Western blot. The results showed that both of them could bind to HRP II specifically and had a Mr of about 31 000. The work provided a solid basis for developing kits for malaria diagnosis.
, 百拇医药
As a new bio-technique, phage-displayed antibody library has several advantages in screening〔9〕 . However, lots of work still needs to be done to improve it〔10〕 . As in practice, some kinds of problems may be unavoidable. Here are the possible causes and the solutions of some troubles we met in practice. Firstly, after rounds of panning and reinfection, the picked colonies showed no positive signal in the ELISA. The possible causes may be:① The mouse from which the spleen cells were obtained for mRNA does not mount a successful antibody response. Detection of antigen-specific antibody in serum is indicated.② An insufficient number of rounds of panning/reinfection are performed. At least two rounds of phage antibody panning/reinfection should be performed to enrich for antigen-specific phage antibodies when hybridoma cells are used and 4-7 rounds should be performed when immunized spleen cells are used for construction of the library.③ The antigen-coating concentration, microt-iter plates and/or blocking reagents are not optimal for the phage antibodies. Or the HRP/anti-M13 mAb conjugate is non-functional. It will lead to a weak positive signal. An optimal antigen working concentration should be determined before screening and integrity of the conjugate should be detected with M13 phage. Secondly, the causes of weak positive signal may be:① The phage displayed antibody is poorly expressed.The phage should be concentrated by PEG precipitation before used in ELISA. And chaperonin protein may be helpful to improve the expression level〔11〕 . ② The rescue of enriched phage clones is not successful. It is important to spin the plates and remove the sup ernatant before addition of the final medium in the rescue since any residual glucose may inhibit expression of the recombinant phage antibody. Additionally, the shaking speed around 150 r/min is ideal during rescue. ③ A prolonged antigen-antibody reaction may be helpful when performing ELISA. Thirdly, clones might show high background or cross-reactivity with the negative control antigen in ELISA. The possible causes are:① When recombinant phages used in the ELISA are PEG-preicipitated, residual PEG may artificially enhance ELISA signal. So one should try to remove the supernatant thoroughly. ② The blocking does not work. Blocking agent (20 g/L nonfat dry milk in PBS) is superior to bovine albumin.③ A non-specific reaction occurs between protein-protein. In this situation, the recombinant antibody sample could be diluted 1:1 in blocking agent containing 2 mL/L Triton X-100. Washing the microtiter plates more vigorously between steps may also help. ■
, http://www.100md.com
Foundation item:by WHO Foundation, No. ID 970498; and by the Na tional Natural Science Foundation of China, No.39600127.
Author's brief: Xu WW, female, thirty-year-old,assistant researcher, M.D. Tonghe, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China Tel.(020)85148321
REFERENCES
〔1〕 Xu WW, Li M, Yu SY. The situation and the treatments of malaria〔J〕 . Foreign Med Sci Parasitol, 1999;26(5):200-203.
, 百拇医药
〔2〕 Xu WW, Li M, Yu SY. The situation and the treatments of malaria in China〔J〕 . Chin J Zoonoses, 1999;15(3):83-84.
〔3〕 http://www. malaria. org/malaria foundation international/roll back malaria.
〔4〕 McCafferty J, Griffiths AD, Winter G, et al. Phage antibodies: filamentous phage displaying antibody variable domains〔J〕 . Nature, 1990;348:552-554.
〔5〕 Xu WW, Dong WQ, LI M, et al. The construction of phage-displayed anti-erythrocytic stage antibody library of P.f. Chinese〔J〕 . J Epidemiol, 1998;19( 5-B) :68-72.
, 百拇医药
〔6〕 Beadle C,Taylor. Diagnosis of malaria by detection of Plasmodium falciparum HRP-2 antigen with a rapid dipstick antigen-capture assay〔J〕 . Lancet. 1994;343(8897):564-568.
〔7〕 Shiff C, Minjas J, Premji Z.The ParaSightR-F test: a simple rapid manual dipstick test to detect Plasmodium falciparum infection〔J〕 . Parasite Today, 1994;10(2):494-495.
〔8〕 Thepsamarn P, Prayoollawongsa N, Puksupa P,et al. The ICT Malaria Pf.:a simple, rapid dipstick test for the diagnosis of Plasmodium falciparum malaria at the Thai-Myanmar border〔J〕 . Southeast Asian J Trop. Med Pub Hlth. 1997;28:723.
, http://www.100md.com
〔9〕 Aujame L, Sodoyer R, Teillaud JL . Phage display and antibody engineering:A Franch Overview〔J〕 . Trends Biotechnol. 1997;15(5):87-94.
〔10〕 Xu WW,Yu SY. The technique of phage-displayed antibody library〔J〕 . Chin J Epidemiol, 1998;19(5-B):289-293.
〔11〕 Soderlind E, Lagerkvist ACS, Duenas M,et al. Chaperonin assisted phage display of antibody fragments on filamentous bacteriophage〔J〕 . Bio/Technol, 1993;11:503-507.
Received data: 1999-10-10
revised date: 2000-01-24, 百拇医药
单位:徐伟文(第一军医大学热带病研究室,广东 广州 510515);董文其(第一军医大学热带病研究室,广东 广州 510515);李明(第一军医大学热带病研究室,广东 广州 510515);毕惠祥(第一军医大学热带病研究室,广东 广州 510515);陈白虹(第一军医大学热带病研究室,广东 广州 510515);王萍(第一军医大学热带病研究室,广东 广州 510515)
关键词:噬菌体抗体库;单链抗体;富组胺酸蛋白(HRP-11);恶性疟
细胞与分子免疫学杂志000301 摘要:目的研究开发简便、快速和有效的疟疾诊断技术。方法利用噬菌体抗体库技术,在构建抗恶性疟原虫红内期噬菌体抗体库的基础上,经3轮“吸附-洗脱-扩增”的富集反应后,筛选抗HRP-II阳性克隆株并进行可溶性诱导表达,最后用ELISA和Western blot等进行鉴定。结果筛选 出6株抗HRP-II阳性克隆株,表达的单链抗体Mr为31000左右,能与HRP-II抗原起特异性结合反应。结论本研究为研制疟疾快速诊断试剂盒奠定了基础。
, http://www.100md.com
中图号:R72.3+1 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1007-8738(2000)03-0185-04
Screening and identification of anti-HRPII single chain Fv antibodies of Plasmodium falciparum
XU Wei-wen DONG Wen-qi LI Ming BI Hui-xiang CHEN Bai-hong WANG Ping
(Institute of Tropical Diseases, 1st Military Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China)
Abstract: To develop simple, rapid, and efficacious diagnostic methods for malaria is one of the remaining key tasks for malaria control. Previously, we have created a phage-displayed antibody library against Plasmodium falciparum. Six clones of antibody with good reactivity to HRP II in ELISA were isolated from the library after 3 rounds of enrichment. Soluble ScFvs were produced and the characteristics were determined. The results of Western blot showed that they could bind to HRP II specifically and had a relative molecular mass(Mr) about 31 000. The work provided a solid fund for diagnostic kit development for malaria.
, 百拇医药
Keywords: phage-display antibody library; single-chain Fv antibody; histidine-rich protein II▲
Malaria remains one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in the tropic〔1, 2〕 . Early rapid and accurate diagnostic method is one of the key measures for malaria control, remaining to be improved urgently and becomes to be a main task according to roll back malaria〔3〕 . Recently, a new tool called phagedispla-yed antibody library, based on the phage display biotechnology and PCR, has shown great power on screening and panning because it united not only the genotype and phonotype but also the ability of antigen recognition and amplification together〔4〕 .We have constructed an anti-Plasimodium falciparum(P.f) phage-displayed antibody library previously〔5〕 . In this study, the recombinant histidine-rich protein II (HRP II) were used as a target antigen for screening of anti-HRP II single chain Fv antibodies from the library. HRP II as an immunological target for diagnosis of malaria was confirmed〔6〕 and it was well engineered and ready for use in our laboratory. Additionally, the ParaSightTM F and ICT Malaria P.f.TM based on the monoclonal antibody(mAb) against HRP II of P.f for detecting of plasmodium parasites were accepted by WHO and the products were proved to have a promising future as a rapid diagnostic technique. The objective of this study is to develop anti-HRP II ScFv antibodies for malaria diagnosis.
, http://www.100md.com
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Panning and enrichment of anti-HRPII recombinant phage antibodies
For panning and enrichment, rescue was firstly performed for the initial recombinant phage antibody library incubated for 1 hour at 37℃ with shaking at 250 r/min, and helper phage M13KO7 was added and incubated for another hour at 37℃ with shaking at 250 r/min. It was spinned at 1000 g in a clinical centrifuge for 10 minutes to sediment the cells. Then the entire sample gently was resuspended in 10 mL of 2× YT-AK medium. After an overnight incubation at 37℃ with shaking at 250 r/min, it was spined at 1 000 g for 20 minutes and the supernatant which contained the recombinant phages was collected. Then 2 mL of PEG/NaCl was added to the 10 mL of supernatant containing phage antibodies and placed on ice for 45 minutes for precipitation first. It was spinned at 10 000 g for 20 minutes at 4℃ and the pellet resuspended in 16 mL of 2× YT medium diluted with 14 ml of blocking buffer containing 0.1 g/L sodium azide and incubated at room temperature for 15 minutes. Then 20 mL of the diluted recombinant phage was added to the flask which was coated overnight with 10 g/L HRP II antigen in PBS and well blocked. The flask was incubated for 2 hours at 37℃ , washed for 10 times with PBS and another 10 times with PBS containing 1 mL/L Tween -20.10 mL of log-phase TG1 cells were added to the flask and incubated with shaking at 37℃ for 1 hour for reinfection. After three rounds of panning, reinfected TG1 cells with bound phages directly in the panning flask were plated for colony isolation.
, 百拇医药
Screening for anti-HRPII recombinant phages
Recombinant phages were rescued from individual clones and screened for HRP II binding by ELISA. In brief, microtiter wells were coated with recombinant HRP II-β -galactosidase fusion protein and β -galactos-idase overnight at 4° C, respectively. Bound phages were detected by incubation with a 1∶ 5 000 dilution of conjugate (Pharmacia Biotech). And the detection was achieved by addition of ABTS substrate. Clones reacted to HRP II-β -galactosidase only were selected as positives. And the positive phages were trans-infected into E.coli HB2151 cells, which recognize the amber stop codon between the ScFv and the gene III fragment and this led to the production of a soluble form of the ScFv antibody fragments.
, http://www.100md.com
Production and identification of soluble ScFv antibodies
Overnight induction of 5 mL of E.coli HB2151 cells containing phagemid DNA with 1 mmoL/L isopropyl β -D-thiogalactopyanoside(IPTG) led the ScFvs to secret to the periplasm. Cells were pelleted by centrifugation, and supernatants(containing any extracellular soluble ScFvs)were collected too.To prepare periplasmic extracts, osmotic shock method was used. The soluble ScFvs were detected and identified by ELISA,dot-ELISA, and Western-blot〔7, 8〕 .
, http://www.100md.com
RESULTS
Panning Phagemid-containing bacterial colonies were infected with M13KO7 helper phages to yield recombinant phages which display ScFv antibodies. Recombinant HRP II protein was used as a target antigen for panning and screening. After three rounds of rescue and panning, phage antibody library against P.f was generated and the interested phages were obviously enriched. The titer was increased from 6.0× 107cfu/L at the first round to 1.6× 1010 cfu/L at the second round and 4.1× 108 cfu/L at the third round. The titer reducing at the end of the third round may be due to the 20 more washes we added.
, http://www.100md.com
Screening Using ELISA assay, we yielded six strains of positive clones which had a good reaction with HRP II(Table 1).
Tab 1 ELISA results of screening from phage-displayed antibody library No.
+
-
PF7
PF13
PF22
PF112
PF180
, 百拇医药
PF184
A405
0.65
0.10
0.20
0.20
0.27
0.21
0.24
0.34
“ + ” :Positive control; “ -” :Negative control.
Detection and identification Following identification of antigen-positive clones, all six positive clones were used to infect E.coli HB2151 nonsupressor strain for the purpose of large-scale production of soluble antibodies. The expressed soluble antibodies were detected by ELISA and the results were showed in table 2. Two of them(PF22, PF184) were chosen for further research such as Dot-ELISA and Western-blot to identify their binding specificity to target antigen HRP II and relative molecular mass(Mr)and the cell compartment(s) in which they were concentrated. The results were showed in figure 1,2,3 and 4. And it indicated that both of the two positive clones could bind to HRP II specifically. The Mr of expressed antibody was about 31 000. And it was the supernatant that the soluble antibody concentrated.
, http://www.100md.com
Tab 2 ELISA results of ScFvs from different cell compartments ( A450)
Supernatant
Periplasmic extract
Whole cell extract
PF22
0.493
0.487
0.412
PF184
0.460
, http://www.100md.com
0.458
0.408
+
1.904
-
-
-
0.078
-
-
“ + ” : Positive control; “ -” : Negative control.

, 百拇医药
Fig 1 Dot-ELISA of soluble ScFv using anti-tag E
1:Positive control; 2:Soluble antibody in supernatant of PF22; 3: Periplasmic soluble antibody of PF22; 4: Intracellular soluble antibody of PF22; 5: Soluble antibody in supernatant of PF184; 6: Periplasmic soluble antibody of PF184; 7: Intracellular soluble antibody of PF184; 8:Negative control; 9:Blank control.
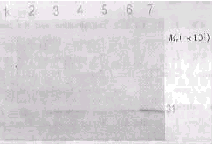
Fig 2 Analysis of soluble ScFvs from different sites by Western blot using anti-tag E 1:E.coli HB2151; 2:Intracellular soluble antibody of PF184;3: Periplasmic soluble antibody of PF184; 4: Soluble antibody in supernatant of PF184; 5:Intracellular soluble antibody of PF22; 6: Periplasmic soluble antibody of PF22; 7: Soluble antibody in supernatant of PF22.

, 百拇医药
Fig 3 SDS-PAGE analysis of anti-HRPII(ScFvs) on 120 g/L gel
1:E. coli HB2151; 2:Soluble antibody in supernatant of PF22;3: Periplasmic soluble antibody of PF22; 4: Intracellular soluble antibody of PF22; 5: Soluble antibody in supernatant of PF184; 6: Periplasmic soluble antibody of PF184; 7: Intracellular soluble antibody of PF184.

Fig 4 Specificity of ScFv binding to HRP II by Western blot
, http://www.100md.com
1: Vector self-ligated clone used as a negative; 2: PF184 ScFv;3:PF22 ScFv; 4:anti-HRPII mAb(3A3); 5:anti-β -galactosidase mAb;6: HRP II SDS-PAGE gel;7:β -galactosidase SDS-PAGE gel. HRP II-β -galacto-sidase; b: β -galactosidase.
DISCUSSION
Malaria remains one of the important infectious diseases in tropic and sub-tropic area. A rapid and convenient method for early diagnosis of malaria contributes a lot to malaria control. In recent years, antigen-capture with monoclonal antibody(mAb) has been proved to be very useful in immunologic diagnosis. The techniques based on it such as dipstick have the virtue as rapid, simple and accurate. The ParaSightTM F and ICT Malaria P.f.TM, based on the mAb against histidine-rich protein II(HRP II) of P.f, one of the best confirmed immunological targets for diagnosis of malaria, have been proved to have a promising future for detecting plasmodium parasites and accepted by WHO〔7,8〕 . Regretfully, there are still some obstacles hinge its wide use (e.g. the products are very expensive, stable large-scale production of the mAbs has some difficulty). The power of recombinant phage antibodies, coupled with the ease and versatility of recombinant DNA methodology, offer an improved route for the production of high specific antibodies quickly in bacterial cultures.
, 百拇医药
For those reasons, we have constructed a phage-displayed antibody library against Plasmodium falciparum using this new bio-technique. After three rounds of panning with recombinant HRP II, an enrichment of sub-library against HRP II with content about 4.1× 108cfu/L was generated. Consequently, six clones expressing antibodies against HRP II were isolated from the library. Two of them(PF22 and PF184) were chosen for further research. ScFvs were produced by inducing with IPTG and their characteristics as anti-HRP II ScFvs were determined by ELISA and Western blot. The results showed that both of them could bind to HRP II specifically and had a Mr of about 31 000. The work provided a solid basis for developing kits for malaria diagnosis.
, 百拇医药
As a new bio-technique, phage-displayed antibody library has several advantages in screening〔9〕 . However, lots of work still needs to be done to improve it〔10〕 . As in practice, some kinds of problems may be unavoidable. Here are the possible causes and the solutions of some troubles we met in practice. Firstly, after rounds of panning and reinfection, the picked colonies showed no positive signal in the ELISA. The possible causes may be:① The mouse from which the spleen cells were obtained for mRNA does not mount a successful antibody response. Detection of antigen-specific antibody in serum is indicated.② An insufficient number of rounds of panning/reinfection are performed. At least two rounds of phage antibody panning/reinfection should be performed to enrich for antigen-specific phage antibodies when hybridoma cells are used and 4-7 rounds should be performed when immunized spleen cells are used for construction of the library.③ The antigen-coating concentration, microt-iter plates and/or blocking reagents are not optimal for the phage antibodies. Or the HRP/anti-M13 mAb conjugate is non-functional. It will lead to a weak positive signal. An optimal antigen working concentration should be determined before screening and integrity of the conjugate should be detected with M13 phage. Secondly, the causes of weak positive signal may be:① The phage displayed antibody is poorly expressed.The phage should be concentrated by PEG precipitation before used in ELISA. And chaperonin protein may be helpful to improve the expression level〔11〕 . ② The rescue of enriched phage clones is not successful. It is important to spin the plates and remove the sup ernatant before addition of the final medium in the rescue since any residual glucose may inhibit expression of the recombinant phage antibody. Additionally, the shaking speed around 150 r/min is ideal during rescue. ③ A prolonged antigen-antibody reaction may be helpful when performing ELISA. Thirdly, clones might show high background or cross-reactivity with the negative control antigen in ELISA. The possible causes are:① When recombinant phages used in the ELISA are PEG-preicipitated, residual PEG may artificially enhance ELISA signal. So one should try to remove the supernatant thoroughly. ② The blocking does not work. Blocking agent (20 g/L nonfat dry milk in PBS) is superior to bovine albumin.③ A non-specific reaction occurs between protein-protein. In this situation, the recombinant antibody sample could be diluted 1:1 in blocking agent containing 2 mL/L Triton X-100. Washing the microtiter plates more vigorously between steps may also help. ■
, http://www.100md.com
Foundation item:by WHO Foundation, No. ID 970498; and by the Na tional Natural Science Foundation of China, No.39600127.
Author's brief: Xu WW, female, thirty-year-old,assistant researcher, M.D. Tonghe, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China Tel.(020)85148321
REFERENCES
〔1〕 Xu WW, Li M, Yu SY. The situation and the treatments of malaria〔J〕 . Foreign Med Sci Parasitol, 1999;26(5):200-203.
, 百拇医药
〔2〕 Xu WW, Li M, Yu SY. The situation and the treatments of malaria in China〔J〕 . Chin J Zoonoses, 1999;15(3):83-84.
〔3〕 http://www. malaria. org/malaria foundation international/roll back malaria.
〔4〕 McCafferty J, Griffiths AD, Winter G, et al. Phage antibodies: filamentous phage displaying antibody variable domains〔J〕 . Nature, 1990;348:552-554.
〔5〕 Xu WW, Dong WQ, LI M, et al. The construction of phage-displayed anti-erythrocytic stage antibody library of P.f. Chinese〔J〕 . J Epidemiol, 1998;19( 5-B) :68-72.
, 百拇医药
〔6〕 Beadle C,Taylor. Diagnosis of malaria by detection of Plasmodium falciparum HRP-2 antigen with a rapid dipstick antigen-capture assay〔J〕 . Lancet. 1994;343(8897):564-568.
〔7〕 Shiff C, Minjas J, Premji Z.The ParaSightR-F test: a simple rapid manual dipstick test to detect Plasmodium falciparum infection〔J〕 . Parasite Today, 1994;10(2):494-495.
〔8〕 Thepsamarn P, Prayoollawongsa N, Puksupa P,et al. The ICT Malaria Pf.:a simple, rapid dipstick test for the diagnosis of Plasmodium falciparum malaria at the Thai-Myanmar border〔J〕 . Southeast Asian J Trop. Med Pub Hlth. 1997;28:723.
, http://www.100md.com
〔9〕 Aujame L, Sodoyer R, Teillaud JL . Phage display and antibody engineering:A Franch Overview〔J〕 . Trends Biotechnol. 1997;15(5):87-94.
〔10〕 Xu WW,Yu SY. The technique of phage-displayed antibody library〔J〕 . Chin J Epidemiol, 1998;19(5-B):289-293.
〔11〕 Soderlind E, Lagerkvist ACS, Duenas M,et al. Chaperonin assisted phage display of antibody fragments on filamentous bacteriophage〔J〕 . Bio/Technol, 1993;11:503-507.
Received data: 1999-10-10
revised date: 2000-01-24, 百拇医药