口腔癌肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞对人舌癌裸鼠移植瘤的生长抑制作用
作者:廖贵清 毛祖彝 徐平平
单位:510060 广州,中山医科大学口腔医学院(廖贵清);华西医科大学口腔医学院(毛祖彝、徐平平)
关键词:口腔肿瘤;淋巴细胞,肿瘤浸润
中华口腔医学杂志980305 【摘要】 目的 探讨在体外具有强大细胞毒活性的口腔癌浸润淋巴细胞在体内的抑瘤效果以及化疗药物环磷酰胺(cyclophosphamide, Cy)与肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞(tumor-infiltration lymphocyte, TIL)联合应用治疗口腔癌的可能性。方法 将舌鳞癌细胞系Tca 8113 注入裸鼠背部皮下建立移植瘤模型,取培养4周的TIL联合低剂量Cy局部注射,观察肿瘤体积变化及肿瘤生长情况。结果 ①TIL+rIL-2和TIL+rIL-2+Cy组在3周内抑瘤率较高(分别为:86.1%±0.4%和97.7%±0.6%),3周后抑瘤作用减弱;②TIL+rIL-2+Cy组抑瘤率较TIL+rIL-2组高(第8周抑瘤率分别为:20.0%±1.4%和75.5%±2.5%,P<0.01)。结论 口腔癌TIL在应用后3周内具较强抑瘤作用,3周后减弱;联合应用Cy可获得更佳抑瘤效果。
, http://www.100md.com
Inhibition effects of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes from oral cancer on nude mice transplanted tumor established with human tongue carcinoma cell lines Liao Guiqing*,Mao Zuyi, Xu Pingping.*School of Stomatology, Sun Yat-Sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510060
【Abstract】 Objective To observe the in vivo inhibition effects on nude mice transplanted tumor with tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) isolated from primary mass of oral cancer.Methods Established the transplanted tumor model of human tongue cancer at the back of BALB/C nude mice with subcutaneous injection of squamous cell carcinoma lines Tca 8113. TILs isolated from patients with Oral cancer, combining with low dose of cyclophosphamide (Cy: 50mg/kg), were locally injected into the peripheral site of tumor. The inhibition rate (IR) was calculated by the volume of tumor mass from the 1 st to the 8th week, and the weights at the 8th week after tumor dissection. Results ①Group TIL+rIL-2 and group TIL+rIL-2+Cy both exerted a strong inhibition effect on the transplanted tumor within three weeks. The Inhibition rate (IR) were 86.1%±0.4% and 97.7%±0.6% respectively at the 3rd week, while 32.1%±0.3% and 80.6%±0.3% at the 8th week. ②TIL+rIL-2+Cy expressed a stronger effect and a longer inhibition time. The IR of TIL+rIL-2 and TIL+rIL-2+Cy were 20.0%±1.4% and 75.5%±2.5% respeetively at the 8th week (P<0.01).Conclusion This study demonstrated that TILs from patients with oral carcer possess strong in vivo inhibition on nude mice transplanted tumor, and low dose of cyclophasophamide can enhance the inhibition effect and prolong the inhibition time.
, http://www.100md.com
【Key words】 Mouth neoplasms Lymphocytes, tumor-infiltrating
近年来,通过回输特异性免疫细胞的方法治疗恶性肿瘤是倍受关注的研究课题[1],我们在成功地制备了口腔癌肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞(tumor-infiltration lymphocyte, TIL)的基础上,检测了其表型及体外抗瘤活性,发现口腔癌TIL在体外具有强大的抗瘤作用[2]。但由于体内、外环境的差别,TIL在体内发挥作用要受许多因素的影响,故体内外抗瘤作用必然会有差别。鉴于此,我们在建立人舌癌Tca 8113裸鼠移植瘤的基础上,联合应用环磷酰胺(cyclophosphamide, Cy),观察其体内抑瘤效果,以期为口腔癌TIL的临床应用提供资料。
材料和方法
1.材料:
, http://www.100md.com
(1)实验动物:裸小鼠BALB/C-nu/nu 15只(华西医科大学实验动物中心提供),鼠龄6~8周,体重18~24g。
(2)细胞系:Tca 8113人舌鳞癌细胞系(上海第二医科大学口腔医学院建株)。
(3)rIL-2:由第二军医大学提供。
(4)环磷酰胺(Cy):购自Sigma公司。
2.方法:
(1)制备口腔癌TIL[2]。
(2)荷瘤鼠模型的建立及治疗方法[3]:取处于对数生长期的Tca 8113细胞经0.25%胰酶消化后,用Hank液洗3遍,计数后配成1×1010/L的瘤细胞悬液,给每只裸鼠背部皮下注射0.2ml,然后随机分为3组,即对照组、TIL+rIL-2组和TIL+rIL-2+Cy组,每组5只裸鼠。治疗方法:①对照组在相应部位注射等量的生理盐水;②TIL+rIL-2组于接种瘤细胞后12小时,在瘤细胞接种区注射2×1010/L TIL及1×104rIL-2各0.2ml;③TIL+rIL-2+Cy组:其中的TIL及rIL-2应用方法同②,在接种瘤细胞前24小时(即TIL和rIL-2应用前36小时)给每只裸鼠腹腔注射Cy 50mg/kg体重(表1)。
, 百拇医药
表1 各实验组的治疗方法(n=5) 组别
TCa8113细胞
(1×1010/L)
TIL
(2×1010/L)
rIL-2
(1×104U)
Cy
(2g/L)
对照组
0.2ml
, 百拇医药
0
0
0
TIL+rIL-2
0.2ml
0.2ml
0.2ml
0
TIL+rIL-2+Cy
0.2ml
0.2ml
0.2ml
0.5ml
, 百拇医药
注:效/靶=10∶1;TIL:浸润肿瘤淋巴细胞;Cy:环磷酰胺;rIL-2:人白细胞介素2,下表同
(3)移植瘤生长情况及抑瘤作用评价:荷瘤裸鼠饲养在SPF条件下,每周测瘤体大小,于接种肿瘤后第8周处死裸鼠,解剖称重,按下列公式计算抑瘤率: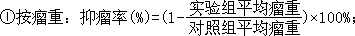

肿瘤体积与三维测量值的换算: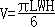 ,L、W、H分别代表肿瘤的3径。
,L、W、H分别代表肿瘤的3径。
结果
1.对照组肿瘤生长情况:从第1周开始,肿瘤生长很快,到第8周肿瘤已近4 000mm3(表2)。
, 百拇医药
2.TIL+rIL-2组肿瘤生长情况:前3周肿瘤生长缓慢,第4周生长加快,到第8周达2 700mm3(表2)。
3.TIL+rIL-2+Cy组肿瘤生长情况:与TIL+rIL-2组相比肿瘤生长被抑制的时间更长,且在第8周末,其体积仅有775mm3(表2)。
4.抑瘤率:TIL+rIL-2组抑瘤率在前3周均保持较高水平,第4周则迅速减弱,说明TIL+rIL-2在前3周有较好的抑瘤作用;TIL+rIL-2+Cy组在观察的8周内,始终具有较高的抑瘤率,虽然在3周后抑瘤率有所下降,但仍保持较高水平,说明TIL+rIL-2+Cy在8周甚至更长的时间内均有较好的抑瘤效果。同时也说明,Cy的联合应用使TIL在体内的抑瘤作用更强,效果更持久(表3,4,附图)。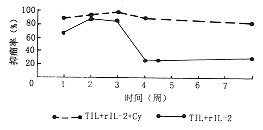
, http://www.100md.com 附图 各组平均抑瘤率的动态变化
讨论
口腔癌TIL在体外具有强大的杀瘤活性[2]。自从成功地人工合成rIL-2后,过继免疫治疗发展了一大步。LAK/IL-2治疗恶性肿瘤已取得了一定效果,但由于LAK特异性差,活性的维持需大剂量IL-2,而大剂量的rIL-2的应用常导致严重的副作用,故应用受限。TIL特异性强,抗瘤功效是LAK细胞的50~100倍[4],维持其活性所需的IL-2比LAK少100倍[5]。实验证明,适当剂量的IL-2就能维持TIL在体内的增殖能力和抗瘤活性[6]。我们采用104UrIL-2与TIL合用,取得了较好的体内抑瘤作用。
TIL是由不同细胞亚群组成的集合体,其中有一种表型为CD8的T抑制细胞(Ts),可对其他亚型
, 百拇医药
表2 各组肿瘤平均体积动态观察( ±s, mm3) 组别
±s, mm3) 组别
时间(周)
1
2
3
4
8
对照组
54.5±1.5
148.5±11.3
230.3±15.4
, http://www.100md.com
341.3±18.5
3 998.7±35.5
TIL+rIL-2
17.6±0.7
18.0±0.8
32.0±1.2
243.6±16.3
2 717.1±30.9
TIL+rIL-2+Cy
5.2±0.3
5.2±0.3
5.2±0.3
, 百拇医药
25.1±1.1
775.1±25.3
表3 各组按体积计算平均抑瘤率
动态变化( ±s, %, n=5) 组别
±s, %, n=5) 组别
时间(周)
1
2
3
4
8
TIL+rIL-2
, http://www.100md.com
67.8±0.3
87.9±0.4
86.1±0.4
26.6±0.2
32.1±0.3
TIL+rIL-2
+Cy
90.4±0.5
96.5±0.4
97.7±0.6
89.6±0.5
80.6±0.3
, 百拇医药
表4 第8周平均瘤重及按瘤重计算抑瘤率(n=5) 组别
平均瘤重(g)
平均抑瘤率(%)
P值
对照组
4.0±0.3
TIL+rIL-2
3.2±0.2
20.0±1.4
<0.01
TIL+rIL-2+Cy
1.0±0.1
, 百拇医药
75.5±2.5
<0.01
细胞起抑制作用。Ts的量越高,活性越大,TIL受到的抑制作用越强,抑瘤作用就越低。培养激活后的TIL仍有相当数量的Ts细胞。Cy是细胞毒素类化疗药物。低剂量(50mg/kg)应用时,能选择性抑制Ts细胞,从而提高了TIL的整体抑瘤水平[7]。另外,Cy对肿瘤也有一定的杀伤作用,在一定程度上减轻TIL的肿瘤负荷。本组联合应用低剂量Cy,从抑瘤率可看出,TIL+Cy比单独TIL在体内的抑瘤作用更强,时间更长。至于Cy与TIL相互作用的关系(拮抗作用、协同作用、增强作用)及机制尚有待进一步深入研究。
口腔癌TIL在rIL-2条件下能发挥较大的体内抑瘤作用,TIL+rIL-2和TIL+rIL-2+Cy两个方案治疗后产生最佳抑瘤效果的时间是在注射后2~3周内,在此之后肿瘤的生长加快,特别是在治疗后期,肿瘤有反跳趋势,因此,TIL应与放疗或其他抗瘤措施结合,以获得更好的临床效果。
, 百拇医药
本课题为卫生部基金资助(94-1-224)
参考文献
1Rosenberg SA, Spiess P, Lafreniere R. A new approach to the adoptive immunotherpy of cancer with tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. Science, 1986, 233:1318-1321.
2廖贵清,毛祖彝,章崇杰,等.口腔癌TIL的提取,培养,表型分析及体外抗瘤活性研究.口腔颌面外科杂志,1996,6:95-98.
3郭伟,何荣根,邱蔚六,等.舌鳞癌引流区淋巴结细胞联合平阳霉素的抑瘤作用.上海口腔医学,1992,1:40-43.
4Moertel CG. On lymphokines, cytokines, and breakthroughs. JAMA, 1986, 256:3141.
, http://www.100md.com
5Rosenberg SA, Packard BS, Aebersold PM, et al. Use of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and interleukin-2 in the immunotherpy of patients with metastatic melanoma: a preliminary report. N Engl J Med, 1988, 319:1676-1680.
6Kradin R, Dubinett S, Mullin J, et al. Treatmant of patients with advanced cancer using tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and interleukin-2. Transplant Proc, 1988, 20:336-338.
7Aoki Y, Takakuwa K, Kodama S, et al. Use of adoptive transfer of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes alone or in combination with cisplatin-containing chemotherapy in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res, 1991, 51:1934-1939.
(收稿:1996-09-25 修回:1998-01-12), 百拇医药
单位:510060 广州,中山医科大学口腔医学院(廖贵清);华西医科大学口腔医学院(毛祖彝、徐平平)
关键词:口腔肿瘤;淋巴细胞,肿瘤浸润
中华口腔医学杂志980305 【摘要】 目的 探讨在体外具有强大细胞毒活性的口腔癌浸润淋巴细胞在体内的抑瘤效果以及化疗药物环磷酰胺(cyclophosphamide, Cy)与肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞(tumor-infiltration lymphocyte, TIL)联合应用治疗口腔癌的可能性。方法 将舌鳞癌细胞系Tca 8113 注入裸鼠背部皮下建立移植瘤模型,取培养4周的TIL联合低剂量Cy局部注射,观察肿瘤体积变化及肿瘤生长情况。结果 ①TIL+rIL-2和TIL+rIL-2+Cy组在3周内抑瘤率较高(分别为:86.1%±0.4%和97.7%±0.6%),3周后抑瘤作用减弱;②TIL+rIL-2+Cy组抑瘤率较TIL+rIL-2组高(第8周抑瘤率分别为:20.0%±1.4%和75.5%±2.5%,P<0.01)。结论 口腔癌TIL在应用后3周内具较强抑瘤作用,3周后减弱;联合应用Cy可获得更佳抑瘤效果。
, http://www.100md.com
Inhibition effects of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes from oral cancer on nude mice transplanted tumor established with human tongue carcinoma cell lines Liao Guiqing*,Mao Zuyi, Xu Pingping.*School of Stomatology, Sun Yat-Sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510060
【Abstract】 Objective To observe the in vivo inhibition effects on nude mice transplanted tumor with tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) isolated from primary mass of oral cancer.Methods Established the transplanted tumor model of human tongue cancer at the back of BALB/C nude mice with subcutaneous injection of squamous cell carcinoma lines Tca 8113. TILs isolated from patients with Oral cancer, combining with low dose of cyclophosphamide (Cy: 50mg/kg), were locally injected into the peripheral site of tumor. The inhibition rate (IR) was calculated by the volume of tumor mass from the 1 st to the 8th week, and the weights at the 8th week after tumor dissection. Results ①Group TIL+rIL-2 and group TIL+rIL-2+Cy both exerted a strong inhibition effect on the transplanted tumor within three weeks. The Inhibition rate (IR) were 86.1%±0.4% and 97.7%±0.6% respectively at the 3rd week, while 32.1%±0.3% and 80.6%±0.3% at the 8th week. ②TIL+rIL-2+Cy expressed a stronger effect and a longer inhibition time. The IR of TIL+rIL-2 and TIL+rIL-2+Cy were 20.0%±1.4% and 75.5%±2.5% respeetively at the 8th week (P<0.01).Conclusion This study demonstrated that TILs from patients with oral carcer possess strong in vivo inhibition on nude mice transplanted tumor, and low dose of cyclophasophamide can enhance the inhibition effect and prolong the inhibition time.
, http://www.100md.com
【Key words】 Mouth neoplasms Lymphocytes, tumor-infiltrating
近年来,通过回输特异性免疫细胞的方法治疗恶性肿瘤是倍受关注的研究课题[1],我们在成功地制备了口腔癌肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞(tumor-infiltration lymphocyte, TIL)的基础上,检测了其表型及体外抗瘤活性,发现口腔癌TIL在体外具有强大的抗瘤作用[2]。但由于体内、外环境的差别,TIL在体内发挥作用要受许多因素的影响,故体内外抗瘤作用必然会有差别。鉴于此,我们在建立人舌癌Tca 8113裸鼠移植瘤的基础上,联合应用环磷酰胺(cyclophosphamide, Cy),观察其体内抑瘤效果,以期为口腔癌TIL的临床应用提供资料。
材料和方法
1.材料:
, http://www.100md.com
(1)实验动物:裸小鼠BALB/C-nu/nu 15只(华西医科大学实验动物中心提供),鼠龄6~8周,体重18~24g。
(2)细胞系:Tca 8113人舌鳞癌细胞系(上海第二医科大学口腔医学院建株)。
(3)rIL-2:由第二军医大学提供。
(4)环磷酰胺(Cy):购自Sigma公司。
2.方法:
(1)制备口腔癌TIL[2]。
(2)荷瘤鼠模型的建立及治疗方法[3]:取处于对数生长期的Tca 8113细胞经0.25%胰酶消化后,用Hank液洗3遍,计数后配成1×1010/L的瘤细胞悬液,给每只裸鼠背部皮下注射0.2ml,然后随机分为3组,即对照组、TIL+rIL-2组和TIL+rIL-2+Cy组,每组5只裸鼠。治疗方法:①对照组在相应部位注射等量的生理盐水;②TIL+rIL-2组于接种瘤细胞后12小时,在瘤细胞接种区注射2×1010/L TIL及1×104rIL-2各0.2ml;③TIL+rIL-2+Cy组:其中的TIL及rIL-2应用方法同②,在接种瘤细胞前24小时(即TIL和rIL-2应用前36小时)给每只裸鼠腹腔注射Cy 50mg/kg体重(表1)。
, 百拇医药
表1 各实验组的治疗方法(n=5) 组别
TCa8113细胞
(1×1010/L)
TIL
(2×1010/L)
rIL-2
(1×104U)
Cy
(2g/L)
对照组
0.2ml
, 百拇医药
0
0
0
TIL+rIL-2
0.2ml
0.2ml
0.2ml
0
TIL+rIL-2+Cy
0.2ml
0.2ml
0.2ml
0.5ml
, 百拇医药
注:效/靶=10∶1;TIL:浸润肿瘤淋巴细胞;Cy:环磷酰胺;rIL-2:人白细胞介素2,下表同
(3)移植瘤生长情况及抑瘤作用评价:荷瘤裸鼠饲养在SPF条件下,每周测瘤体大小,于接种肿瘤后第8周处死裸鼠,解剖称重,按下列公式计算抑瘤率:
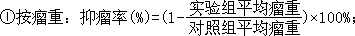

肿瘤体积与三维测量值的换算:
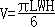 ,L、W、H分别代表肿瘤的3径。
,L、W、H分别代表肿瘤的3径。结果
1.对照组肿瘤生长情况:从第1周开始,肿瘤生长很快,到第8周肿瘤已近4 000mm3(表2)。
, 百拇医药
2.TIL+rIL-2组肿瘤生长情况:前3周肿瘤生长缓慢,第4周生长加快,到第8周达2 700mm3(表2)。
3.TIL+rIL-2+Cy组肿瘤生长情况:与TIL+rIL-2组相比肿瘤生长被抑制的时间更长,且在第8周末,其体积仅有775mm3(表2)。
4.抑瘤率:TIL+rIL-2组抑瘤率在前3周均保持较高水平,第4周则迅速减弱,说明TIL+rIL-2在前3周有较好的抑瘤作用;TIL+rIL-2+Cy组在观察的8周内,始终具有较高的抑瘤率,虽然在3周后抑瘤率有所下降,但仍保持较高水平,说明TIL+rIL-2+Cy在8周甚至更长的时间内均有较好的抑瘤效果。同时也说明,Cy的联合应用使TIL在体内的抑瘤作用更强,效果更持久(表3,4,附图)。

, http://www.100md.com 附图 各组平均抑瘤率的动态变化
讨论
口腔癌TIL在体外具有强大的杀瘤活性[2]。自从成功地人工合成rIL-2后,过继免疫治疗发展了一大步。LAK/IL-2治疗恶性肿瘤已取得了一定效果,但由于LAK特异性差,活性的维持需大剂量IL-2,而大剂量的rIL-2的应用常导致严重的副作用,故应用受限。TIL特异性强,抗瘤功效是LAK细胞的50~100倍[4],维持其活性所需的IL-2比LAK少100倍[5]。实验证明,适当剂量的IL-2就能维持TIL在体内的增殖能力和抗瘤活性[6]。我们采用104UrIL-2与TIL合用,取得了较好的体内抑瘤作用。
TIL是由不同细胞亚群组成的集合体,其中有一种表型为CD8的T抑制细胞(Ts),可对其他亚型
, 百拇医药
表2 各组肿瘤平均体积动态观察(
 ±s, mm3) 组别
±s, mm3) 组别时间(周)
1
2
3
4
8
对照组
54.5±1.5
148.5±11.3
230.3±15.4
, http://www.100md.com
341.3±18.5
3 998.7±35.5
TIL+rIL-2
17.6±0.7
18.0±0.8
32.0±1.2
243.6±16.3
2 717.1±30.9
TIL+rIL-2+Cy
5.2±0.3
5.2±0.3
5.2±0.3
, 百拇医药
25.1±1.1
775.1±25.3
表3 各组按体积计算平均抑瘤率
动态变化(
 ±s, %, n=5) 组别
±s, %, n=5) 组别时间(周)
1
2
3
4
8
TIL+rIL-2
, http://www.100md.com
67.8±0.3
87.9±0.4
86.1±0.4
26.6±0.2
32.1±0.3
TIL+rIL-2
+Cy
90.4±0.5
96.5±0.4
97.7±0.6
89.6±0.5
80.6±0.3
, 百拇医药
表4 第8周平均瘤重及按瘤重计算抑瘤率(n=5) 组别
平均瘤重(g)
平均抑瘤率(%)
P值
对照组
4.0±0.3
TIL+rIL-2
3.2±0.2
20.0±1.4
<0.01
TIL+rIL-2+Cy
1.0±0.1
, 百拇医药
75.5±2.5
<0.01
细胞起抑制作用。Ts的量越高,活性越大,TIL受到的抑制作用越强,抑瘤作用就越低。培养激活后的TIL仍有相当数量的Ts细胞。Cy是细胞毒素类化疗药物。低剂量(50mg/kg)应用时,能选择性抑制Ts细胞,从而提高了TIL的整体抑瘤水平[7]。另外,Cy对肿瘤也有一定的杀伤作用,在一定程度上减轻TIL的肿瘤负荷。本组联合应用低剂量Cy,从抑瘤率可看出,TIL+Cy比单独TIL在体内的抑瘤作用更强,时间更长。至于Cy与TIL相互作用的关系(拮抗作用、协同作用、增强作用)及机制尚有待进一步深入研究。
口腔癌TIL在rIL-2条件下能发挥较大的体内抑瘤作用,TIL+rIL-2和TIL+rIL-2+Cy两个方案治疗后产生最佳抑瘤效果的时间是在注射后2~3周内,在此之后肿瘤的生长加快,特别是在治疗后期,肿瘤有反跳趋势,因此,TIL应与放疗或其他抗瘤措施结合,以获得更好的临床效果。
, 百拇医药
本课题为卫生部基金资助(94-1-224)
参考文献
1Rosenberg SA, Spiess P, Lafreniere R. A new approach to the adoptive immunotherpy of cancer with tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. Science, 1986, 233:1318-1321.
2廖贵清,毛祖彝,章崇杰,等.口腔癌TIL的提取,培养,表型分析及体外抗瘤活性研究.口腔颌面外科杂志,1996,6:95-98.
3郭伟,何荣根,邱蔚六,等.舌鳞癌引流区淋巴结细胞联合平阳霉素的抑瘤作用.上海口腔医学,1992,1:40-43.
4Moertel CG. On lymphokines, cytokines, and breakthroughs. JAMA, 1986, 256:3141.
, http://www.100md.com
5Rosenberg SA, Packard BS, Aebersold PM, et al. Use of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and interleukin-2 in the immunotherpy of patients with metastatic melanoma: a preliminary report. N Engl J Med, 1988, 319:1676-1680.
6Kradin R, Dubinett S, Mullin J, et al. Treatmant of patients with advanced cancer using tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and interleukin-2. Transplant Proc, 1988, 20:336-338.
7Aoki Y, Takakuwa K, Kodama S, et al. Use of adoptive transfer of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes alone or in combination with cisplatin-containing chemotherapy in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res, 1991, 51:1934-1939.
(收稿:1996-09-25 修回:1998-01-12), 百拇医药