兔下颌钛种植体周多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基在骨愈合中的动态研究
作者:白薇 宫苹 肖邦良 鲜苏琴
单位:白薇(华西医科大学口腔医学院 610041);宫苹(华西医科大学口腔医学院 610041);鲜苏琴(华西医科大学口腔医学院 610041);肖邦良(华西医科大学公共卫生学院)
关键词:牙种植;钛;蛋白多糖;糖蛋白
华西口腔医学杂志000105 摘 要:目的:研究钛种植体周结缔组织中多糖-蛋白复合物在骨愈合过程中的变化规律及可能的作用机制。方法:采用爱尔蓝及生物素标记的植物血凝素方法对兔下颌钛种植体周围组织中的多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基进行观察。结果:钛种植体周结缔组织膜、新生骨基质及成骨细胞中此物质的含量较高。结论:多糖-蛋白复合物在钛种植体形成骨附着及维持钛的生物相容性方面可能具有重要作用,并推测其与骨代谢活性密切相关。
A Study of Polysaccharide-protein Complex and Glycosyls in the Tissue Surrounding Titanium Implant of Rabbit
, 百拇医药
Bai Wei Gong Ping Xian Suqin
(College of Stomatology, West China University of Medical Sciences)
Xiao Bangliang
(College of Public Health, West China University of Medical Sciences)
Abstract:Objective:The absorption of the polysaccharide-protein complex to the implant surface may be the first reaction between the implant and the surrounding tissue. So we observed the distribution and the relative amount of the polysaccharide-protein complex and glycosyls in order to find out the possible functions and changing rules of these substances. Methods: 12 rabbits were selected according to the age, sex, weight, and health conditions. Bilateral mandibular premolar teeth of rabbits were extracted under abdomen anesthesia (2% glutababituratic acid), then l2 titanium implants were placed into the teeth extraction holes of one side and left the other side to be the control one. All of the implants were required to be placed 2mm below the alveolar crest, and tissue closure was achieved with mattress and interrupted single sutures. Antibiotic injections were given to the rabbits in the following 3 days. The animals were sacrificed at the end of l week, 4 weeks and 24 weeks. Tissue blocks (4mm×4mm×4mm) containing the titanium implants and the control ones were removed, then fixed with l0% formaldehyde for 2 weeks, and decalcified with 10% EDTA (pH7.0) for 8 weeks. Carefully removed the titanium implants, the tissue blocks were embedded into the paraffin wax, then the sections were obtained and stained using following methods. ①Alcian Blue Method: Alcian blue (pH2.5) staining displayed the acidic proteoglycans; Alcian blue (pH1.0) displayed the proteoglycans containing sulfonyl; Alcian blue/periodix acid-shiff staining demonstrated the acidic and neutral proteoglycans respectively. Alcian blue-MgCl2 with different ionic concentration identified the different kinds of proteoglycans. ②Lectin Method: 5 kinds of lectins were used to locate 5 kinds of glycosyls. 2.5 μg/ml ConA located the glucose; 10μg/ml PNA located the galactose; 10μg/ml WGA located the N-acetylglucosamine; 25μg/ml PHA-E located N-acetylgalactosamine, 10μg/ml WPL loacted the fucose. Results: high level of proteoglycans and glycosyls were observed in the peri-implant connective tissue during all phases of the experiment. It was also observed that polysaccharide-protein complex and glycosyls reached a high level in new bone matrix as well as osteoblasts. Conclusion: Polysaccharide-protein complex and glycosyls do play an important role in the implant-bone attachment, and titanium compatibility and may be closely related to the bone metabolic activity.
, 百拇医药
Key words:dental implant titanium proteoglycans glycosyls▲
钛是一种具有良好生物相容性的牙种植材料,被广泛应用于临床,其生物相容性的基础在于它能与周围骨组织形成紧密的附着。近年来研究表明,多糖-蛋白复合物(polysaccharide-protein complex)与骨愈合的过程及病理改变均有密切关系,多糖-蛋白复合物在种植体表面的吸附,很可能是种植体周围组织发生的最早期反应[1,2],人为削弱此吸附,最终会导致骨附着强度的降低。有学者发现,在种植体骨愈合的早期,其龈沟液内多糖-蛋白复合物水平升高,形成骨附着后,成功种植体龈沟液多糖-蛋白复合物水平下降,而失败者则升高[3]。这些初步的研究结果提示,作为“异己”的钛种植体无论在与周围组织相容或发生松动的过程中,多糖-蛋白复合物均可能发挥着重要作用。但目前,对此问题的研究尚缺乏肯定的证据。
本文通过研究兔下颌钛种植体周多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基在骨愈合中的分布及相对含量的动态变化,探讨可能的作用机制,为临床种植修复失败的病理研究提供实验依据和基础资料。
, 百拇医药
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料
商业纯钛种植体(cpTi,宝鸡有色金属研究所),长4 mm,直径3 mm,圆柱状,表面光滑;健康新西兰兔12只,雄性,6月龄,体重1.5~2.0 kg;主要染色液有:8 GX爱尔蓝染液(alcian blue,AB),过碘酸西夫试剂(periodic acid-schiff,PAS),刀豆蛋白(concanavalin ensiformis,Con A) 2.5 μg/ml,花生凝集素(arachis hypogaea,PNA)10 μg/ml,腰子豆凝集素(phaseolus vulgaris,PHA-E)25 μg/ml,麦胚凝集素(triticum vulgaris,WGA)10 μg/ml,tetragonolobus purpurea,WPL10 μg/ml。
1.2 实验方法
, 百拇医药 在3%戊巴比妥钠溶液腹腔全麻(35~40 mg/kg体重)下,拔除双侧下颌第一前磨牙,清理拔牙窝,各埋入1颗cpTi种植体,使其最高点位于牙槽骨嵴下2 mm处,严密缝合创面,术后3 d肌注庆大霉素(80万u/d)抗感染。此后分别于不同实验程期(1周,1月,6月)处死动物取样。
所有标本立即放入10%福尔马林溶液固定2~3周,再经10%EDTA(0.1 mol/L Tris/HCl缓冲液配制,pH7.0)脱钙8周后,按常规脱水,包埋,切片,进行下述染色。
1.2.1 爱尔蓝及过碘酸-西夫试剂染色法 染色结果可显示并鉴别各种不同性质的蛋白多糖(PG)的分布及相对含量。PAS红色显示中性糖蛋白;pH 2.5 AB蓝色显示酸性PG;pH 1.0 AB蓝色显示硫酸化PG;0.06 mol/L MgCl2AB蓝色显示酸性PG;0.3 mol/L MgCl2 AB蓝色显示硫酸化PG;0.5 mol/L MgCl2 AB蓝色显示强硫酸PG。
, 百拇医药
1.2.2 植物血凝素糖基染色法(Lectin法) 棕黄色显示阳性反应:Con A阳性显示葡萄糖基(glucose,Glc);PNA阳性显示半乳糖基(galactose,Gal);WGA阳性显示乙酰氨基葡萄糖基(N-acetylglucosamine,GlcNAc);PHA-E阳性显示乙酸氨基半乳糖基(N-acetylgalactosamine,GalNAc);WPL阳性显示岩藻糖基(fucose,Fuc)。根据不同方法所显示不同颜色深浅,将染色程度分为六级: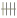 强阳性,
强阳性,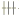 次强阳性,
次强阳性,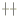 阳性,+弱阳性,±可疑,-阴性。
阳性,+弱阳性,±可疑,-阴性。
2 结 果
2.1 组织学观察结果
, 百拇医药
正常牙周膜由致密而排列有序的胶原纤维束及其间丰富的成纤维细胞、神经、血管组成,固有牙槽骨内骨质致密,骨陷窝较多,分布规整。钛种植体植入1周,其与固有牙槽骨间可见大量结缔组织,近种植体处较致密,纤维平行排列,形成结缔组织膜。沿固有牙槽骨边缘,可见分支状新生骨组织向种植体周结缔组织中增生,新骨基质着色稍浅,周围可见立方状成骨细胞,也可见成骨细胞埋在基质中,胞核较大,可见胞浆。成骨活跃处,毛细血管丰富,部分固有牙槽骨周可见破骨细胞。
钛种植体植入1月,新生骨组织继续向种植体方向增生,并相互吻合成网状,钛周结缔组织明显减少。
钛种植体植入6个月,新生骨组织充满种植体周间隙,骨小梁彼此融合,形态上接近于固有牙槽骨,部分新生骨似与种植体表面直接接触,钛种植体与骨之间结缔组织极薄且不连续。
2.2 多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基染色结果
, 百拇医药 2.2.1 钛周结缔组织膜染色 钛周结缔组织膜中多糖-蛋白复合物尤其是PG含量明显高于正常牙周膜,并且在种植术后各个实验程期都保持较高水平,糖基染色结果有同样规律,此外近钛结缔组织中可见许多棱形成纤维细胞,其内糖基含量较高(表1)。
表1 钛周结缔组织膜染色结果 组别
中性
糖蛋白
酸性PG
硫酸化PG
强硫酸PG
Glc
Gal
GlcNAc
, 百拇医药
GalNAc
Fuc
AB
MgCl2AB
AB
MgCl2AB
正常牙周膜
+
+
+
-
-
-




, 百拇医药
植入1周




+




, http://www.100md.com
植入1月




+




, 百拇医药
植入6月




+




, 百拇医药
2.2.2 骨基质染色 钛种植体植入早期,新生骨基质中多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基都明显增多,以后随时间延长而递减,至实验截止时与固有牙槽骨基质相近(表2)。
表2 骨基质染色结果 组别
中性
糖蛋白
(酸性PG
硫酸化PG
强硫酸PG
Glc
Gal
GlcNAc
GalNAc
, 百拇医药
Fuc
AB
MgCl2AB
AB
MgCl2AB
固有牙槽骨
+
+
+
-
-
±
, 百拇医药
-
-
-
-
植入1周




-
, http://www.100md.com
+
+
+
+
植入1月
+
+
+
-
+
+
, 百拇医药
+
-
+
植入6月
+
+
+
+
-
+
±
±
-
, 百拇医药
±
2.2.3 骨细胞染色结果 新生的成骨细胞内含有较多的多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基,但当其被基质包埋而成为骨细胞且基质钙盐沉着后,上述物质减少。3 讨 论
本实验结果显示,种植体周结缔组织膜中多糖-蛋白复合物,尤其是PG及糖基含量明显高于正常牙周膜,并且在种植术后各个实验程期都保持较高水平,说明多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基在种植体形成骨附着的过程中及在维持钛的生物相容性方面可能具有重要作用。许多学者报道了在骨附着的过程中,种植体与骨之间出现了一20~40 nm宽的有机蛋白多糖层,在电子显微镜下呈现出一无细胞的均质区,并认为这层PG类物质在种植体表面的附着是种植体与周围骨组织发生的最早期的反应。研究证明,大多数PG都可吸附于钛表面[4,5]。Albreksson等[4]用糖蛋白预处理钛种植体,使其吸附组织蛋白质的能力下降,最终导致了骨附着强度的降低。一些体外实验对其附着机制进行了研究,较为公认的是静电吸附理论,即通过Ca2+的桥接作用,使带有负电荷的种植体表面与同样带有负电荷的蛋白多糖层紧密相连。尽管本实验采用的方法,不能显示出种植体表面的PG层,但所观察到的种植体周结缔组织近钛处持续高酸性PG的现象很可能与这层物质有关。实验结果还发现,在邻近钛表面的结缔组织中有许多棱形成纤维细胞,其内富含各种糖基,由此可见除了血清、血浆、组织间液外,结缔组织中的某些细胞产生的PG,很可能是种植体周PG层的来源之一。目前种植体周PG层的化学组成及作用机制还不十分清楚,但可能至少具有以下几种功能:作为最早粘附于种植体表面的物质而介导其他分子在种植体表面的粘附;有利于组织修复等功能,以促进种植体与骨的生物相容性;调节细胞与细胞,细胞与基质的粘附过程,从而促进骨与种植体的附着[6]。
, http://www.100md.com
本实验还观察到,钛植入早期,成骨活跃时,新生骨基质中多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基都明显增多,而植入6个月成骨活性大为减低时,基质中多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基含量均减少。新生的成骨细胞处于高度活跃状态时,细胞内多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基较多,当成骨细胞被基质包埋成为骨细胞,基质发生矿化后,细胞中此物质含量减少,这表明,多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基含量与骨代谢活性密切相关。当骨代谢旺盛时,此物质含量增高,一方面,新生的糖蛋白(胶原),可作为骨的主要有机物,为其提供支持、负重的能力;另一方面,生成的PG可等[7]研究发现,使用糖胺多糖(GAG)与胶原的复合物可加速骨创的愈合。Last等研究发现,GAG含量的增加与种植体周骨代谢活性的升高密切相关;Oksalo等通过对创伤区PG表达强度的研究发现,创伤区硫酸肝素PG、硫酸皮肤素PG、透明质酸PG在骨愈合的不同时期都显示出有意义的增加。所有这些研究表明,多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基在种植区骨的愈合过程中具有重要作用。■
基金项目:本课题为四川省科委基金资助项目(编号 G96007)
, 百拇医药
参考文献:
[1]Larsson C, Thomsen P, Lausman J, et al. Bone response to surface modified titanium implats: studies on electropolished implants with different oxide thicknesses and morphology. Biomaterials, l994,15(15):1062~1074
[2]Dion I, Baquey C, Monties JR, et al. Haemocompatibility of Ti6A14V alloy. Biomaterials, l993,14(2):122~126
[3]Last KS, Cawood JI, Howell RA. Monitoring of tubinogen endosseous dental implants by glycosaminoglycan analysis of gingiva crevicular fluid. Int J Oral Maxillofc Implants, 1991,6(1):42~59
, 百拇医药
[4]Collis JJ, Embery G. Adsorption of glycosaminoglycans to commercially pure titanium. Biomaterials, l992,13(8):548~552
[5]Diana T, Embery G. Adsorption of chondroitin-4-sulphate and heparin onto tianium: effect of bovine serum albumin. Biomateaials, 1997,18(16):1121~1126
[6]Haidl ID, Jefferies WA. The macrophage cell surface glycoprotein F4/80 is a highly glycosylated proteoglycan. Eur J Immunol, 1996,26(5);1139~1146
[7]Phunkova H, Stehlik J, Vachal J, et al. Morphological features of bone healing under the effect of collagen-graft-glycosaminoglycan copolymer supplemented with the tripeptide Gly-His-Lys. Biomaterials, 1996,17(16):1567~1574
收稿日期:1999-01-12
修稿日期:1999-12-17, 百拇医药
单位:白薇(华西医科大学口腔医学院 610041);宫苹(华西医科大学口腔医学院 610041);鲜苏琴(华西医科大学口腔医学院 610041);肖邦良(华西医科大学公共卫生学院)
关键词:牙种植;钛;蛋白多糖;糖蛋白
华西口腔医学杂志000105 摘 要:目的:研究钛种植体周结缔组织中多糖-蛋白复合物在骨愈合过程中的变化规律及可能的作用机制。方法:采用爱尔蓝及生物素标记的植物血凝素方法对兔下颌钛种植体周围组织中的多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基进行观察。结果:钛种植体周结缔组织膜、新生骨基质及成骨细胞中此物质的含量较高。结论:多糖-蛋白复合物在钛种植体形成骨附着及维持钛的生物相容性方面可能具有重要作用,并推测其与骨代谢活性密切相关。
A Study of Polysaccharide-protein Complex and Glycosyls in the Tissue Surrounding Titanium Implant of Rabbit
, 百拇医药
Bai Wei Gong Ping Xian Suqin
(College of Stomatology, West China University of Medical Sciences)
Xiao Bangliang
(College of Public Health, West China University of Medical Sciences)
Abstract:Objective:The absorption of the polysaccharide-protein complex to the implant surface may be the first reaction between the implant and the surrounding tissue. So we observed the distribution and the relative amount of the polysaccharide-protein complex and glycosyls in order to find out the possible functions and changing rules of these substances. Methods: 12 rabbits were selected according to the age, sex, weight, and health conditions. Bilateral mandibular premolar teeth of rabbits were extracted under abdomen anesthesia (2% glutababituratic acid), then l2 titanium implants were placed into the teeth extraction holes of one side and left the other side to be the control one. All of the implants were required to be placed 2mm below the alveolar crest, and tissue closure was achieved with mattress and interrupted single sutures. Antibiotic injections were given to the rabbits in the following 3 days. The animals were sacrificed at the end of l week, 4 weeks and 24 weeks. Tissue blocks (4mm×4mm×4mm) containing the titanium implants and the control ones were removed, then fixed with l0% formaldehyde for 2 weeks, and decalcified with 10% EDTA (pH7.0) for 8 weeks. Carefully removed the titanium implants, the tissue blocks were embedded into the paraffin wax, then the sections were obtained and stained using following methods. ①Alcian Blue Method: Alcian blue (pH2.5) staining displayed the acidic proteoglycans; Alcian blue (pH1.0) displayed the proteoglycans containing sulfonyl; Alcian blue/periodix acid-shiff staining demonstrated the acidic and neutral proteoglycans respectively. Alcian blue-MgCl2 with different ionic concentration identified the different kinds of proteoglycans. ②Lectin Method: 5 kinds of lectins were used to locate 5 kinds of glycosyls. 2.5 μg/ml ConA located the glucose; 10μg/ml PNA located the galactose; 10μg/ml WGA located the N-acetylglucosamine; 25μg/ml PHA-E located N-acetylgalactosamine, 10μg/ml WPL loacted the fucose. Results: high level of proteoglycans and glycosyls were observed in the peri-implant connective tissue during all phases of the experiment. It was also observed that polysaccharide-protein complex and glycosyls reached a high level in new bone matrix as well as osteoblasts. Conclusion: Polysaccharide-protein complex and glycosyls do play an important role in the implant-bone attachment, and titanium compatibility and may be closely related to the bone metabolic activity.
, 百拇医药
Key words:dental implant titanium proteoglycans glycosyls▲
钛是一种具有良好生物相容性的牙种植材料,被广泛应用于临床,其生物相容性的基础在于它能与周围骨组织形成紧密的附着。近年来研究表明,多糖-蛋白复合物(polysaccharide-protein complex)与骨愈合的过程及病理改变均有密切关系,多糖-蛋白复合物在种植体表面的吸附,很可能是种植体周围组织发生的最早期反应[1,2],人为削弱此吸附,最终会导致骨附着强度的降低。有学者发现,在种植体骨愈合的早期,其龈沟液内多糖-蛋白复合物水平升高,形成骨附着后,成功种植体龈沟液多糖-蛋白复合物水平下降,而失败者则升高[3]。这些初步的研究结果提示,作为“异己”的钛种植体无论在与周围组织相容或发生松动的过程中,多糖-蛋白复合物均可能发挥着重要作用。但目前,对此问题的研究尚缺乏肯定的证据。
本文通过研究兔下颌钛种植体周多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基在骨愈合中的分布及相对含量的动态变化,探讨可能的作用机制,为临床种植修复失败的病理研究提供实验依据和基础资料。
, 百拇医药
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料
商业纯钛种植体(cpTi,宝鸡有色金属研究所),长4 mm,直径3 mm,圆柱状,表面光滑;健康新西兰兔12只,雄性,6月龄,体重1.5~2.0 kg;主要染色液有:8 GX爱尔蓝染液(alcian blue,AB),过碘酸西夫试剂(periodic acid-schiff,PAS),刀豆蛋白(concanavalin ensiformis,Con A) 2.5 μg/ml,花生凝集素(arachis hypogaea,PNA)10 μg/ml,腰子豆凝集素(phaseolus vulgaris,PHA-E)25 μg/ml,麦胚凝集素(triticum vulgaris,WGA)10 μg/ml,tetragonolobus purpurea,WPL10 μg/ml。
1.2 实验方法
, 百拇医药 在3%戊巴比妥钠溶液腹腔全麻(35~40 mg/kg体重)下,拔除双侧下颌第一前磨牙,清理拔牙窝,各埋入1颗cpTi种植体,使其最高点位于牙槽骨嵴下2 mm处,严密缝合创面,术后3 d肌注庆大霉素(80万u/d)抗感染。此后分别于不同实验程期(1周,1月,6月)处死动物取样。
所有标本立即放入10%福尔马林溶液固定2~3周,再经10%EDTA(0.1 mol/L Tris/HCl缓冲液配制,pH7.0)脱钙8周后,按常规脱水,包埋,切片,进行下述染色。
1.2.1 爱尔蓝及过碘酸-西夫试剂染色法 染色结果可显示并鉴别各种不同性质的蛋白多糖(PG)的分布及相对含量。PAS红色显示中性糖蛋白;pH 2.5 AB蓝色显示酸性PG;pH 1.0 AB蓝色显示硫酸化PG;0.06 mol/L MgCl2AB蓝色显示酸性PG;0.3 mol/L MgCl2 AB蓝色显示硫酸化PG;0.5 mol/L MgCl2 AB蓝色显示强硫酸PG。
, 百拇医药
1.2.2 植物血凝素糖基染色法(Lectin法) 棕黄色显示阳性反应:Con A阳性显示葡萄糖基(glucose,Glc);PNA阳性显示半乳糖基(galactose,Gal);WGA阳性显示乙酰氨基葡萄糖基(N-acetylglucosamine,GlcNAc);PHA-E阳性显示乙酸氨基半乳糖基(N-acetylgalactosamine,GalNAc);WPL阳性显示岩藻糖基(fucose,Fuc)。根据不同方法所显示不同颜色深浅,将染色程度分为六级:
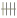 强阳性,
强阳性,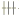 次强阳性,
次强阳性,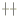 阳性,+弱阳性,±可疑,-阴性。
阳性,+弱阳性,±可疑,-阴性。2 结 果
2.1 组织学观察结果
, 百拇医药
正常牙周膜由致密而排列有序的胶原纤维束及其间丰富的成纤维细胞、神经、血管组成,固有牙槽骨内骨质致密,骨陷窝较多,分布规整。钛种植体植入1周,其与固有牙槽骨间可见大量结缔组织,近种植体处较致密,纤维平行排列,形成结缔组织膜。沿固有牙槽骨边缘,可见分支状新生骨组织向种植体周结缔组织中增生,新骨基质着色稍浅,周围可见立方状成骨细胞,也可见成骨细胞埋在基质中,胞核较大,可见胞浆。成骨活跃处,毛细血管丰富,部分固有牙槽骨周可见破骨细胞。
钛种植体植入1月,新生骨组织继续向种植体方向增生,并相互吻合成网状,钛周结缔组织明显减少。
钛种植体植入6个月,新生骨组织充满种植体周间隙,骨小梁彼此融合,形态上接近于固有牙槽骨,部分新生骨似与种植体表面直接接触,钛种植体与骨之间结缔组织极薄且不连续。
2.2 多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基染色结果
, 百拇医药 2.2.1 钛周结缔组织膜染色 钛周结缔组织膜中多糖-蛋白复合物尤其是PG含量明显高于正常牙周膜,并且在种植术后各个实验程期都保持较高水平,糖基染色结果有同样规律,此外近钛结缔组织中可见许多棱形成纤维细胞,其内糖基含量较高(表1)。
表1 钛周结缔组织膜染色结果 组别
中性
糖蛋白
酸性PG
硫酸化PG
强硫酸PG
Glc
Gal
GlcNAc
, 百拇医药
GalNAc
Fuc
AB
MgCl2AB
AB
MgCl2AB
正常牙周膜
+
+
+
-
-
-





, 百拇医药
植入1周





+





, http://www.100md.com
植入1月





+





, 百拇医药
植入6月





+





, 百拇医药
2.2.2 骨基质染色 钛种植体植入早期,新生骨基质中多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基都明显增多,以后随时间延长而递减,至实验截止时与固有牙槽骨基质相近(表2)。
表2 骨基质染色结果 组别
中性
糖蛋白
(酸性PG
硫酸化PG
强硫酸PG
Glc
Gal
GlcNAc
GalNAc
, 百拇医药
Fuc
AB
MgCl2AB
AB
MgCl2AB
固有牙槽骨

+
+
+
-
-
±
, 百拇医药
-
-
-
-
植入1周





-

, http://www.100md.com
+
+
+
+
植入1月

+

+
+
-
+
+
, 百拇医药
+
-
+
植入6月

+
+
+
+
-
+
±
±
-
, 百拇医药
±
2.2.3 骨细胞染色结果 新生的成骨细胞内含有较多的多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基,但当其被基质包埋而成为骨细胞且基质钙盐沉着后,上述物质减少。3 讨 论
本实验结果显示,种植体周结缔组织膜中多糖-蛋白复合物,尤其是PG及糖基含量明显高于正常牙周膜,并且在种植术后各个实验程期都保持较高水平,说明多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基在种植体形成骨附着的过程中及在维持钛的生物相容性方面可能具有重要作用。许多学者报道了在骨附着的过程中,种植体与骨之间出现了一20~40 nm宽的有机蛋白多糖层,在电子显微镜下呈现出一无细胞的均质区,并认为这层PG类物质在种植体表面的附着是种植体与周围骨组织发生的最早期的反应。研究证明,大多数PG都可吸附于钛表面[4,5]。Albreksson等[4]用糖蛋白预处理钛种植体,使其吸附组织蛋白质的能力下降,最终导致了骨附着强度的降低。一些体外实验对其附着机制进行了研究,较为公认的是静电吸附理论,即通过Ca2+的桥接作用,使带有负电荷的种植体表面与同样带有负电荷的蛋白多糖层紧密相连。尽管本实验采用的方法,不能显示出种植体表面的PG层,但所观察到的种植体周结缔组织近钛处持续高酸性PG的现象很可能与这层物质有关。实验结果还发现,在邻近钛表面的结缔组织中有许多棱形成纤维细胞,其内富含各种糖基,由此可见除了血清、血浆、组织间液外,结缔组织中的某些细胞产生的PG,很可能是种植体周PG层的来源之一。目前种植体周PG层的化学组成及作用机制还不十分清楚,但可能至少具有以下几种功能:作为最早粘附于种植体表面的物质而介导其他分子在种植体表面的粘附;有利于组织修复等功能,以促进种植体与骨的生物相容性;调节细胞与细胞,细胞与基质的粘附过程,从而促进骨与种植体的附着[6]。
, http://www.100md.com
本实验还观察到,钛植入早期,成骨活跃时,新生骨基质中多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基都明显增多,而植入6个月成骨活性大为减低时,基质中多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基含量均减少。新生的成骨细胞处于高度活跃状态时,细胞内多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基较多,当成骨细胞被基质包埋成为骨细胞,基质发生矿化后,细胞中此物质含量减少,这表明,多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基含量与骨代谢活性密切相关。当骨代谢旺盛时,此物质含量增高,一方面,新生的糖蛋白(胶原),可作为骨的主要有机物,为其提供支持、负重的能力;另一方面,生成的PG可等[7]研究发现,使用糖胺多糖(GAG)与胶原的复合物可加速骨创的愈合。Last等研究发现,GAG含量的增加与种植体周骨代谢活性的升高密切相关;Oksalo等通过对创伤区PG表达强度的研究发现,创伤区硫酸肝素PG、硫酸皮肤素PG、透明质酸PG在骨愈合的不同时期都显示出有意义的增加。所有这些研究表明,多糖-蛋白复合物及糖基在种植区骨的愈合过程中具有重要作用。■
基金项目:本课题为四川省科委基金资助项目(编号 G96007)
, 百拇医药
参考文献:
[1]Larsson C, Thomsen P, Lausman J, et al. Bone response to surface modified titanium implats: studies on electropolished implants with different oxide thicknesses and morphology. Biomaterials, l994,15(15):1062~1074
[2]Dion I, Baquey C, Monties JR, et al. Haemocompatibility of Ti6A14V alloy. Biomaterials, l993,14(2):122~126
[3]Last KS, Cawood JI, Howell RA. Monitoring of tubinogen endosseous dental implants by glycosaminoglycan analysis of gingiva crevicular fluid. Int J Oral Maxillofc Implants, 1991,6(1):42~59
, 百拇医药
[4]Collis JJ, Embery G. Adsorption of glycosaminoglycans to commercially pure titanium. Biomaterials, l992,13(8):548~552
[5]Diana T, Embery G. Adsorption of chondroitin-4-sulphate and heparin onto tianium: effect of bovine serum albumin. Biomateaials, 1997,18(16):1121~1126
[6]Haidl ID, Jefferies WA. The macrophage cell surface glycoprotein F4/80 is a highly glycosylated proteoglycan. Eur J Immunol, 1996,26(5);1139~1146
[7]Phunkova H, Stehlik J, Vachal J, et al. Morphological features of bone healing under the effect of collagen-graft-glycosaminoglycan copolymer supplemented with the tripeptide Gly-His-Lys. Biomaterials, 1996,17(16):1567~1574
收稿日期:1999-01-12
修稿日期:1999-12-17, 百拇医药