老年大鼠空间记忆减退与cNOS基因表达变化*
作者:高国全 姚志彬 张 静 马涧泉
单位:高国全 马涧泉:生化教研室;姚志彬:神经生物学研究室;张静:生理学教研室;中山医科大学(广州 510089)
关键词:;衰老;记忆;一氧化氮合酶;基因表达;大鼠
老年大鼠空间记忆减退与cNOS基因表达变化 摘 要 目的:从基因表达角度研究原生型NOS(cNOS, 包括神经元型nNOS 和内皮型eNOS)与老年记忆减退发生的关系。方法:用Morris水迷宫将老年大鼠筛选为记忆正常和记忆减退两组,以老年记忆减退大鼠作为老年记忆减退模型; 用半定量反转录-聚合酶链反应(RT-PCR)方法测定 nNOS和eNOS的mRNA含量。结果:(1) 海马组织中老年记忆正常组和老年记忆减退组较青年组 nNOS 和eNOS mRNA含量均下降,nNOS以记忆减退组下降更为显著; (2)小脑组织中老年记忆减退组nNOS和eNOSmRNA含量的下降与老年记忆正常组和青年组均有显著差异。(3)额叶组织nNOS mRNA含量三组之间均无显著差异; eNOSmRNA含量老年记忆正常组和老年记忆减退组较青年组均下降,以记忆减退组下降更为显著。结论:老年记忆减退的发生可能与有关脑区cNOS基因表达下降有关。
, 百拇医药
Changes of nitric oxide synthase activity and constitutive NOS gene
expression in the brain of memory-impaired aged rats
GAO Guo-Quan1, YAO Zhi-Bin2, ZHANG Jing3, MA Jian-Quan1
1 Department of Biochemistry, 2 Department of Neurobiology, 3 Department of Physiology,Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences,Guangzhou,(510089)
, 百拇医药
Abstract AIM: The relationship between nitric oxide(NO) and aged memory impairment was investigated to study the mechanism of aged memory impairment and find out a new method of treatment.METHODS: Aged rats were divided into aged memory-impaired group and aged memory-normal group using Morris water maze. The reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction(RT-PCR) method was used for semi-quantity determining of nNOS and eNOS mRNA content. RESULTS: In hippocampus, eNOS and nNOS mRNA content were decreased in both memory-normal aged rats and memory-impaired aged rats in comparison to that in young rats; nNOS mRNA content but eNOS reduced more significantly in memory-impaired aged rats than that in memory-normal rats. In cerebellum, both nNOS and eNOS mRNA content appeared significantly reduced in memory-impaired aged rats than that in young rats and memory normal aged rats. In frontal cortex, nNOS mRNA content had no significant change in all three groups; but eNOS mRNA content was decreased in both memory-normal aged rats and impaired aged rats in comparison to that in young rats, memory-impaired aged rats reduced more significantly. mRNA content changes appeared differences between nNOS and eNOS: nNOS is dominate in hippocampus, eNOS is dominate in frontal cortex, nNOS and eNOS co-operate in cerebellum. CONCLUSION:Occurring of aged memory impairment may be related with decreased cNOS gene expression in some brain area.
, 百拇医药
MeSH Aging; Memory; Nitric oxide synthase; Gene expression; Rats
学习记忆减退是脑衰老的重要表现之一,其神经机制尚不清楚。现有的研究资料表明衰老时一些脑区NO神经元形态和代谢呈现退行性改变[1~3];NO对学习记忆的作用主要是在长时程增强作用(long-term potentiation, LTP)和长时程抑制作用(long-term depression,LTD的形成中起逆向信使的作用。LTP和LTD被认为是研究突触传递可塑性的模式。大量的实验表明记忆保持好的动物其LTP效应增大显著;影响学习和记忆的因素往往影响LTP,同时影响LTP的因素或药物也能影响学习和记忆过程。因此LTP是目前公认的学习记忆的神经基础。NO也可诱导小脑产生LTD[4]。
本文用Morris水迷宫建立老年记忆减退大鼠模型,用分子生物学方法探索老年记忆减退时NO的变化规律,为最近提出的诱导NO的生成治疗老年记忆减退以及选择NOS类型提供进一步的理论依据。
, 百拇医药
材料和方法
一、实验动物:
SD雄性大鼠, 由本校动物中心提供。老年鼠(24 月龄)40只, 日夜交替分笼饲养8个月, 青年鼠(3月龄)20只, 在同样环境下饲养1个月。
二、方法:
(一)Morris 水迷宫行为检测参照文献[5]进行。
(二)mRNA含量的半定量测定: 1.组织总RNA制备参照文献[6]。 2.反转录和定量PCR。所用引物根据Bredt等[7]发表的大鼠小脑NOS cDNA序列和eNOS cDNA序列[8]设计合成, 选择同源性低的区域, 并同时避开与iNOS高同源性区域, 保证扩增产物的高度特异性。扩增nNOS cDNA序列的2463-2943(480 bp)片段和eNOS cDNA序列的2331-3143(813bp) 片段。
, 百拇医药
反转录:取5.0 μg RNA,65℃变性3 min,依次加入0.8 mmol/L dNTPs,5.0 μmol/L Oligo(dT)12-18,8.0 mmol/L Mg2+,10.0 mmol/L DTT,RNasin 10U,5×buffer 4.0 mL,M-MLV 200 U或AMV 5 U,总反应体积20 μL。在37℃(M-MLV)或42℃(AMV)反应60 min,99℃ 5 min终止反应。
PCR:取2.0 μL反转录液(cDNA),加入0.2 mmol/L dNTPs,1.0 μmol/L寡核苷酸引物,1.5 mmol/L Mg2+,10×buffer 2.0 μL,Taq DNA聚合酶1.0 U,总反应体积20 μL。最后加入20 μL石蜡油。PCR反应条件为94℃ 2 min,然后进行下列循环:94 ℃ 60 s,55℃ 60 s,72 ℃ 90 s,共35次循环,末次循环置72℃ 5 min。
, 百拇医药
半定量RT-PCR方法的规范:(1)设立β-actin 作为内对照,扩增产物大小为492 bp,由于内对照引物与NOS引物之间可能存在相互抑制和干扰且大小接近,两个系统在PCR时分开进行;(2) 定量分析中,起始RNA量相同(均为5.0 μg),三组样本反转录和PCR条件完全一致,结果重复性良好;(3)电泳检测时同一脑区3组之间在同一凝胶上进行,使各样本之间具有可比性。扩增产物电泳后用IBAS Rel 2.0型全自动图像分析系统定量, 单位用积分光密度( ODI, integrated optical density)表示, 积分光密度为平均光密度与条带面积的乘积。
(三)所得数据均用x±s表示,用ANOVA统计分析软件进行单因素方差分析,方差齐,用t检验,方差不齐,则用秩和检验进行统计。
结果
一、水迷宫行为测试:
, 百拇医药 (一)行为分组结果:测得青年组平均逃避潜伏期为(13.8±10.6) s, 老年组平均逃避潜伏期为(34.4±9.5) s,其中老年学习记忆正常组是:(21.7±5.1) s; 老年学习记忆减退组为:(45.6±4.2) s。以青年组平均逃避潜伏期的95%(31.2 s)和99%(38.5s)正常值的上限值为界, 潜伏期大于99%上限值的老年大鼠为老年学习记忆减退大鼠(15只), 小于95%上限值的老年学习记忆正常大鼠(20只), 潜伏期在两上限值之间的鼠剔除不用(5只)。
(二) 3组大鼠空间探索试验中的游泳轨迹:青年组和老年正常组大鼠的游泳轨迹主要集中在平台象限, 老年记忆减退组的游泳轨迹呈随机分布。利用数字电脑系统计算大鼠在平台所在象限的游泳距离占总距离的百分比, 青年组和老年记忆正常组分别为67.7%和50.2%, t检验明显高于非平台象限(P<0.01); 老年记忆减退鼠为28.7%, 与非平台象限无显著差异(P>0.05)。(图1)。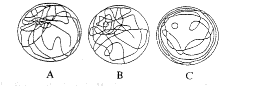
, 百拇医药
Fig 1 Swim path of rats in Morris water maze A,B and C represent the typical swim path of young, memory-normal and memory-impaired aged rats respectively 图1 大鼠在Morris水迷宫中的游泳轨迹
二、老年记忆减退大鼠nNOS 和eNOS mRNA含量变化(表2):
表1 老年记忆减退大鼠脑nNOS 和eNOS mRNA含量变化
Tab 1 Change of nNOS and eNOS mRNA content in brain of memory-impaired aged rats(x±s)
NOS types
, 百拇医药
Regions
GroupⅠ
GroupⅡ
Group Ⅲ
nNOS
Hippocampus
103±12
67±10*
30±6*#
Cerebellum
124±28
112±18
, http://www.100md.com
81±21*#
Frontal cortex
37±11
38±8
36±13
eNOS
Hippocampus
82±8
52±8*
54±8*
Cerebellum
, 百拇医药 100±12
103±12
52±9*#
Frontal cortex
89±13
59±10*
20±10*#
GroupⅠ(Young rats,n=10);GroupⅡ(Memory-normal aged rats,n=10); GroupⅢ(Memory-impaired aged rats,n=8)
* P<0.05, vs group 1; # P<0.05, vs group 2
, 百拇医药
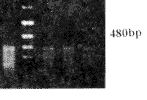
海马组织老年记忆正常组和记忆减退组同青年组相比, nNOS mRNA含量显著降低, 老年记忆减退组比老年正常组降低更为显著; 在小脑,同青年组相比, 老年记忆正常组nNOS mRNA含量无明显变化, 老年记忆减退组则显著下降; 额叶组织三组之间nNOS mRNA含量无显著变化(图2A)。
海马组织老年记忆正常组和记忆减退组同青年组相比, eNOS mRNA含量显著低下, 但老年记忆正常组和减退组之间无差异; 小脑组织的变化和nNOS一致;额叶组织eNOS mRNA含量和nNOS明显不同, 老年记忆正常组比青年组显著低下, 老年记忆减退组比老年正常组又显著低下(图2B)。
在相同条件下,用β-actin 作为内对照进行RT-PCR,结果表明3组(青年组、老年记忆正常组和记忆减退组)大鼠在同一脑区(海马、小脑或额叶)的mRNA含量无显著变化(图3)。β-actin作为常用的保守基因,其基因表达一般不受机体状态的影响而稳定表达,本研究发现衰老和记忆衰减对β-actin的表达影响不明显,此时NOS表达的差异可以说明体内的真实代谢变化。


, 百拇医药
Fig 2A Agarose gel electrophoresis of RT-PCR products of nNOS in hippocampus of rats
M:DNA markers(1543,994,695,515,377,237);1~3:Young rats; 4~6:Memory-normal aged rats;7~9:Memory-impaired aged rats
图2A 大鼠海马组织nNOS RT-PCR产物琼脂糖凝胶电泳图谱
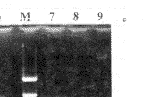


, http://www.100md.com
Fig 2B Agarose gel electrophoresis of RT-PCR products of eNOS in frontal cortex of rats
M:DNA markers(1543,994,695,515,377,237);1~3:Young rats;4~6:Memory-normal aged rats;7~9:Memory-impaired aged rats
图2B 大鼠额叶组织eNOS RT-PCR产物琼脂糖凝胶电泳图谱
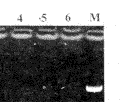


, 百拇医药
Fig 3 Agarose gel electrophoresis of RT-PCR products of β-actin in hippocampus of rats
M:DNA markers(1543,994,695,515,377,237);1~2:Young rats; 3~4:Memory-normal aged rats;5~6:Memory-impaired aged rats OPTDI are 94,101,90,96,92,97 respectively
图3 大鼠海马组织β-actin RT-PCR产物琼脂糖凝胶电泳图谱
讨论
NO在学习记忆功能中发挥重要的作用。老龄大鼠大脑皮质和纹状体NOS神经元数目明显减少[1]。Alzheimer's病人颞叶皮层和杏仁核 NOS 神经元及突起显著皱缩,海马分子层内侧1/3缺少NOS 神经元,整个海马分子层 NOS 神经元减少18%~30%[2]。 Mollace 等发现衰老时海马NOS活性只有青年鼠的33%,而小脑和大脑皮质NOS活性未见显著下降[3]。以上研究说明衰老时一些脑区NOS神经元形态和NO代谢呈现退行性改变。
, 百拇医药
从分子水平对老年记忆减退时NOS的变化的研究尚未见报道。本文利用Morris水迷宫根据老年大鼠空间记忆能力的差异区分老年记忆减退鼠和老年记忆正常鼠,突出了记忆因素的作用。从老年大鼠潜伏期动态观察的结果可见相同年龄的老年大鼠有近三分之二的大鼠潜伏期接近青年鼠,即此部分老年大鼠在水迷宫中定位平台的学习获得过程较快,接近青年鼠,属学习记忆能力正常大鼠,约三分之一的老年大鼠潜伏期远远大于青年鼠和老年正常鼠,属学习记忆能力减退大鼠。
本文同时检测了老年记忆减退时nNOS和eNOS mRNA含量的变化。结果发现老年记忆减退组海马、小脑nNOS mRNA 表达下降,而额叶下降不明显;eNOS mRNA的表达则在小脑和额叶显著下降,海马无明显改变。提示在衰老和记忆减退的发生中,大脑皮质部位起作用的主要是eNOS,在海马组织中主要与nNOS有关,而在小脑则两种都起作用。
NO对学习记忆的作用主要是参与LTP和LTD的形成。 LTP是研究学习记忆机制的一种模式,被认为是记忆形成的神经基础。NO从突触后释放通过扩散作用于突触前膜,起逆向信使的作用,增加突触前谷氨酸的释放,使突触前突触后共同参与形成LTP。用 NOS抑制剂N-硝基精氨酸能阻断大鼠海马LTP的形成,同时在行为实验中发现空间记忆、工作记忆和嗅觉记忆均受损[9]。小脑NO释放可以诱发LTD,外源性NO也可引起小脑切片上产生LTD;血红蛋白和N-硝基精氨酸则可阻断LTD的产生[10],说明内源性NO是小脑可塑性变化的基础。本研究发现老年记忆减退大鼠海马、小脑这些记忆相关脑区cNOS mRNA表达下降,更加明确提示老年记忆减退的发生可能与NO生成减少有关,为诱导NO的生成治疗老年记忆减退提供了进一步的理论依据。但如何在基因水平调控NOS的生成种类和含量仍是今后的重要研究方向。
, http://www.100md.com
*卫生部基金资助(No.962058)
参考文献
1 Noda Y, Yamada K, Nabeshima T. Role of nitric oxide in the effect of aging on spatial memory in rats. Behav Brain Res,1997, 83(1-2):153.
2 Unger JW, Lange W. NADPH-diaphorase-positive cell population in the human amygdala and temporal cortex:neuroanatomy, peptidergic characteristics and aspects of aging and Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neurophathol Berl, 1992,83(67):636.
, 百拇医药
3 Mollace V, Rodino P, Massoud R, et al. Aged-dependent changes of NO synthase activity in rat brain. Biochem Biophy Res Commun,1995,215(3):822.
4 O'Dell TJ, Hawkins RD, Kandel ER, et al. Test of the roles of two diffusible substances in long-term potentiation: evidence for nitric oxide as a possible early retrograde messenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,1991,88:11 285.
5 Hong An, Yao Zhibin, Gu Yaoming,et al. Changes of hippocampal synaptophysin in aged learning and memory deficits rat(in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Anatomica Sinica, 1996, 279(2):164.
, 百拇医药
6 Chomezynski P,Sacchi N.Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem, 1987,162:156.
7 Gao Guoquan,Yao Zhibin, Ma Jianquan. The demonstration of mRNA expression of NOS in rat brain , liver and prostate (in Chinese with English abstract). Academic Journal of Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, 1997,18(supplement):25.
8 Vjize K ,Yuen J,Hogarth L,et al.Localization and regulation of endothelial NO synthase mRNA expression in rat kidney. Am J Physiol, 1994,267(36):F269 .
, http://www.100md.com
9 Bohme GA,Bon C,Lemaire M,et al.Altered synaptic plasticity and memory formation in nitric oxide synthase inhibitor-treated rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,1993,90:9 191 .
10 Shibiki K,Okada D.Endogenous nitric oxide release required for long-term synaptic depression in the cerebellem. Nature,1991,349:326 .
(1998年10月23日收稿,1999年3月19日修回), 百拇医药
单位:高国全 马涧泉:生化教研室;姚志彬:神经生物学研究室;张静:生理学教研室;中山医科大学(广州 510089)
关键词:;衰老;记忆;一氧化氮合酶;基因表达;大鼠
老年大鼠空间记忆减退与cNOS基因表达变化 摘 要 目的:从基因表达角度研究原生型NOS(cNOS, 包括神经元型nNOS 和内皮型eNOS)与老年记忆减退发生的关系。方法:用Morris水迷宫将老年大鼠筛选为记忆正常和记忆减退两组,以老年记忆减退大鼠作为老年记忆减退模型; 用半定量反转录-聚合酶链反应(RT-PCR)方法测定 nNOS和eNOS的mRNA含量。结果:(1) 海马组织中老年记忆正常组和老年记忆减退组较青年组 nNOS 和eNOS mRNA含量均下降,nNOS以记忆减退组下降更为显著; (2)小脑组织中老年记忆减退组nNOS和eNOSmRNA含量的下降与老年记忆正常组和青年组均有显著差异。(3)额叶组织nNOS mRNA含量三组之间均无显著差异; eNOSmRNA含量老年记忆正常组和老年记忆减退组较青年组均下降,以记忆减退组下降更为显著。结论:老年记忆减退的发生可能与有关脑区cNOS基因表达下降有关。
, 百拇医药
Changes of nitric oxide synthase activity and constitutive NOS gene
expression in the brain of memory-impaired aged rats
GAO Guo-Quan1, YAO Zhi-Bin2, ZHANG Jing3, MA Jian-Quan1
1 Department of Biochemistry, 2 Department of Neurobiology, 3 Department of Physiology,Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences,Guangzhou,(510089)
, 百拇医药
Abstract AIM: The relationship between nitric oxide(NO) and aged memory impairment was investigated to study the mechanism of aged memory impairment and find out a new method of treatment.METHODS: Aged rats were divided into aged memory-impaired group and aged memory-normal group using Morris water maze. The reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction(RT-PCR) method was used for semi-quantity determining of nNOS and eNOS mRNA content. RESULTS: In hippocampus, eNOS and nNOS mRNA content were decreased in both memory-normal aged rats and memory-impaired aged rats in comparison to that in young rats; nNOS mRNA content but eNOS reduced more significantly in memory-impaired aged rats than that in memory-normal rats. In cerebellum, both nNOS and eNOS mRNA content appeared significantly reduced in memory-impaired aged rats than that in young rats and memory normal aged rats. In frontal cortex, nNOS mRNA content had no significant change in all three groups; but eNOS mRNA content was decreased in both memory-normal aged rats and impaired aged rats in comparison to that in young rats, memory-impaired aged rats reduced more significantly. mRNA content changes appeared differences between nNOS and eNOS: nNOS is dominate in hippocampus, eNOS is dominate in frontal cortex, nNOS and eNOS co-operate in cerebellum. CONCLUSION:Occurring of aged memory impairment may be related with decreased cNOS gene expression in some brain area.
, 百拇医药
MeSH Aging; Memory; Nitric oxide synthase; Gene expression; Rats
学习记忆减退是脑衰老的重要表现之一,其神经机制尚不清楚。现有的研究资料表明衰老时一些脑区NO神经元形态和代谢呈现退行性改变[1~3];NO对学习记忆的作用主要是在长时程增强作用(long-term potentiation, LTP)和长时程抑制作用(long-term depression,LTD的形成中起逆向信使的作用。LTP和LTD被认为是研究突触传递可塑性的模式。大量的实验表明记忆保持好的动物其LTP效应增大显著;影响学习和记忆的因素往往影响LTP,同时影响LTP的因素或药物也能影响学习和记忆过程。因此LTP是目前公认的学习记忆的神经基础。NO也可诱导小脑产生LTD[4]。
本文用Morris水迷宫建立老年记忆减退大鼠模型,用分子生物学方法探索老年记忆减退时NO的变化规律,为最近提出的诱导NO的生成治疗老年记忆减退以及选择NOS类型提供进一步的理论依据。
, 百拇医药
材料和方法
一、实验动物:
SD雄性大鼠, 由本校动物中心提供。老年鼠(24 月龄)40只, 日夜交替分笼饲养8个月, 青年鼠(3月龄)20只, 在同样环境下饲养1个月。
二、方法:
(一)Morris 水迷宫行为检测参照文献[5]进行。
(二)mRNA含量的半定量测定: 1.组织总RNA制备参照文献[6]。 2.反转录和定量PCR。所用引物根据Bredt等[7]发表的大鼠小脑NOS cDNA序列和eNOS cDNA序列[8]设计合成, 选择同源性低的区域, 并同时避开与iNOS高同源性区域, 保证扩增产物的高度特异性。扩增nNOS cDNA序列的2463-2943(480 bp)片段和eNOS cDNA序列的2331-3143(813bp) 片段。
, 百拇医药
反转录:取5.0 μg RNA,65℃变性3 min,依次加入0.8 mmol/L dNTPs,5.0 μmol/L Oligo(dT)12-18,8.0 mmol/L Mg2+,10.0 mmol/L DTT,RNasin 10U,5×buffer 4.0 mL,M-MLV 200 U或AMV 5 U,总反应体积20 μL。在37℃(M-MLV)或42℃(AMV)反应60 min,99℃ 5 min终止反应。
PCR:取2.0 μL反转录液(cDNA),加入0.2 mmol/L dNTPs,1.0 μmol/L寡核苷酸引物,1.5 mmol/L Mg2+,10×buffer 2.0 μL,Taq DNA聚合酶1.0 U,总反应体积20 μL。最后加入20 μL石蜡油。PCR反应条件为94℃ 2 min,然后进行下列循环:94 ℃ 60 s,55℃ 60 s,72 ℃ 90 s,共35次循环,末次循环置72℃ 5 min。
, 百拇医药
半定量RT-PCR方法的规范:(1)设立β-actin 作为内对照,扩增产物大小为492 bp,由于内对照引物与NOS引物之间可能存在相互抑制和干扰且大小接近,两个系统在PCR时分开进行;(2) 定量分析中,起始RNA量相同(均为5.0 μg),三组样本反转录和PCR条件完全一致,结果重复性良好;(3)电泳检测时同一脑区3组之间在同一凝胶上进行,使各样本之间具有可比性。扩增产物电泳后用IBAS Rel 2.0型全自动图像分析系统定量, 单位用积分光密度( ODI, integrated optical density)表示, 积分光密度为平均光密度与条带面积的乘积。
(三)所得数据均用x±s表示,用ANOVA统计分析软件进行单因素方差分析,方差齐,用t检验,方差不齐,则用秩和检验进行统计。
结果
一、水迷宫行为测试:
, 百拇医药 (一)行为分组结果:测得青年组平均逃避潜伏期为(13.8±10.6) s, 老年组平均逃避潜伏期为(34.4±9.5) s,其中老年学习记忆正常组是:(21.7±5.1) s; 老年学习记忆减退组为:(45.6±4.2) s。以青年组平均逃避潜伏期的95%(31.2 s)和99%(38.5s)正常值的上限值为界, 潜伏期大于99%上限值的老年大鼠为老年学习记忆减退大鼠(15只), 小于95%上限值的老年学习记忆正常大鼠(20只), 潜伏期在两上限值之间的鼠剔除不用(5只)。
(二) 3组大鼠空间探索试验中的游泳轨迹:青年组和老年正常组大鼠的游泳轨迹主要集中在平台象限, 老年记忆减退组的游泳轨迹呈随机分布。利用数字电脑系统计算大鼠在平台所在象限的游泳距离占总距离的百分比, 青年组和老年记忆正常组分别为67.7%和50.2%, t检验明显高于非平台象限(P<0.01); 老年记忆减退鼠为28.7%, 与非平台象限无显著差异(P>0.05)。(图1)。

, 百拇医药
Fig 1 Swim path of rats in Morris water maze A,B and C represent the typical swim path of young, memory-normal and memory-impaired aged rats respectively 图1 大鼠在Morris水迷宫中的游泳轨迹
二、老年记忆减退大鼠nNOS 和eNOS mRNA含量变化(表2):
表1 老年记忆减退大鼠脑nNOS 和eNOS mRNA含量变化
Tab 1 Change of nNOS and eNOS mRNA content in brain of memory-impaired aged rats(x±s)
NOS types
, 百拇医药
Regions
GroupⅠ
GroupⅡ
Group Ⅲ
nNOS
Hippocampus
103±12
67±10*
30±6*#
Cerebellum
124±28
112±18
, http://www.100md.com
81±21*#
Frontal cortex
37±11
38±8
36±13
eNOS
Hippocampus
82±8
52±8*
54±8*
Cerebellum
, 百拇医药 100±12
103±12
52±9*#
Frontal cortex
89±13
59±10*
20±10*#
GroupⅠ(Young rats,n=10);GroupⅡ(Memory-normal aged rats,n=10); GroupⅢ(Memory-impaired aged rats,n=8)
* P<0.05, vs group 1; # P<0.05, vs group 2
, 百拇医药
海马组织老年记忆正常组和记忆减退组同青年组相比, nNOS mRNA含量显著降低, 老年记忆减退组比老年正常组降低更为显著; 在小脑,同青年组相比, 老年记忆正常组nNOS mRNA含量无明显变化, 老年记忆减退组则显著下降; 额叶组织三组之间nNOS mRNA含量无显著变化(图2A)。
海马组织老年记忆正常组和记忆减退组同青年组相比, eNOS mRNA含量显著低下, 但老年记忆正常组和减退组之间无差异; 小脑组织的变化和nNOS一致;额叶组织eNOS mRNA含量和nNOS明显不同, 老年记忆正常组比青年组显著低下, 老年记忆减退组比老年正常组又显著低下(图2B)。
在相同条件下,用β-actin 作为内对照进行RT-PCR,结果表明3组(青年组、老年记忆正常组和记忆减退组)大鼠在同一脑区(海马、小脑或额叶)的mRNA含量无显著变化(图3)。β-actin作为常用的保守基因,其基因表达一般不受机体状态的影响而稳定表达,本研究发现衰老和记忆衰减对β-actin的表达影响不明显,此时NOS表达的差异可以说明体内的真实代谢变化。




, 百拇医药
Fig 2A Agarose gel electrophoresis of RT-PCR products of nNOS in hippocampus of rats
M:DNA markers(1543,994,695,515,377,237);1~3:Young rats; 4~6:Memory-normal aged rats;7~9:Memory-impaired aged rats
图2A 大鼠海马组织nNOS RT-PCR产物琼脂糖凝胶电泳图谱




, http://www.100md.com
Fig 2B Agarose gel electrophoresis of RT-PCR products of eNOS in frontal cortex of rats
M:DNA markers(1543,994,695,515,377,237);1~3:Young rats;4~6:Memory-normal aged rats;7~9:Memory-impaired aged rats
图2B 大鼠额叶组织eNOS RT-PCR产物琼脂糖凝胶电泳图谱




, 百拇医药
Fig 3 Agarose gel electrophoresis of RT-PCR products of β-actin in hippocampus of rats
M:DNA markers(1543,994,695,515,377,237);1~2:Young rats; 3~4:Memory-normal aged rats;5~6:Memory-impaired aged rats OPTDI are 94,101,90,96,92,97 respectively
图3 大鼠海马组织β-actin RT-PCR产物琼脂糖凝胶电泳图谱
讨论
NO在学习记忆功能中发挥重要的作用。老龄大鼠大脑皮质和纹状体NOS神经元数目明显减少[1]。Alzheimer's病人颞叶皮层和杏仁核 NOS 神经元及突起显著皱缩,海马分子层内侧1/3缺少NOS 神经元,整个海马分子层 NOS 神经元减少18%~30%[2]。 Mollace 等发现衰老时海马NOS活性只有青年鼠的33%,而小脑和大脑皮质NOS活性未见显著下降[3]。以上研究说明衰老时一些脑区NOS神经元形态和NO代谢呈现退行性改变。
, 百拇医药
从分子水平对老年记忆减退时NOS的变化的研究尚未见报道。本文利用Morris水迷宫根据老年大鼠空间记忆能力的差异区分老年记忆减退鼠和老年记忆正常鼠,突出了记忆因素的作用。从老年大鼠潜伏期动态观察的结果可见相同年龄的老年大鼠有近三分之二的大鼠潜伏期接近青年鼠,即此部分老年大鼠在水迷宫中定位平台的学习获得过程较快,接近青年鼠,属学习记忆能力正常大鼠,约三分之一的老年大鼠潜伏期远远大于青年鼠和老年正常鼠,属学习记忆能力减退大鼠。
本文同时检测了老年记忆减退时nNOS和eNOS mRNA含量的变化。结果发现老年记忆减退组海马、小脑nNOS mRNA 表达下降,而额叶下降不明显;eNOS mRNA的表达则在小脑和额叶显著下降,海马无明显改变。提示在衰老和记忆减退的发生中,大脑皮质部位起作用的主要是eNOS,在海马组织中主要与nNOS有关,而在小脑则两种都起作用。
NO对学习记忆的作用主要是参与LTP和LTD的形成。 LTP是研究学习记忆机制的一种模式,被认为是记忆形成的神经基础。NO从突触后释放通过扩散作用于突触前膜,起逆向信使的作用,增加突触前谷氨酸的释放,使突触前突触后共同参与形成LTP。用 NOS抑制剂N-硝基精氨酸能阻断大鼠海马LTP的形成,同时在行为实验中发现空间记忆、工作记忆和嗅觉记忆均受损[9]。小脑NO释放可以诱发LTD,外源性NO也可引起小脑切片上产生LTD;血红蛋白和N-硝基精氨酸则可阻断LTD的产生[10],说明内源性NO是小脑可塑性变化的基础。本研究发现老年记忆减退大鼠海马、小脑这些记忆相关脑区cNOS mRNA表达下降,更加明确提示老年记忆减退的发生可能与NO生成减少有关,为诱导NO的生成治疗老年记忆减退提供了进一步的理论依据。但如何在基因水平调控NOS的生成种类和含量仍是今后的重要研究方向。
, http://www.100md.com
*卫生部基金资助(No.962058)
参考文献
1 Noda Y, Yamada K, Nabeshima T. Role of nitric oxide in the effect of aging on spatial memory in rats. Behav Brain Res,1997, 83(1-2):153.
2 Unger JW, Lange W. NADPH-diaphorase-positive cell population in the human amygdala and temporal cortex:neuroanatomy, peptidergic characteristics and aspects of aging and Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neurophathol Berl, 1992,83(67):636.
, 百拇医药
3 Mollace V, Rodino P, Massoud R, et al. Aged-dependent changes of NO synthase activity in rat brain. Biochem Biophy Res Commun,1995,215(3):822.
4 O'Dell TJ, Hawkins RD, Kandel ER, et al. Test of the roles of two diffusible substances in long-term potentiation: evidence for nitric oxide as a possible early retrograde messenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,1991,88:11 285.
5 Hong An, Yao Zhibin, Gu Yaoming,et al. Changes of hippocampal synaptophysin in aged learning and memory deficits rat(in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Anatomica Sinica, 1996, 279(2):164.
, 百拇医药
6 Chomezynski P,Sacchi N.Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem, 1987,162:156.
7 Gao Guoquan,Yao Zhibin, Ma Jianquan. The demonstration of mRNA expression of NOS in rat brain , liver and prostate (in Chinese with English abstract). Academic Journal of Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, 1997,18(supplement):25.
8 Vjize K ,Yuen J,Hogarth L,et al.Localization and regulation of endothelial NO synthase mRNA expression in rat kidney. Am J Physiol, 1994,267(36):F269 .
, http://www.100md.com
9 Bohme GA,Bon C,Lemaire M,et al.Altered synaptic plasticity and memory formation in nitric oxide synthase inhibitor-treated rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,1993,90:9 191 .
10 Shibiki K,Okada D.Endogenous nitric oxide release required for long-term synaptic depression in the cerebellem. Nature,1991,349:326 .
(1998年10月23日收稿,1999年3月19日修回), 百拇医药