肺癌患者手术前后血清p53抗体的动态变化及其临床意义
作者:赵峰 周清华 王兰兰 伍伫 刘伦旭 王允 刘静 冯伟华
单位:赵峰 周清华 王兰兰 伍伫 刘伦旭 王允 刘静 冯伟华(610041 成都,华西医科大学附属第一医院胸心外科)
关键词:肺肿瘤;p53基因;血清p53抗体;酶联免疫吸附法
中国肺癌杂志000404
【摘要】 目的 探讨肺癌患者血清p53抗体与临床病理特征之间的关系,以及手术后p53抗体的动态变化规律。方法 采用酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)分别于术前1天、术后7、30、90天动态检测120例肺癌患者血清p53抗体,并以30例肺部良性疾病患者和120例正常健康人作对照。结果 肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平和阳性率均明显高于肺部良性疾病患者和正常人(P<0.05),而正常人与肺部良性疾病患者间无显著性差异(P>0.05)。肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平和阳性率均与肺癌细胞分化程度和病期有密切关系(P<0.01或P<0.05)。在行根治性切除术后,肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平逐渐降低,术后30天左右可降至正常人水平;而行姑息性切除者,术后30天血清p53抗体水平不能降至正常水平;如术后有肺癌复发和转移者,术后血清p53抗体水平可再度升高。结论 检测血清p53抗体水平有助于肺部良恶性疾病的诊断;手术前后动态测定肺癌患者血清p53抗体的变化规律,有助于判断疗效,监测预后和指导肺癌术后的综合治疗。
, http://www.100md.com
【中图分类号】 R730.3
Pre- and post-operative sequential changes of serum p53 antibodies and clinical significance in patients with lung cancer
ZHAO Feng ZHOU Qinghua WANG Lanlan WU Zhu LIU Lunxu WANG Yu LIU Jing FENG Weihua (Department of Thoracocardiac Surgery, The First University Hospital, West China University of Medical Sciences, Chengdu, Sichuan 610041, P.R.China)
【Abstract】 Objective To explore the relationship between serum p53 antibodies and clinicopathological characteristics in patients with lung cancer and to investigate sequential changing regularity of serum p53 antibodies after surgical resection. Methods The serum p53 antibody level was detected in 120 patients with lung cancer, and in 30 patients with benign pulmonary lesion and 120 healthy adults as control by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The blood samples were collected on the day before operation and on the 7th, 30th and 90th days postoperatively. Results The level and positive rate of serum p53 antibodies in patients with lung cancer were significantly higher than those in patients with benign pulmonary disease and normal individuals (P<0.05), but there was no significant difference between patients with benign pulmonary disease and normal individuals (P>0.05). The level and positive rate of pre-operative serum p53 antibodies in patients with lung cancer were closely related to cell differentiation and stage of lung cancer (P<0.01 or P<0.05). The level of serum p53 antibodies decreased gradually in patients with lung cancer underwent radical removal of the cancer, and completely returned to the normal level around the 30th day after operation, but the level of serum p53 antibodies in patients with lung cancer underwent palliative operation didn't reduce to the normal level on the 30th day after operation. It would increase again when tumor metastasis or recurrence developed. Conclusion Detection of serum p53 antibodies is helpful to defferentiate benign from malignant pulmonary diseases. Monitoring of sequential change of pre- and post-operative serum p53 antibodies in patients with lung cancer is helpful to evaluate response to treatment, to judge prognosis and to guide the comprehensive treatment of patients with lung cancer after operation.
, 百拇医药
【Key Words】 Lung neoplasms p53 gene Serum p53 antibodies ELISA
近年的研究发现,肺癌的发生、发展是一个多基因参与的复杂过程,其中p53基因结构和功能异常在肺癌的发生、发展过程中起重要作用[1]。分析p53基因变化可采用分子生物学、免疫组化、血清学等多种方法[2],前两种方法由于操作复杂和繁琐不易在临床推广,而血清学方法具有操作简便、重复性好,不需肿瘤标本等优点,目前越来越受到广泛重视。本研究应用酶链免疫吸附试验(enzyme linked immunosorbent assay, ELISA)法检测120例肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平,并与肺良性疾病患者和正常健康人作比较,同时对肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平进行手术前后的动态观察,以探讨检测肺癌患者血清p53抗体的临床意义。
1 材料与方法
, 百拇医药
1.1 检测对象 正常组120例,均为本院门诊作健康体检者。男60例,女60例,年龄21~62岁,平均38.7岁。肺良性疾病组30例,男21例,女9例,年龄20~65岁,平均45.3岁,所有病例均有术后病理诊断,其中炎性假瘤14例,结核瘤10例,肺囊肿6例。
肺癌组120例,男98例,女22例;年龄22~74岁,平均56.4岁;所有病例均有术后病理诊断,其中鳞癌60例,腺癌36例,腺鳞癌14例,未分化癌10例(包括小细胞癌9例,大细胞癌1例)。病理分期采用国际抗癌联盟(UICC)1997年修订的分期标准,其中Ⅰ期10例,Ⅱ期32例,Ⅲ期75例,Ⅳ期3例。根治性肺癌切除术100例,姑息性肺癌切除术20例。
1.2 标本的收集 肺癌组分别于术前1天、术后7、30和90天时抽取静脉血2ml。肺良性疾病组分别于术前1天、术后7天抽取静脉血2ml。正常组清晨空腹采集静脉血2ml。上述标本当日离心分离血清,置于-20℃冰箱保存备测。
, 百拇医药
1.3 检测方法 应用法国Immunotech公司anti-p53 ELISA试剂盒,操作严格按说明书进行:洗涤重组p53蛋白或质控蛋白包被的聚苯乙烯微量反应板,将稀释的样本和质控各100ml分别加入到相应反应板微孔内,20~25℃震荡温育1小时,取出后洗涤4次吹干,加入过氧化物酶标记的抗人IgG抗体反应液100ml,20~25℃震荡温育1小时,再次洗涤4次后吹干,加入酶反应底物TMB100ml,室温避光反应10分钟,加入100ml H2SO4终止酶反应。用酶标仪测定450nm波长吸光度。p53抗体浓度用两个不同参数确定:
指数(index)=(样品p53蛋白净吸光值-质控蛋白净吸光值)/(低值阳性质控p53蛋白净吸光值-质控蛋白净吸光值)
吸收率(ratio)=(样品p53蛋白净吸光值)/(质控蛋白净吸光值)
1.4 统计学处理 本实验数据采用t检验、F检验、χ2检验、Logistic回归分析进行统计分析,在华西医科大学统计教研室采用SPSS7.5系统软件处理。
, http://www.100md.com
2 结果
2.1 不同组别血清p53抗体指数和吸收率的比较 正常人、肺良性疾病患者和肺癌患者血清p53抗体指数和吸收率经F检验有显著性差异(P<0.05);两两比较:肺癌组与正常组和肺良性疾病组间均有显著性差异(P<0.05),正常组与肺良性疾病组间无显著性差异(P>0.05)(表1)。
表1 肺癌组与正常组、肺良性疾病组间血清
p53抗体指数和吸收率的比较
Tab 1 Comparison of index and ratio of serum p53 antibodies
among patients with lung cancer, benign pulmonary diseases
, http://www.100md.com
and normal individuals Groups
n
Index
Ratio
Normal
120
0.2358±0.1539
1.0383±0.2275
Benign
30
0.2567±0.1127
1.1276±0.4768
, 百拇医药
Cancer
120
1.6475±0.5714
3.0191±0.6932
2.2 术前不同组别血清p53抗体阳性率的比较 120例正常人血清p53抗体指数的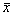 =0.2358,s=0.1539,吸收率的
=0.2358,s=0.1539,吸收率的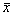 =1.0383,s=0.2275,以超过
=1.0383,s=0.2275,以超过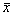 +1.645s为判断阳性标准,即指数>0.4890和吸收率>1.4125,分别判定指数和吸收率阳性,当二者同为阳性,即判定为p53抗体阳性。肺良性疾病患者和正常健康人无一例阳性。120例肺癌患者中有26例血清p53抗体阳性,阳性率为21.7%。三组间经χ2检验,有非常显著差异(P<0.01);两两比较,正常组与肺良性疾病组间无显著性差异(P>0.05),肺癌组与正常组和肺良性疾病组间均有非常显著性差异(P<0.01)。
+1.645s为判断阳性标准,即指数>0.4890和吸收率>1.4125,分别判定指数和吸收率阳性,当二者同为阳性,即判定为p53抗体阳性。肺良性疾病患者和正常健康人无一例阳性。120例肺癌患者中有26例血清p53抗体阳性,阳性率为21.7%。三组间经χ2检验,有非常显著差异(P<0.01);两两比较,正常组与肺良性疾病组间无显著性差异(P>0.05),肺癌组与正常组和肺良性疾病组间均有非常显著性差异(P<0.01)。
, http://www.100md.com
2.3 肺癌患者手术前后血清p53抗体的动态变化 手术前后不同时间的血清p53抗体指数、吸收率和阳性率经F检验和χ2检验有非常显著性差异(P<0.01);两两比较:术前与术后7、30与90天间比较,均无显著性差异(P>0.05),其余不同时间组间比较均有显著性差异(P<0.05或P<0.01)(图1、2)。
图1 肺癌患者手术前后血清p53抗体水平的动态变化
Fig 1 Pre- and post-operative sequential change of serum p53 antibodies in patients with lung cancer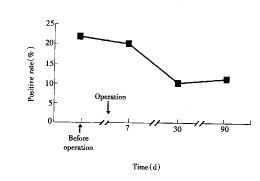
图2 肺癌患者手术前后血清p53抗体阳性率的动态变化
, 百拇医药
Fig 2 Pre- and post-operative sequential change of positive rate of serum p53 antibodies in patients with lung cancer
2.4 肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平与肺癌临床病理生理特征的关系 肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平与肿瘤分化程度、病理分期有密切关系(P值均<0.05),与肺癌组织类型,原发肿瘤大小、部位、淋巴结转移,患者性别、年龄、吸烟无明显关系(P>0.05)(表2)。
表2 肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平与临床病理生理特征的关系
Tab 2 The relationship between the level of serum p53 antibodies and clinical
pathophysiological characteristics in patients with lung cancer Groups
, http://www.100md.com
n
Index
Ratio
P value
P-TNM
Ⅰ+Ⅱ
42
0.2384±0.0675
1.3545±1.5627
P<0.01
Ⅲ+Ⅳ
78
2.4063±0.8978
, 百拇医药
4.0226±1.5365
Undifferentiated and poor-differentiated
63
2.6795±0.8714
4.0038±1.7651
P<0.01
Moderate-well differentiated
47
0.5870±0.1275
2.0029±0.8675
, 百拇医药 Size of the primary tumor
T1+T2
46
1.3672±0.6574
2.7048±1.2132
P>0.05
T3+T4
74
2.0624±0.9831
3.3317±0.4232
Lymph node metastasis
, 百拇医药
N0
59
1.1523±0.2345
2.4547±1.0456
P>0.05
N1-3
61
2.1265±0.6575
3.7072±0.2175
Histological classification
Undifferentiated cell carcinoma
, 百拇医药
10
1.5448±0.1678
2.5636±1.1048
Squamous cell carcinoma
Adenocarcinoma
60
36
1.8167±0.4578
1.0778±0.2153
3.3353±1.6578
2.5550±1.2345
, 百拇医药
P>0.05
Adeno-squamous cell carcinoma
14
1.1754±0.3750
2.1571±1.0321
Site of the tumor
Central type
62
2.0536±0.8761
3.3563±1.8972
P>0.05
, 百拇医药
Periphenal type
58
1.5872±0.3421
1.0163±1.8673
Age
<50
35
1.7192±0.6376
2.9322±0.6732
50~60
34
2.5331±1.0172
, 百拇医药
2.9322±0.6732
>60
51
1.6475±0.5671
3.2653±1.2959
P>0.05
Sex
Male
98
1.9454±0.5671
1.9865±1.2351
Female
, http://www.100md.com
22
1.303±0.0832
1.2345±0.4372
P>0.05
Smoking
Smoker
70
1.5709±0.1576
3.0345±0.8651
Non-smoker
50
2.4165±1.0231
, 百拇医药
3.8463±1.2321
P>0.05
2.5 肺癌患者血清p53抗体与肺癌临床病理生理特征相关性的多因素分析 Logistic回归分析结果表明,血清p53抗体阳性率与肺癌P-TNM分期呈正相关,与肺癌细胞分化程度呈负相关(P值均<0.05),与肿瘤组织学类型、部位、大小、淋巴结转移,患者的性别、年龄、吸烟史等无相关关系(P>0.05)(表3)。
表3 肺癌患者血清p53抗体阳性率与临床病理生理特征的Logistic回归分析
Tab 3 Logistic analysis on the relationship between positive rate of serum p53 antibodies and clinical pathophysiological characteristics in patients with lung cancer Variable
, http://www.100md.com
B
OR
95%CI for OR
P value
Age
0.0234
1.0237
0.9686--1.0819
0.4070
Lymph node metastasis
-0.4988
0.6073
, 百拇医药
0.3233--1.1406
0.1209
Stage
1.8389
6.2899
2.4839--15.9290
0.0252
Sex
-0.6230
0.5363
0.0861--3.3398
0.5043
, 百拇医药
Smoking
-0.0089
0.9912
0.9558--1.0279
0.6326
Tumor size
0.6427
1.9015
0.7859--4.6007
0.1540
Site
-0.0747
, 百拇医药
0.9280
0.3240--2.6575
0.8893
Differentiation
-4.1430
0.0159
0.0040--0.5979
0.0178
Histology
-0.4819
0.6176
0.3868--0.9860
, 百拇医药
0.672
3 讨论
p53基因突变是人类肿瘤最常见的基因改变[3],约50%~60%的非小细胞肺癌和80%小细胞肺癌有p53突变[4,5]。突变的结果导致异常的p53蛋白产生,其构象异常使半衰期延长至数小时,从而在细胞内聚积。聚积的突变型p53蛋白作为靶抗原引发机体的自身免疫应答,产生血清p53抗体[6]。国外学者应用ELISA方法在多种肿瘤患者血清中检测到p53抗体。并发现有较好的临床意义,有关手术前后动态检测肺癌患者血清p53抗体研究,国内外尚未见报道。
本研究观察到肺癌患者术前血清p53抗体指数和吸收率均明显高于肺部良性疾病患者和正常人(P<0.05),而正常人与肺部良性疾病患者间无显著差异(P>0.05)。120例肺癌中有26例p53抗体阳性,阳性率为21.7%,而30例肺部良性疾病患者和120例正常人无一例阳性者。本研究结果与文献报道结果一致,表明检测肺癌患者血清p53抗体,用于肺部良恶性疾病的诊断和鉴别诊断,具有较好的特异性,这一点在其它恶性肿瘤亦得到了证实[7]。
, 百拇医药
本研究还观察到p53抗体水平和阳性率均与肺癌细胞分化程度和病期有密切关系(P<0.01或P<0.05),而与肺癌的组织类型,原发肿瘤大小、部位、淋巴结转移,患者性别、年龄、吸烟无明显关系(P>0.05)。肿瘤组织分化程度差、临床分期晚的肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平明显升高,表明血清中p53抗体阳性是肺癌的一种不良生物学特征。
经手术前后动态检测肺癌患者血清p53抗体发现,术后血清p53抗体水平呈逐渐下降趋势。术后30天与术前比较有显著性差异(P<0.05)。同时,肺癌患者血清p53抗体阳性率术后亦逐渐下降,术后30天26例p53抗体阳性患者中有14例p53抗体恢复至正常水平。且术后30天p53抗体阳性恢复至正常的14例均为行根治性肺癌切除患者,而术后30天p53抗体未恢复至正常的12例中仅2例为根治术者。上述结果表明:在行肺癌根治性切除术切除了原发肺癌和可能并存的转移淋巴结后,消除了突变型p53蛋白的来源,进而根除了突变型p53蛋白诱发机体产生抗p53抗体的免疫反应。而行姑息性肺癌切除术者,由于仅切除了大部分肿瘤,仅使突变型p53蛋白的量减少,因而患者手术后血清抗p53抗体抗体水平较术前明显降低,但不能降至正常水平。本组1例非小细胞肺癌患者,由于病变广泛,仅行姑息性切除,术后30天血清p53抗体未降至正常水平,术后90天再次升高。另一例非小细胞肺癌患者,术后30天血清p53抗体水平仍然在高水平状态,术后90天较术前进一步升高,后经脑CT扫描发现患者有颅内转移。本研究结果证明:动态检测肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平,对于监测肺癌的复发转移,判断预后可能有一定帮助。由于本研究术后观察周期较短,其可靠性尚有待以后继续研究,加以证实。
, 百拇医药
本课题受国家自然科学基金资助(39170808)
参考文献
1,Minna JD. The molecular biology of lung cancer pathogenesis. Chest,1993,103(Suppl 1)∶449S-456S.
2,Soussi T, Legros Y, Lubin R, et al. Multifactorial analysis of p53 alteration in human cancer: a review. Int J Cancer,1994,57(1)∶1-9.
3,Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vagelstein B, et al. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science,1991,253(5015)∶49-53.
, 百拇医药
4,Zhou QH(周清华), Wang GL, Sun ZL, et al. Mutation patterns of p53 gene in human lung cancer. Lung Cancer,1997,18(Suppl 2): S487-S491.
5,Miller CW, Simon K, Aslo A, et al. p53 Mutations in human lung tumors. Cancer Res,1992,52(7)∶1695-1701.
6,Angelopoulou K, Diamandis EP, Sutherland DJ, et al. Prevalence of serum antibodies against the p53 tumor suppressor gene protein in various cancers. Int J Cancer,1994,58(4)∶480-487.
7,Lubin R, Schlichtholz B, Teilland JL, et al. p53 antibodies in patients with various types of cancer identification and characterization. Clin Cancer Res, 1995,1(5)∶1463-1469.
(收稿:1999-10-29 修回:2000-01-21), http://www.100md.com
单位:赵峰 周清华 王兰兰 伍伫 刘伦旭 王允 刘静 冯伟华(610041 成都,华西医科大学附属第一医院胸心外科)
关键词:肺肿瘤;p53基因;血清p53抗体;酶联免疫吸附法
中国肺癌杂志000404
【摘要】 目的 探讨肺癌患者血清p53抗体与临床病理特征之间的关系,以及手术后p53抗体的动态变化规律。方法 采用酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)分别于术前1天、术后7、30、90天动态检测120例肺癌患者血清p53抗体,并以30例肺部良性疾病患者和120例正常健康人作对照。结果 肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平和阳性率均明显高于肺部良性疾病患者和正常人(P<0.05),而正常人与肺部良性疾病患者间无显著性差异(P>0.05)。肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平和阳性率均与肺癌细胞分化程度和病期有密切关系(P<0.01或P<0.05)。在行根治性切除术后,肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平逐渐降低,术后30天左右可降至正常人水平;而行姑息性切除者,术后30天血清p53抗体水平不能降至正常水平;如术后有肺癌复发和转移者,术后血清p53抗体水平可再度升高。结论 检测血清p53抗体水平有助于肺部良恶性疾病的诊断;手术前后动态测定肺癌患者血清p53抗体的变化规律,有助于判断疗效,监测预后和指导肺癌术后的综合治疗。
, http://www.100md.com
【中图分类号】 R730.3
Pre- and post-operative sequential changes of serum p53 antibodies and clinical significance in patients with lung cancer
ZHAO Feng ZHOU Qinghua WANG Lanlan WU Zhu LIU Lunxu WANG Yu LIU Jing FENG Weihua (Department of Thoracocardiac Surgery, The First University Hospital, West China University of Medical Sciences, Chengdu, Sichuan 610041, P.R.China)
【Abstract】 Objective To explore the relationship between serum p53 antibodies and clinicopathological characteristics in patients with lung cancer and to investigate sequential changing regularity of serum p53 antibodies after surgical resection. Methods The serum p53 antibody level was detected in 120 patients with lung cancer, and in 30 patients with benign pulmonary lesion and 120 healthy adults as control by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The blood samples were collected on the day before operation and on the 7th, 30th and 90th days postoperatively. Results The level and positive rate of serum p53 antibodies in patients with lung cancer were significantly higher than those in patients with benign pulmonary disease and normal individuals (P<0.05), but there was no significant difference between patients with benign pulmonary disease and normal individuals (P>0.05). The level and positive rate of pre-operative serum p53 antibodies in patients with lung cancer were closely related to cell differentiation and stage of lung cancer (P<0.01 or P<0.05). The level of serum p53 antibodies decreased gradually in patients with lung cancer underwent radical removal of the cancer, and completely returned to the normal level around the 30th day after operation, but the level of serum p53 antibodies in patients with lung cancer underwent palliative operation didn't reduce to the normal level on the 30th day after operation. It would increase again when tumor metastasis or recurrence developed. Conclusion Detection of serum p53 antibodies is helpful to defferentiate benign from malignant pulmonary diseases. Monitoring of sequential change of pre- and post-operative serum p53 antibodies in patients with lung cancer is helpful to evaluate response to treatment, to judge prognosis and to guide the comprehensive treatment of patients with lung cancer after operation.
, 百拇医药
【Key Words】 Lung neoplasms p53 gene Serum p53 antibodies ELISA
近年的研究发现,肺癌的发生、发展是一个多基因参与的复杂过程,其中p53基因结构和功能异常在肺癌的发生、发展过程中起重要作用[1]。分析p53基因变化可采用分子生物学、免疫组化、血清学等多种方法[2],前两种方法由于操作复杂和繁琐不易在临床推广,而血清学方法具有操作简便、重复性好,不需肿瘤标本等优点,目前越来越受到广泛重视。本研究应用酶链免疫吸附试验(enzyme linked immunosorbent assay, ELISA)法检测120例肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平,并与肺良性疾病患者和正常健康人作比较,同时对肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平进行手术前后的动态观察,以探讨检测肺癌患者血清p53抗体的临床意义。
1 材料与方法
, 百拇医药
1.1 检测对象 正常组120例,均为本院门诊作健康体检者。男60例,女60例,年龄21~62岁,平均38.7岁。肺良性疾病组30例,男21例,女9例,年龄20~65岁,平均45.3岁,所有病例均有术后病理诊断,其中炎性假瘤14例,结核瘤10例,肺囊肿6例。
肺癌组120例,男98例,女22例;年龄22~74岁,平均56.4岁;所有病例均有术后病理诊断,其中鳞癌60例,腺癌36例,腺鳞癌14例,未分化癌10例(包括小细胞癌9例,大细胞癌1例)。病理分期采用国际抗癌联盟(UICC)1997年修订的分期标准,其中Ⅰ期10例,Ⅱ期32例,Ⅲ期75例,Ⅳ期3例。根治性肺癌切除术100例,姑息性肺癌切除术20例。
1.2 标本的收集 肺癌组分别于术前1天、术后7、30和90天时抽取静脉血2ml。肺良性疾病组分别于术前1天、术后7天抽取静脉血2ml。正常组清晨空腹采集静脉血2ml。上述标本当日离心分离血清,置于-20℃冰箱保存备测。
, 百拇医药
1.3 检测方法 应用法国Immunotech公司anti-p53 ELISA试剂盒,操作严格按说明书进行:洗涤重组p53蛋白或质控蛋白包被的聚苯乙烯微量反应板,将稀释的样本和质控各100ml分别加入到相应反应板微孔内,20~25℃震荡温育1小时,取出后洗涤4次吹干,加入过氧化物酶标记的抗人IgG抗体反应液100ml,20~25℃震荡温育1小时,再次洗涤4次后吹干,加入酶反应底物TMB100ml,室温避光反应10分钟,加入100ml H2SO4终止酶反应。用酶标仪测定450nm波长吸光度。p53抗体浓度用两个不同参数确定:
指数(index)=(样品p53蛋白净吸光值-质控蛋白净吸光值)/(低值阳性质控p53蛋白净吸光值-质控蛋白净吸光值)
吸收率(ratio)=(样品p53蛋白净吸光值)/(质控蛋白净吸光值)
1.4 统计学处理 本实验数据采用t检验、F检验、χ2检验、Logistic回归分析进行统计分析,在华西医科大学统计教研室采用SPSS7.5系统软件处理。
, http://www.100md.com
2 结果
2.1 不同组别血清p53抗体指数和吸收率的比较 正常人、肺良性疾病患者和肺癌患者血清p53抗体指数和吸收率经F检验有显著性差异(P<0.05);两两比较:肺癌组与正常组和肺良性疾病组间均有显著性差异(P<0.05),正常组与肺良性疾病组间无显著性差异(P>0.05)(表1)。
表1 肺癌组与正常组、肺良性疾病组间血清
p53抗体指数和吸收率的比较
Tab 1 Comparison of index and ratio of serum p53 antibodies
among patients with lung cancer, benign pulmonary diseases
, http://www.100md.com
and normal individuals Groups
n
Index
Ratio
Normal
120
0.2358±0.1539
1.0383±0.2275
Benign
30
0.2567±0.1127
1.1276±0.4768
, 百拇医药
Cancer
120
1.6475±0.5714
3.0191±0.6932
2.2 术前不同组别血清p53抗体阳性率的比较 120例正常人血清p53抗体指数的
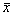 =0.2358,s=0.1539,吸收率的
=0.2358,s=0.1539,吸收率的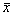 =1.0383,s=0.2275,以超过
=1.0383,s=0.2275,以超过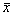 +1.645s为判断阳性标准,即指数>0.4890和吸收率>1.4125,分别判定指数和吸收率阳性,当二者同为阳性,即判定为p53抗体阳性。肺良性疾病患者和正常健康人无一例阳性。120例肺癌患者中有26例血清p53抗体阳性,阳性率为21.7%。三组间经χ2检验,有非常显著差异(P<0.01);两两比较,正常组与肺良性疾病组间无显著性差异(P>0.05),肺癌组与正常组和肺良性疾病组间均有非常显著性差异(P<0.01)。
+1.645s为判断阳性标准,即指数>0.4890和吸收率>1.4125,分别判定指数和吸收率阳性,当二者同为阳性,即判定为p53抗体阳性。肺良性疾病患者和正常健康人无一例阳性。120例肺癌患者中有26例血清p53抗体阳性,阳性率为21.7%。三组间经χ2检验,有非常显著差异(P<0.01);两两比较,正常组与肺良性疾病组间无显著性差异(P>0.05),肺癌组与正常组和肺良性疾病组间均有非常显著性差异(P<0.01)。, http://www.100md.com
2.3 肺癌患者手术前后血清p53抗体的动态变化 手术前后不同时间的血清p53抗体指数、吸收率和阳性率经F检验和χ2检验有非常显著性差异(P<0.01);两两比较:术前与术后7、30与90天间比较,均无显著性差异(P>0.05),其余不同时间组间比较均有显著性差异(P<0.05或P<0.01)(图1、2)。

图1 肺癌患者手术前后血清p53抗体水平的动态变化
Fig 1 Pre- and post-operative sequential change of serum p53 antibodies in patients with lung cancer

图2 肺癌患者手术前后血清p53抗体阳性率的动态变化
, 百拇医药
Fig 2 Pre- and post-operative sequential change of positive rate of serum p53 antibodies in patients with lung cancer
2.4 肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平与肺癌临床病理生理特征的关系 肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平与肿瘤分化程度、病理分期有密切关系(P值均<0.05),与肺癌组织类型,原发肿瘤大小、部位、淋巴结转移,患者性别、年龄、吸烟无明显关系(P>0.05)(表2)。
表2 肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平与临床病理生理特征的关系
Tab 2 The relationship between the level of serum p53 antibodies and clinical
pathophysiological characteristics in patients with lung cancer Groups
, http://www.100md.com
n
Index
Ratio
P value
P-TNM
Ⅰ+Ⅱ
42
0.2384±0.0675
1.3545±1.5627
P<0.01
Ⅲ+Ⅳ
78
2.4063±0.8978
, 百拇医药
4.0226±1.5365
Undifferentiated and poor-differentiated
63
2.6795±0.8714
4.0038±1.7651
P<0.01
Moderate-well differentiated
47
0.5870±0.1275
2.0029±0.8675
, 百拇医药 Size of the primary tumor
T1+T2
46
1.3672±0.6574
2.7048±1.2132
P>0.05
T3+T4
74
2.0624±0.9831
3.3317±0.4232
Lymph node metastasis
, 百拇医药
N0
59
1.1523±0.2345
2.4547±1.0456
P>0.05
N1-3
61
2.1265±0.6575
3.7072±0.2175
Histological classification
Undifferentiated cell carcinoma
, 百拇医药
10
1.5448±0.1678
2.5636±1.1048
Squamous cell carcinoma
Adenocarcinoma
60
36
1.8167±0.4578
1.0778±0.2153
3.3353±1.6578
2.5550±1.2345
, 百拇医药
P>0.05
Adeno-squamous cell carcinoma
14
1.1754±0.3750
2.1571±1.0321
Site of the tumor
Central type
62
2.0536±0.8761
3.3563±1.8972
P>0.05
, 百拇医药
Periphenal type
58
1.5872±0.3421
1.0163±1.8673
Age
<50
35
1.7192±0.6376
2.9322±0.6732
50~60
34
2.5331±1.0172
, 百拇医药
2.9322±0.6732
>60
51
1.6475±0.5671
3.2653±1.2959
P>0.05
Sex
Male
98
1.9454±0.5671
1.9865±1.2351
Female
, http://www.100md.com
22
1.303±0.0832
1.2345±0.4372
P>0.05
Smoking
Smoker
70
1.5709±0.1576
3.0345±0.8651
Non-smoker
50
2.4165±1.0231
, 百拇医药
3.8463±1.2321
P>0.05
2.5 肺癌患者血清p53抗体与肺癌临床病理生理特征相关性的多因素分析 Logistic回归分析结果表明,血清p53抗体阳性率与肺癌P-TNM分期呈正相关,与肺癌细胞分化程度呈负相关(P值均<0.05),与肿瘤组织学类型、部位、大小、淋巴结转移,患者的性别、年龄、吸烟史等无相关关系(P>0.05)(表3)。
表3 肺癌患者血清p53抗体阳性率与临床病理生理特征的Logistic回归分析
Tab 3 Logistic analysis on the relationship between positive rate of serum p53 antibodies and clinical pathophysiological characteristics in patients with lung cancer Variable
, http://www.100md.com
B
OR
95%CI for OR
P value
Age
0.0234
1.0237
0.9686--1.0819
0.4070
Lymph node metastasis
-0.4988
0.6073
, 百拇医药
0.3233--1.1406
0.1209
Stage
1.8389
6.2899
2.4839--15.9290
0.0252
Sex
-0.6230
0.5363
0.0861--3.3398
0.5043
, 百拇医药
Smoking
-0.0089
0.9912
0.9558--1.0279
0.6326
Tumor size
0.6427
1.9015
0.7859--4.6007
0.1540
Site
-0.0747
, 百拇医药
0.9280
0.3240--2.6575
0.8893
Differentiation
-4.1430
0.0159
0.0040--0.5979
0.0178
Histology
-0.4819
0.6176
0.3868--0.9860
, 百拇医药
0.672
3 讨论
p53基因突变是人类肿瘤最常见的基因改变[3],约50%~60%的非小细胞肺癌和80%小细胞肺癌有p53突变[4,5]。突变的结果导致异常的p53蛋白产生,其构象异常使半衰期延长至数小时,从而在细胞内聚积。聚积的突变型p53蛋白作为靶抗原引发机体的自身免疫应答,产生血清p53抗体[6]。国外学者应用ELISA方法在多种肿瘤患者血清中检测到p53抗体。并发现有较好的临床意义,有关手术前后动态检测肺癌患者血清p53抗体研究,国内外尚未见报道。
本研究观察到肺癌患者术前血清p53抗体指数和吸收率均明显高于肺部良性疾病患者和正常人(P<0.05),而正常人与肺部良性疾病患者间无显著差异(P>0.05)。120例肺癌中有26例p53抗体阳性,阳性率为21.7%,而30例肺部良性疾病患者和120例正常人无一例阳性者。本研究结果与文献报道结果一致,表明检测肺癌患者血清p53抗体,用于肺部良恶性疾病的诊断和鉴别诊断,具有较好的特异性,这一点在其它恶性肿瘤亦得到了证实[7]。
, 百拇医药
本研究还观察到p53抗体水平和阳性率均与肺癌细胞分化程度和病期有密切关系(P<0.01或P<0.05),而与肺癌的组织类型,原发肿瘤大小、部位、淋巴结转移,患者性别、年龄、吸烟无明显关系(P>0.05)。肿瘤组织分化程度差、临床分期晚的肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平明显升高,表明血清中p53抗体阳性是肺癌的一种不良生物学特征。
经手术前后动态检测肺癌患者血清p53抗体发现,术后血清p53抗体水平呈逐渐下降趋势。术后30天与术前比较有显著性差异(P<0.05)。同时,肺癌患者血清p53抗体阳性率术后亦逐渐下降,术后30天26例p53抗体阳性患者中有14例p53抗体恢复至正常水平。且术后30天p53抗体阳性恢复至正常的14例均为行根治性肺癌切除患者,而术后30天p53抗体未恢复至正常的12例中仅2例为根治术者。上述结果表明:在行肺癌根治性切除术切除了原发肺癌和可能并存的转移淋巴结后,消除了突变型p53蛋白的来源,进而根除了突变型p53蛋白诱发机体产生抗p53抗体的免疫反应。而行姑息性肺癌切除术者,由于仅切除了大部分肿瘤,仅使突变型p53蛋白的量减少,因而患者手术后血清抗p53抗体抗体水平较术前明显降低,但不能降至正常水平。本组1例非小细胞肺癌患者,由于病变广泛,仅行姑息性切除,术后30天血清p53抗体未降至正常水平,术后90天再次升高。另一例非小细胞肺癌患者,术后30天血清p53抗体水平仍然在高水平状态,术后90天较术前进一步升高,后经脑CT扫描发现患者有颅内转移。本研究结果证明:动态检测肺癌患者血清p53抗体水平,对于监测肺癌的复发转移,判断预后可能有一定帮助。由于本研究术后观察周期较短,其可靠性尚有待以后继续研究,加以证实。
, 百拇医药
本课题受国家自然科学基金资助(39170808)
参考文献
1,Minna JD. The molecular biology of lung cancer pathogenesis. Chest,1993,103(Suppl 1)∶449S-456S.
2,Soussi T, Legros Y, Lubin R, et al. Multifactorial analysis of p53 alteration in human cancer: a review. Int J Cancer,1994,57(1)∶1-9.
3,Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vagelstein B, et al. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science,1991,253(5015)∶49-53.
, 百拇医药
4,Zhou QH(周清华), Wang GL, Sun ZL, et al. Mutation patterns of p53 gene in human lung cancer. Lung Cancer,1997,18(Suppl 2): S487-S491.
5,Miller CW, Simon K, Aslo A, et al. p53 Mutations in human lung tumors. Cancer Res,1992,52(7)∶1695-1701.
6,Angelopoulou K, Diamandis EP, Sutherland DJ, et al. Prevalence of serum antibodies against the p53 tumor suppressor gene protein in various cancers. Int J Cancer,1994,58(4)∶480-487.
7,Lubin R, Schlichtholz B, Teilland JL, et al. p53 antibodies in patients with various types of cancer identification and characterization. Clin Cancer Res, 1995,1(5)∶1463-1469.
(收稿:1999-10-29 修回:2000-01-21), http://www.100md.com