P85磷酯肌醇-3激酶-蛋白激酶C-ζ复合物对血管紧张素Ⅱ激活平滑肌细胞p70核蛋白体S6激酶的调节作用
作者:廖端芳 Berk BC 关永源
单位:廖端芳(衡阳医学院心肺药理研究室,衡阳 421001);Berk BC(Center for Cardiovascular Research, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York 14642, USA);关永源(中山医科大学药理学教研室,广州 510089)
关键词:肌,平滑,血管;磷酯肌醇-3激酶;血管紧张素Ⅱ;蛋白激酶C;p70核蛋白体S6激酶
中国动脉硬化杂志000302[摘 要] 作者以前的研究发现蛋白激酶C-ζ介导血管紧张素Ⅱ经Ras-MEK途径激活血管平滑肌细胞丝裂素活化的蛋白激酶MAPK或细胞外信号调节激酶ERK1/2。本文研究了P85磷酯肌醇-3激酶-蛋白激酶C-ζ复合物核蛋白体激酶p70S6激酶活性的调节作用及其信号传递途径。 Western Blot分析显示正常培养的血管平滑肌细胞表达p70S6激酶、p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶和蛋白激酶C-ζ。100 nmol血管紧张素Ⅱ和 10 μg/L 血小板源生长因子刺激并不影响p70S6激酶、p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶和蛋白激酶C-ζ表达。 p70S6激酶磷酸转移酶活性分析发现血管紧张素Ⅱ与血管平滑肌细胞作用5 min 即开始激活p70S6激酶, 20 min达高峰, 并呈剂量依赖性。磷酯肌醇-3激酶抑制剂wortmannin (10 nmol)、蛋白激酶C-ζ 抑制剂Pseudo Z (50 μmol) 和p70S6激酶抑制剂rapamycin (100 μg/L) 均可明显阻断血管紧张素Ⅱ诱导的p70S6激酶激活。有趣的是,我们观察到p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶和蛋白激酶C-ζ受血管紧张素Ⅱ和血小板源生长因子刺激后均向Ras转位并与之结合, 抗Ras抗体可将p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶或蛋白激酶C-ζ混合沉淀, 抗p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶抗体亦可使蛋白激酶C-ζ沉淀下来。 提示Ras、p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶和蛋白激酶C-ζ三种蛋白结合在一起形成一个功能复合体,Wortmannin和Pseudo Z可阻断这个功能复合体的形成。此外,血管紧张素Ⅱ和血小板源生长因子与血管平滑肌细胞孵育24 h 明显促进细胞增殖,氚标胸腺嘧啶脱氧核苷掺入率增加约50%, Wortmannin和非特异性蛋白激酶C抑制剂Chelerythine均抑制血管紧张素Ⅱ和血小板源生长因子对血管平滑肌细胞的促增殖作用。综合上述结果, 说明血管紧张素Ⅱ通过Ras-磷酯肌醇-3激酶-蛋白激酶C-ζ途径激活p70S6激酶和刺激血管平滑肌细胞增殖, p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶-蛋白激酶C-ζ 复合物在其中起重要调节作用。
, http://www.100md.com
[中图分类号] Q55 [文献标识码] A
[文章编号] 1007-3949(2000)-03-0193-06
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Protein Kinase C-ζ Complex Regulates Angiotensin Ⅱ Activation of p70 Ribosomal S6 Kinase in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
LIAO Duan-Fang
(Division of Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology, Hengyang Medical College, Hengyang 421001, China.)
Bradford C BERK
, 百拇医药
(Center for Cardiovascular Research, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York 14642, USA)
GUAN Yong-Yuan
(Department of Pharmacology, Sun Yat-sen University of Medicine Sciences, Guangzhou 510089)
ABSTRACT Aim To investigate the effects of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase C-ζ (PKC-ζ)complex on regulating angiotensin Ⅱ(AngⅡ) activation of p70 ribosomal S6 kinase (p70S6K) in vascular smooth muscle cells(VSMC). Methods VSMC isolated from 200 g to 250 g male Sprague-Dawley rats were cultured to 70% to 80% confluence and were growth-arrested by incubation in 0.1% calf serum/DMEM for 48 h before use. Both 3 H-TdR incorporation and cell counting were used to estimate the proliferation of VSMC. Western blot, immunoprecipitation and immunoblot analyses were performed to valuate the AngⅡ-stimulated kinase expression and Ras-PI3K-PKC-ζ association of VSMC. Phosphotransferase assay by using S6 peptide as substrate was employed to measure the p70 S6K activity. Results VSMC expressed p85PI3K, PKC-ζ and p70S6K; AngⅡ and PDGF stimulation did not affect the p85PI3K, PKC-ζ and p70S6K expression. 2) 100 nmol AngⅡ treatment obviously stimulated p70S6K activity of VSMC at 5 min with peak at 20 min. PI3K inhibitor wortmannin (10 nmol) and pseudosubstrate of PKC-ζ pseudo Z (50 μmol) blocked AngⅡ activation of p70S6K. 3) In response to AngⅡ, PI3K translocated to the membrane and associated with Ras as shown by PI3K coprecipitation with Ras antibody. Furthermore, both anti-Ras and anti-PI3K antibodies could precipitate PKC-ζ, suggesting that AngⅡ treatment resulted in formation of Ras-PI3K-PKC-ζ complex. Wortmannin and pseudo Z significantly blocked the complex formation. 4) In addition, 100 nmol AngⅡ and 10 ng/mL PDGF incubation with VSMC for 24 hours stimulated VSMC proliferation, which could be abrogated by wortmannin and nonspecific PKC inhibitor chelerythrine. Conclusion This findings demonstrate that AngⅡ stimulation of p70S6K occurs via a pathway of Ras-PI3K-PKC-ζ and p85PI3K-PKC-ζcomplex play an important role in this procedure
, 百拇医药
MeSH Angiotensin Ⅱ; Phosphotransferases, Phosphatidylinositol; Protein Kinase C; Phosphotransferases, RNA Ribosomal S6; Muscle, Smooth, Vascular
血管紧张素Ⅱ(angiotensin Ⅱ, AngⅡ) 在血管平滑肌细胞(vascular smooth muscle cells, VSMC)增殖和肥大过程中起重要作用[1]。文献[2-4]报道AngⅡ增加细胞内钙离子浓度、激活蛋白激酶C(protein kinase C, PKC)、活化一系列由生长因子诱导的信号传导通路,如激活蛋白酪氨酸激酶、激活丝裂素活化的蛋白激酶(mitogine activated-protein kinase, MAPK)或细胞外信号调节激酶(extracelluar signal-regulated kinases 1/2, ERK1/2) 等等。P70核蛋白体激酶(p70 ribosomal S6 kinase, p70S6激酶)系丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶家族成员。当细胞参与对生长因子、分裂等早期反应时,p70S6激酶被激活。文献报道在球囊损伤的大鼠主动脉和心衰心脏,p70S6激酶被迅速激活[1,5]。P70S6K通过调节mRNA的翻译过程实现对细胞生长的调控[6,7], p70S6激酶的活化受其上游磷酯肌醇-3激酶(phosphatidylinositol 3-kinse, PI3K)的调节[8]。文献[9,10]报道AngⅡ 可刺激培养的VSMC和心肌细胞 p70S6激酶活性, 然而其信号传导途径并不清楚,推测与Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK1/2有关。作者以前的工作显示Raf 在AngⅡ 激活ERK1/2过程中并不起主要作用,而由PKC-ζ取而代之[11,12]。Saward 等[13]报道1 μmol AngⅡ与VSMC作用15 min可激活PI3K,使PI3K p85亚单位酪氨酸磷酸化并发生膜转位。近年不少文献显示PKC-ζ是PI3K的下游效应蛋白, 同时也参与p70S6激酶的调节, 其活性受PI3K代谢产物PtdIns(3-5)P(3)的调控[14-16]。因而,我们推测PKC-ζ亦可能介导AngⅡ激活p70S6激酶, 并提出PI3K-PKC-ζ联合调控p70S6激酶活性的工作假设。
, 百拇医药
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
抗H-Ras抗体和抗PKC-ζ抗体分别购自Boehringer Mannheim和Santa Cruz公司,抗p70S6激酶抗体和抗p85PI3K抗体购自Upstate Biotechnology Inc公司,S6肽由加拿大Kinetek Pharmaceuticals Inc公司赠送,[r-32P]ATP为Dupont公司产品,Protein A-agarose 为Life Technologies Inc公司产品,wortmannin、chelerythrine和rapamycin 为Sigma公司产品,PKC-ζ假性底物购自Calbiochem公司(La Jolla, CA)。
1.2 血管平滑肌细胞培养
参照文献[17],从200~250 g雄性Sprague Dawley大鼠胸主动脉分离出VSMC,用含10%小牛血清的DMEM培养基培养。取5~13代VSMC于100 cm培养皿中培养至70%~80%融合,用含0.1%小牛血清的DMEM培养基继续培养48 h使VSMC处于静止状态,然后用AngⅡ、 PDGF等刺激20 min。PI3K的抑制剂Wortmnnin、非特异性PKC-抑制剂Chelerythine、PKC-ζ 抑制剂(PKC-ζ假性底物)Pseudo Z和p70S6激酶抑制剂rapamycin于AngⅡ、PDGF之前10 min加入。
, http://www.100md.com
1.3 细胞蛋白提取与浓度测定
血管紧张素Ⅱ(AngⅡ)、 PDGF作用后的VSMC用磷酸缓冲液洗三次,每皿加1.0 mL TME缓冲液(10 mmol Tris, 5 mmol MgCl2, 1 mmol EDTA, 25 mmol NaF, pH 7.5;临用前加100 μmol Na3VO4, 20 mg/L leupeptin, 1 mg/L pepstatin A, 4 mg/L aprotinin, 1 mmol DTT) 裂解细胞。速冻, 冰浴上缓慢复苏,刮下细胞,冰浴上用超声粉碎细胞,15 000g离心30 min, 取上清液,按Bradford蛋白测定盒说明书测定蛋白浓度,样品贮存于-80℃待用。
1.4 p70S6激酶活性测定
参照文献[18],取抗p70S6激酶抗体免疫沉淀物(50% bead slurry) 5 μL, 加30 μL反应缓冲液(25 mmol b-glycerophosphate, 20 mmol MOPS, pH 7.2, 5 mmol EGTA, 2 mmol EDTA, 20 mmol MgCl2, 1 mmol Na3VO4, 0.25 mmol dithiothreitol), 加4 μg 底物S6寡肽和50 μmol [r-32 P]ATP(2×1015 dpm/mol), 于30℃反应15 min, 取20 μL反应混合物点样于2 cm2 p81 phosphocellulose 反应纸(Whatman公司),用含1% orthophosphoric acid 去离子水冲洗三次,用r-计数器记录放射活性。
, http://www.100md.com
1.5 Western Blot 实验
参照文献[11],配制9%的SDS-PAGE分离胶和3%的积层胶,每孔加入20 μg蛋白样品,置电泳缓冲液中,70 V电泳约20 min。待样品进入分离胶后,150 V电泳至所需时间。 将蛋白转印至硝酸纤维薄膜,用Life Technologies公司商用封闭液于室温处理2 h,按1∶200加p70S6激酶、p85PI3K或PKC-ζ单抗, 4℃过夜,TBS液洗膜10 min×3次,用辣根过氧化物酶试剂盒(ECL, Amersham International plc. United Kingdom)显色。
1.6 Ras-磷酯肌醇-3激酶-蛋白激酶C-ζ混合沉淀实验
参照文献[12],取TME缓冲液提取的蛋白,加抗Ras单抗或p85PI3K单抗和protein A-agarose于4℃混合12 h进行免疫沉淀(immunoprecipitation, IP)。 Protein A-agarose用TME缓冲液洗一次,TTBS缓冲液(20 mmol Tris, pH 7.5, 500 mmol NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, 0.1% beta-mercaptoethanol)洗二次, 再用TME缓冲液洗一次。然后,用9%的SDS-PAGE胶将免疫复合物分离, 用抗p85PI3K和PKC-ζ单抗进行免疫印迹(immunoblot, IB)实验。
, 百拇医药
1.7 细胞计数与氚标胸腺嘧啶脱氧核苷掺入实验
参照文献[13],取生长良好的VSMC制成细胞悬液(4×107个/L)接种于24孔培养板中,每孔0.5 mL(2×104个细胞),孵育24 h。换无血清培养基继续孵育24 h后,使VSMC处于静止期,加小牛血清至浓度为10%,同时分组加入100 nmol AngⅡ(终浓度,下同) 或10 μg/L PDGF(终浓度,下同)。 Wortmannin (终浓度10 nmol,下同)、chelerythrine (终浓度10 μmol,下同)和rapamycin(终浓度100 nmol,下同)于AngⅡ、PDGF前10 min 加入,对照组为只含10%小牛血清的DMEM培养基, 继续培养24 h。然后进行下列实验: ①细胞消化液分离细胞,以4%台盼蓝染色计数。② 继续培养18 h, 加氚标胸腺嘧啶脱氧核苷(3 H-thymine deoxyribonucleotide, 3 H-TdR)至终浓度为2 mCi/L, 6 h后收样,弃含3 H-TdR培养基,用D-hanks液洗三次,以细胞消化液消化。用真空泵将细胞抽吸于玻璃纤维滤纸上,5%三氯醋酸固定,无水乙醇脱水,干燥后置闪烁瓶中加闪烁液(甲苯500 mL, PPO 3, POPOP 0.1 g)于液体闪烁分析仪(Packard 公司 )测放射性强度,以每分钟衰减数(decay per minute, dpm或d/min)表示。
, http://www.100md.com
1.8 统计处理
数据以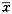 ±s表示,数据经方差分析后进行q检验,差异的显著性用P<0.05和P<0.01判断。
±s表示,数据经方差分析后进行q检验,差异的显著性用P<0.05和P<0.01判断。
2 结 果
2.1 血管平滑肌细胞表达p70核蛋白体S6激酶、p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶和蛋白激酶C-ζ
Western Blot 分析发现正常培养的VSMC表达p70S6激酶、p85PI3K亚单位和PKC-ζ, AngⅡ和 PDGF刺激并不影响p70S6激酶、p85PI3K亚单位和PKC-ζ的表达(图1, Figure 1)。
图1 血管平滑肌细胞表达p70核蛋白体S6激酶、p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶亚型和蛋白激酶C-ζ
, http://www.100md.com
Figure 1 VSMC express p70S6K, p85PI3K subtype and PKC-ζ Western blot analysis was carried out with anti- p70S6K antibody (A), anti-p85PI3K antibody (B) and anti- p70S6K, antibody (C), respectively.
2.2 血管紧张素Ⅱ激活血管平滑肌细胞p70核蛋白体S6激酶
图2 (Figure 2) 显示AngⅡ与VSMC作用5 min即开始激活p70S6激酶, 20 min达高峰,约为处理前的5倍,随后逐渐降低(A), 并呈剂量依赖性(B)。p70S6激酶抑制剂rapamycin (100 nmol)、PI3K抑制剂wortmannin(10 nmol)和PKC-ζ抑制剂Pseudo Z (50 μmol)均可有效阻断AngⅡ的作用(图3, Figure 3)。
, 百拇医药
2.3 血管紧张素Ⅱ刺激Ras-磷酯肌醇-3激酶-蛋白激酶C-ζ复合物形成
细胞受AngⅡ和 PDGF刺激后,可观察到PI3K向Ras转位并与之结合的现象, 在抗Ras抗体沉淀的蛋白中有PI3K存在。图3A(Figure 3A)中可见抗Ras抗体沉淀的蛋白电泳分离转膜后再用抗PI3K抗体杂交可显示p85条带, wortmannin 10 nmol可阻断Ras-PI3K相互结合。图4B和图4C(Figure 4B and 4C)中可见不但抗Ras抗体可将PKC-ζ混合沉淀(B); 而且抗PI3K抗体也可将PKC-ζ沉淀下来, PI3K、PKC-ζ之间的相互作用亦可被wortmannin和pseudo Z阻断(C)。由此,我们可以推断细胞受AngⅡ和 PDGF刺激后, Ras、PI3K、PKC-ζ三种蛋白结合在一起形成一个功能复合体。Wortmannin和pseudo Z可阻断这个功能复合体的形成, 说明PI3K-PKC-ζ在这个功能复合体中起重要作用。
, 百拇医药
图2 血管紧张素Ⅱ对血管平滑肌细胞p70核蛋白体S6激酶活性的影响
Figure 2 The effects of AngⅡ on p70S6K activity of VSMC A: Time-course of AngⅡ on p70S6K activity. B: Concentration-response of AngⅡ on p70S6K activity.
图3 p70核蛋白体S6激酶抑制剂rapamycin、磷酯肌醇-3激酶抑制剂wortmannin和蛋白激酶C-ζ抑制剂pseudo Z对血管紧张素Ⅱ活化血管平滑肌细胞p70核蛋白体S6激酶的影响
Figure 3 The effects of p70S6K inhibitor rapamycin,PI3K inhibitor wortmannin and PKC-ζ inhibitor pseudo Z on AngⅡ activation of p70S6K in VSMC a: P<0.01 compared with control grpip, b: P<0.01 compared with AngⅡ group, c: P<0.01 compared with PDGF group.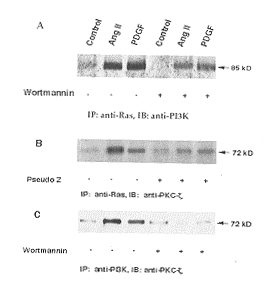
, 百拇医药
图4 p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶和蛋白激酶C与Ras的联系
Figure 4 Ras association with p85PI3K and PKC-ζ A and B. p85PI3K and PKC-ζ were immuno-precipitated (IP) with Ras antibody. C. PKC-ζ was immuno-precipitated (IP) by p85PI3K antibody.
2.4 Wortmannin和chelerythrine阻断血管紧张素Ⅱ诱导血管平滑肌细胞增殖
台盼蓝染色细胞计数和3 H-TdR掺入法分析显示AngⅡ(100 nmol)和PDGF (10 μg/L)均有较强的刺激VSMC增殖的作用,AngⅡ和PDGF处理组细胞计数明显高于对照组,3 H-TdR掺入量显著增加。Wortmannin 和chelerythrine 均可阻断AngⅡ和PDGF的作用(表1, Table 1)。
, http://www.100md.com
表1 血管紧张素Ⅱ、血小板源生长因子、Wortmannin和chelerythrine对血管平滑肌细胞增殖的影响
Table 1 Effects of Ang Ⅱ, PDGF, wortmannin and chelerythrine on VSMC proliferation (n=6,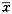 ±s) Groups
±s) Groups
Cell number
(×104)
3 H-TdR incorporation
(dpm)
Control
, 百拇医药
2.26±0.14
503±51
AngⅡ
3.32±0.29a
740±75a
PDGF
3.51±0.46a
754±95a
Wortmannin
2.25±0.21
512±41
, 百拇医药
AngⅡ+Wortmannin
2.32±0.12b
540±34b
PDGF+Wortmannin
2.31±0.23c
542±60c
Chelerythrine
2.42±0.43
493±75
AngⅡ+Chelerythrine
, 百拇医药
2.47±0.43b
550±84b
PDGF+Chelerythrine
2.42±0.36c
560±71c
a:P<0.01 vs control; b: P<0.01 vs Ang Ⅱ; c: P<0.01 vs PDGF
3 讨 论
本文的主要发现是PKC-ζ和PI3K联合调节AngⅡ激活血管平滑肌细胞核蛋白体激酶p70S6激酶。有如下两点支持这一结论:①AngⅡ与VSMC作用5 min 即开始激活p70S6激酶, 20 min达高峰, 并呈剂量依赖性。P70S6K抑制剂rapamycin、 PI3K抑制剂wortmannin和PKC-ζ抑制剂(PKC假性底物) Pseudo Z均可明显阻断AngⅡ诱导的p70S6激酶激活; ② 细胞受AngⅡ和 PDGF刺激后,形成Ras-PI3K-PKC-ζ功能复合体,wortmannin和chelerythrine可抑制这个功能复合体的形成。以前认为AngⅡ主要引起VSMC肥大, 近年发现AngⅡ也具有生长因子的特性,可引起细胞增殖[1,13]。已知生长因子通过其细胞膜上的蛋白酪氨酸受体,将信号传给Ras, Ras发生膜转位并激活丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶Raf, 后者是蛋白酪氨酸激酶受体信号传导的中心,Raf通过MEK激活ERK1/2进行信号联级放大,ERK1/2 (又称丝裂素激活的激酶, mitogen-activated protein kinases, MAPK)将信号传至细胞核,启动DNA合成和相关蛋白合成, 促进VSMC增殖。然而,AngⅡ 并不作用于蛋白酪氨酸受体, 而是作用于7-TM受体(seven transmembrane receptors, 7-TM)。7-TM受体是一种G-蛋白受体, 并不具有酪氨酸激酶活性。那么,AngⅡ是怎样促进细胞增殖的呢? 不少文献报道提示蛋白酪氨酸受体与7-TM受体之间存在相互"对话"(cross talk)[19~21]。AngⅡ可借道生长因子信号传递通路。文献[21,22]报道AngⅡ可激活细胞内多种蛋白激酶及其信号通道,如Raf、PKC、PI3K、PLC等等。一般认为AngⅡ可通过两条途径激活p70S6激酶: 一条可能通过Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK1/2途径。作者以前的研究发现Raf在AngⅡ激活ERK1/2中并不起主要作用,而由PKC-ζ 取而代之[11,12]。另一条可能通过Ras-PI3K途径[8~10,12],然而,其详细通路并不清楚。 文献[14~16]报道PKC-ζ参与p70S6激酶的调节并介导其上游PI3K的效应,PKC-ζ的活性依赖于PI3K的产物PIP3。我们推测PKC-ζ和PI3K联合参与AngⅡ激活p70S6激酶的调节。本实验观察到VSMC优势表达p85PI3K和PKC-ζ, AngⅡ剂量依赖性地激活p70S6激酶。 Rapamycin、wortmannin和Pseudo Z均可阻断AngⅡ的作用。有趣的是,我们发现细胞受AngⅡ和 PDGF刺激后,形成Ras-PI3K-PKC-ζ功能复合体,抗Ras抗体和抗PI3K抗体可混合沉淀PKC-ζ, wortmannin和pseudo Z均可阻断此复合体的形成。此外,我们用VSMC增殖作为终点指标分析了PI3K和PKC-ζ的作用, 观察到PI3K抑制剂wortmannin和非特异性PKC抑制剂chelerythrine均可明显抑制AngⅡ诱导的VSMC增殖。结合以前的工作,我们提出AngⅡ激活血管平滑肌细胞p70S6激酶可能包含如下信号传导途径:AngⅡ 作用于VSMC AT1受体,激活PI3K, 活化的PI3K诱导PKC-ζ一同与Ras结合形成功能复合体, 并激活PKC-ζ, 最终激活p70S6激酶, 导致VSMC增殖(图5, Figure 5)。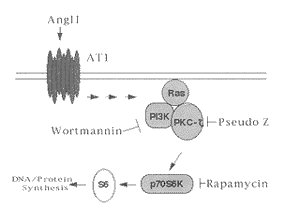
, 百拇医药
图5 血管紧张素Ⅱ经由Ras-磷酶肌醇-3激酶-蛋白激酶C-ζ激活p70核蛋白体S6激酶的途径
Figure 5 AngⅡ activates p70S6K via the Ras-PI3K-PKC-ζ pathway.
[致谢] 本文部分工作在美国华盛顿大学Dr. Berk实验室和加拿大哥伦比亚大学Dr. Pelech实验室完成。
[基金项目] 国家自然科学基金资助课题(39970847)
[作者简介] 廖端芳,男,湖南省沅江市人,1959年出生,博士研究生。关永源,男,广东省人,中山医科大学药理学教授,博士研究生导师,国务院学位委员会药学科评议组成员,《中国药理学通报》常务编委,中国药理学会心血管专业委员会常务委员。
参考文献
, http://www.100md.com
[1] Berk BC. Angiotensin Ⅱ signal transduction in vascular smooth muscle: pathways activated by specific tyrosine kinases [J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 1999, 10: S62-S68
[2] Taubman MB, Berk BC, Izumo S, et al. Angiotensin Ⅱ induces c-fos mRNA in aortic smooth muscle cells: role of Ca2+ mobilization and protein kinase C activation [J]. J Biol Chem, 1989, 264: 526-530
[3] Molloy CJ, Taylor DS, Weber H. Angiotensin Ⅱ stimulation of rapid protein tyrosine phosphorylation and protein kinase activation in rat aortic smooth muscle cells [J]. J Biol Chem, 1993, 268 (10): 7 338-345
, 百拇医药
[4] Duff JL, Berk BC, Corson MA. Angiotensin Ⅱ stimulates the pp44 and pp42 mitogen-activated protein kinases in cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells [J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 1992, 188: 257-264
[5] Griendling KK, Ushio-Fukai M, Lassegue B, et al. Angiotensin Ⅱ signaling in vascular smooth muscle. New concepts [J]. Hypertension, 1997, 29 (1 Pt 2): 366-373
[6] Pullen N, Thomas G. The modular phosphorylation and activation of p70S6k [J]. FEBS Lett, 1997, 410 (1): 78-82
, 百拇医药
[7] Avruch J. Insulin signal transduction through protein kinase cascades [J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 1998, 182 (1-2): 31-48
[8] Chung J, Grammer TC, Lemon KP, et al. PDGF- and insulin-dependent pp70S6k activation mediated by phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase [J]. Nature, 1994, 370 (6484): 71-75
[9] Giasson E, Meloche S. Role of p70S6 protein kinase in angiotensin Ⅱ-induced protein synthesis in vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. J Biol Chem, 1995, 270 (10): 5 225-231
, 百拇医药
[10] Sadoshima J, Izumo S. Rapamycin selectively inhibits angiotensin Ⅱ-induced increase in protein synthesis in cardiac myocytes in vitro. Potential role of 70-kD S6 kinase in angiotensin Ⅱ-induced cardiac hypertrophy [J]. Circ Res, 1995, 77 (6): 1 040-052
[11] Liao DF, Duff JL, Daum G, et al. Angiotension Ⅱ stimulates MAP kinase kinase kinase activity in vascular smooth muscle cell. Role of Raf [J]. Circ Res, 1996, 79 (5): 1 007-014
, 百拇医药
[12] Liao DF, Monia B, Dean N, et al. Protein kinase C-ζ mediates angiotensin Ⅱ activation of ERK1/2 in vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. J Biol Chem, 1997, 272: 6 146-150
[13] Saward L, Zahradka P. Angiotensin Ⅱ activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. Circ Res, 1997, 81 (2): 249-257
[14] Chou MM, Hou W, Johnson J, et al. Regulation of protein kinase C zeta by PI3-kinase and PDK-1 [J]. Curr Biol, 1998, 8 (19): 1 069-077
, 百拇医药
[15] Le Good JA, Ziegler WH, Parekh DB, et al. Protein kinase C isotypes controlled by phosphoinositide 3-kinase through the protein kinase PDK1 [J]. Science, 1998, 281 (5385): 2 042-045
[16] Romanelli A, Martin KA, Toker A, et al. p70S6 kinase is regulated by protein kinase C zeta and participates in a phosphoinositide 3-kinase-regulated signalling complex [J]. Mol Cell Biol, 1999, 19 (4): 2 921-928
[17] Liao DF, Jin ZG, Baas AS, et al. Purification and identification of secreted oxidative stress-induced factors from vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275 (1): 189-196
, 百拇医药
[18] Xu YJ, Ouk Kim S, Liao DF, et al. Stimulation of 90- and 70-kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinases by arginine vasopressin and lysophosphatidic acid in rat cardiomyocytes [J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2000, 59 (9): 1 163-171
[19] Velloso LA, Folli F, Sun XJ, et al. Cross-talk between the insulin and angiotensin signaling systems [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1996, 93 (22): 12 490-495
[20] Eguchi S, Numaguchi K, Iwasaki H, et al. Calcium-dependent epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation mediates the angiotensin Ⅱ-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. J Biol Chem, 1998, 273 (15): 8 890-896
, 百拇医药
[21] Berk BC, Corson MA. Angiotensin Ⅱ signal transduction in vascular smooth muscle: role of tyrosine kinases [J]. Circ Res, 1997, 80 (5): 607-616
[22] Eguchi S, Iwasaki H, Ueno H, et al. Intracellular signaling of angiotensin Ⅱ-induced p70S6 kinase phosphorylation at Ser(411) in vascular smooth muscle cells. Possible requirement of epidermal growth factor receptor, Ras, extracellular signal-regulated kinase, and Akt [J]. J Biol Chem, 1999, 274 (52): 36 843-851
(此文2000-07-11收到, 2000-09-05修回), http://www.100md.com
单位:廖端芳(衡阳医学院心肺药理研究室,衡阳 421001);Berk BC(Center for Cardiovascular Research, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York 14642, USA);关永源(中山医科大学药理学教研室,广州 510089)
关键词:肌,平滑,血管;磷酯肌醇-3激酶;血管紧张素Ⅱ;蛋白激酶C;p70核蛋白体S6激酶
中国动脉硬化杂志000302[摘 要] 作者以前的研究发现蛋白激酶C-ζ介导血管紧张素Ⅱ经Ras-MEK途径激活血管平滑肌细胞丝裂素活化的蛋白激酶MAPK或细胞外信号调节激酶ERK1/2。本文研究了P85磷酯肌醇-3激酶-蛋白激酶C-ζ复合物核蛋白体激酶p70S6激酶活性的调节作用及其信号传递途径。 Western Blot分析显示正常培养的血管平滑肌细胞表达p70S6激酶、p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶和蛋白激酶C-ζ。100 nmol血管紧张素Ⅱ和 10 μg/L 血小板源生长因子刺激并不影响p70S6激酶、p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶和蛋白激酶C-ζ表达。 p70S6激酶磷酸转移酶活性分析发现血管紧张素Ⅱ与血管平滑肌细胞作用5 min 即开始激活p70S6激酶, 20 min达高峰, 并呈剂量依赖性。磷酯肌醇-3激酶抑制剂wortmannin (10 nmol)、蛋白激酶C-ζ 抑制剂Pseudo Z (50 μmol) 和p70S6激酶抑制剂rapamycin (100 μg/L) 均可明显阻断血管紧张素Ⅱ诱导的p70S6激酶激活。有趣的是,我们观察到p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶和蛋白激酶C-ζ受血管紧张素Ⅱ和血小板源生长因子刺激后均向Ras转位并与之结合, 抗Ras抗体可将p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶或蛋白激酶C-ζ混合沉淀, 抗p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶抗体亦可使蛋白激酶C-ζ沉淀下来。 提示Ras、p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶和蛋白激酶C-ζ三种蛋白结合在一起形成一个功能复合体,Wortmannin和Pseudo Z可阻断这个功能复合体的形成。此外,血管紧张素Ⅱ和血小板源生长因子与血管平滑肌细胞孵育24 h 明显促进细胞增殖,氚标胸腺嘧啶脱氧核苷掺入率增加约50%, Wortmannin和非特异性蛋白激酶C抑制剂Chelerythine均抑制血管紧张素Ⅱ和血小板源生长因子对血管平滑肌细胞的促增殖作用。综合上述结果, 说明血管紧张素Ⅱ通过Ras-磷酯肌醇-3激酶-蛋白激酶C-ζ途径激活p70S6激酶和刺激血管平滑肌细胞增殖, p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶-蛋白激酶C-ζ 复合物在其中起重要调节作用。
, http://www.100md.com
[中图分类号] Q55 [文献标识码] A
[文章编号] 1007-3949(2000)-03-0193-06
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Protein Kinase C-ζ Complex Regulates Angiotensin Ⅱ Activation of p70 Ribosomal S6 Kinase in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
LIAO Duan-Fang
(Division of Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology, Hengyang Medical College, Hengyang 421001, China.)
Bradford C BERK
, 百拇医药
(Center for Cardiovascular Research, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York 14642, USA)
GUAN Yong-Yuan
(Department of Pharmacology, Sun Yat-sen University of Medicine Sciences, Guangzhou 510089)
ABSTRACT Aim To investigate the effects of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase C-ζ (PKC-ζ)complex on regulating angiotensin Ⅱ(AngⅡ) activation of p70 ribosomal S6 kinase (p70S6K) in vascular smooth muscle cells(VSMC). Methods VSMC isolated from 200 g to 250 g male Sprague-Dawley rats were cultured to 70% to 80% confluence and were growth-arrested by incubation in 0.1% calf serum/DMEM for 48 h before use. Both 3 H-TdR incorporation and cell counting were used to estimate the proliferation of VSMC. Western blot, immunoprecipitation and immunoblot analyses were performed to valuate the AngⅡ-stimulated kinase expression and Ras-PI3K-PKC-ζ association of VSMC. Phosphotransferase assay by using S6 peptide as substrate was employed to measure the p70 S6K activity. Results VSMC expressed p85PI3K, PKC-ζ and p70S6K; AngⅡ and PDGF stimulation did not affect the p85PI3K, PKC-ζ and p70S6K expression. 2) 100 nmol AngⅡ treatment obviously stimulated p70S6K activity of VSMC at 5 min with peak at 20 min. PI3K inhibitor wortmannin (10 nmol) and pseudosubstrate of PKC-ζ pseudo Z (50 μmol) blocked AngⅡ activation of p70S6K. 3) In response to AngⅡ, PI3K translocated to the membrane and associated with Ras as shown by PI3K coprecipitation with Ras antibody. Furthermore, both anti-Ras and anti-PI3K antibodies could precipitate PKC-ζ, suggesting that AngⅡ treatment resulted in formation of Ras-PI3K-PKC-ζ complex. Wortmannin and pseudo Z significantly blocked the complex formation. 4) In addition, 100 nmol AngⅡ and 10 ng/mL PDGF incubation with VSMC for 24 hours stimulated VSMC proliferation, which could be abrogated by wortmannin and nonspecific PKC inhibitor chelerythrine. Conclusion This findings demonstrate that AngⅡ stimulation of p70S6K occurs via a pathway of Ras-PI3K-PKC-ζ and p85PI3K-PKC-ζcomplex play an important role in this procedure
, 百拇医药
MeSH Angiotensin Ⅱ; Phosphotransferases, Phosphatidylinositol; Protein Kinase C; Phosphotransferases, RNA Ribosomal S6; Muscle, Smooth, Vascular
血管紧张素Ⅱ(angiotensin Ⅱ, AngⅡ) 在血管平滑肌细胞(vascular smooth muscle cells, VSMC)增殖和肥大过程中起重要作用[1]。文献[2-4]报道AngⅡ增加细胞内钙离子浓度、激活蛋白激酶C(protein kinase C, PKC)、活化一系列由生长因子诱导的信号传导通路,如激活蛋白酪氨酸激酶、激活丝裂素活化的蛋白激酶(mitogine activated-protein kinase, MAPK)或细胞外信号调节激酶(extracelluar signal-regulated kinases 1/2, ERK1/2) 等等。P70核蛋白体激酶(p70 ribosomal S6 kinase, p70S6激酶)系丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶家族成员。当细胞参与对生长因子、分裂等早期反应时,p70S6激酶被激活。文献报道在球囊损伤的大鼠主动脉和心衰心脏,p70S6激酶被迅速激活[1,5]。P70S6K通过调节mRNA的翻译过程实现对细胞生长的调控[6,7], p70S6激酶的活化受其上游磷酯肌醇-3激酶(phosphatidylinositol 3-kinse, PI3K)的调节[8]。文献[9,10]报道AngⅡ 可刺激培养的VSMC和心肌细胞 p70S6激酶活性, 然而其信号传导途径并不清楚,推测与Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK1/2有关。作者以前的工作显示Raf 在AngⅡ 激活ERK1/2过程中并不起主要作用,而由PKC-ζ取而代之[11,12]。Saward 等[13]报道1 μmol AngⅡ与VSMC作用15 min可激活PI3K,使PI3K p85亚单位酪氨酸磷酸化并发生膜转位。近年不少文献显示PKC-ζ是PI3K的下游效应蛋白, 同时也参与p70S6激酶的调节, 其活性受PI3K代谢产物PtdIns(3-5)P(3)的调控[14-16]。因而,我们推测PKC-ζ亦可能介导AngⅡ激活p70S6激酶, 并提出PI3K-PKC-ζ联合调控p70S6激酶活性的工作假设。
, 百拇医药
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
抗H-Ras抗体和抗PKC-ζ抗体分别购自Boehringer Mannheim和Santa Cruz公司,抗p70S6激酶抗体和抗p85PI3K抗体购自Upstate Biotechnology Inc公司,S6肽由加拿大Kinetek Pharmaceuticals Inc公司赠送,[r-32P]ATP为Dupont公司产品,Protein A-agarose 为Life Technologies Inc公司产品,wortmannin、chelerythrine和rapamycin 为Sigma公司产品,PKC-ζ假性底物购自Calbiochem公司(La Jolla, CA)。
1.2 血管平滑肌细胞培养
参照文献[17],从200~250 g雄性Sprague Dawley大鼠胸主动脉分离出VSMC,用含10%小牛血清的DMEM培养基培养。取5~13代VSMC于100 cm培养皿中培养至70%~80%融合,用含0.1%小牛血清的DMEM培养基继续培养48 h使VSMC处于静止状态,然后用AngⅡ、 PDGF等刺激20 min。PI3K的抑制剂Wortmnnin、非特异性PKC-抑制剂Chelerythine、PKC-ζ 抑制剂(PKC-ζ假性底物)Pseudo Z和p70S6激酶抑制剂rapamycin于AngⅡ、PDGF之前10 min加入。
, http://www.100md.com
1.3 细胞蛋白提取与浓度测定
血管紧张素Ⅱ(AngⅡ)、 PDGF作用后的VSMC用磷酸缓冲液洗三次,每皿加1.0 mL TME缓冲液(10 mmol Tris, 5 mmol MgCl2, 1 mmol EDTA, 25 mmol NaF, pH 7.5;临用前加100 μmol Na3VO4, 20 mg/L leupeptin, 1 mg/L pepstatin A, 4 mg/L aprotinin, 1 mmol DTT) 裂解细胞。速冻, 冰浴上缓慢复苏,刮下细胞,冰浴上用超声粉碎细胞,15 000g离心30 min, 取上清液,按Bradford蛋白测定盒说明书测定蛋白浓度,样品贮存于-80℃待用。
1.4 p70S6激酶活性测定
参照文献[18],取抗p70S6激酶抗体免疫沉淀物(50% bead slurry) 5 μL, 加30 μL反应缓冲液(25 mmol b-glycerophosphate, 20 mmol MOPS, pH 7.2, 5 mmol EGTA, 2 mmol EDTA, 20 mmol MgCl2, 1 mmol Na3VO4, 0.25 mmol dithiothreitol), 加4 μg 底物S6寡肽和50 μmol [r-32 P]ATP(2×1015 dpm/mol), 于30℃反应15 min, 取20 μL反应混合物点样于2 cm2 p81 phosphocellulose 反应纸(Whatman公司),用含1% orthophosphoric acid 去离子水冲洗三次,用r-计数器记录放射活性。
, http://www.100md.com
1.5 Western Blot 实验
参照文献[11],配制9%的SDS-PAGE分离胶和3%的积层胶,每孔加入20 μg蛋白样品,置电泳缓冲液中,70 V电泳约20 min。待样品进入分离胶后,150 V电泳至所需时间。 将蛋白转印至硝酸纤维薄膜,用Life Technologies公司商用封闭液于室温处理2 h,按1∶200加p70S6激酶、p85PI3K或PKC-ζ单抗, 4℃过夜,TBS液洗膜10 min×3次,用辣根过氧化物酶试剂盒(ECL, Amersham International plc. United Kingdom)显色。
1.6 Ras-磷酯肌醇-3激酶-蛋白激酶C-ζ混合沉淀实验
参照文献[12],取TME缓冲液提取的蛋白,加抗Ras单抗或p85PI3K单抗和protein A-agarose于4℃混合12 h进行免疫沉淀(immunoprecipitation, IP)。 Protein A-agarose用TME缓冲液洗一次,TTBS缓冲液(20 mmol Tris, pH 7.5, 500 mmol NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, 0.1% beta-mercaptoethanol)洗二次, 再用TME缓冲液洗一次。然后,用9%的SDS-PAGE胶将免疫复合物分离, 用抗p85PI3K和PKC-ζ单抗进行免疫印迹(immunoblot, IB)实验。
, 百拇医药
1.7 细胞计数与氚标胸腺嘧啶脱氧核苷掺入实验
参照文献[13],取生长良好的VSMC制成细胞悬液(4×107个/L)接种于24孔培养板中,每孔0.5 mL(2×104个细胞),孵育24 h。换无血清培养基继续孵育24 h后,使VSMC处于静止期,加小牛血清至浓度为10%,同时分组加入100 nmol AngⅡ(终浓度,下同) 或10 μg/L PDGF(终浓度,下同)。 Wortmannin (终浓度10 nmol,下同)、chelerythrine (终浓度10 μmol,下同)和rapamycin(终浓度100 nmol,下同)于AngⅡ、PDGF前10 min 加入,对照组为只含10%小牛血清的DMEM培养基, 继续培养24 h。然后进行下列实验: ①细胞消化液分离细胞,以4%台盼蓝染色计数。② 继续培养18 h, 加氚标胸腺嘧啶脱氧核苷(3 H-thymine deoxyribonucleotide, 3 H-TdR)至终浓度为2 mCi/L, 6 h后收样,弃含3 H-TdR培养基,用D-hanks液洗三次,以细胞消化液消化。用真空泵将细胞抽吸于玻璃纤维滤纸上,5%三氯醋酸固定,无水乙醇脱水,干燥后置闪烁瓶中加闪烁液(甲苯500 mL, PPO 3, POPOP 0.1 g)于液体闪烁分析仪(Packard 公司 )测放射性强度,以每分钟衰减数(decay per minute, dpm或d/min)表示。
, http://www.100md.com
1.8 统计处理
数据以
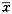 ±s表示,数据经方差分析后进行q检验,差异的显著性用P<0.05和P<0.01判断。
±s表示,数据经方差分析后进行q检验,差异的显著性用P<0.05和P<0.01判断。2 结 果
2.1 血管平滑肌细胞表达p70核蛋白体S6激酶、p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶和蛋白激酶C-ζ
Western Blot 分析发现正常培养的VSMC表达p70S6激酶、p85PI3K亚单位和PKC-ζ, AngⅡ和 PDGF刺激并不影响p70S6激酶、p85PI3K亚单位和PKC-ζ的表达(图1, Figure 1)。

图1 血管平滑肌细胞表达p70核蛋白体S6激酶、p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶亚型和蛋白激酶C-ζ
, http://www.100md.com
Figure 1 VSMC express p70S6K, p85PI3K subtype and PKC-ζ Western blot analysis was carried out with anti- p70S6K antibody (A), anti-p85PI3K antibody (B) and anti- p70S6K, antibody (C), respectively.
2.2 血管紧张素Ⅱ激活血管平滑肌细胞p70核蛋白体S6激酶
图2 (Figure 2) 显示AngⅡ与VSMC作用5 min即开始激活p70S6激酶, 20 min达高峰,约为处理前的5倍,随后逐渐降低(A), 并呈剂量依赖性(B)。p70S6激酶抑制剂rapamycin (100 nmol)、PI3K抑制剂wortmannin(10 nmol)和PKC-ζ抑制剂Pseudo Z (50 μmol)均可有效阻断AngⅡ的作用(图3, Figure 3)。
, 百拇医药
2.3 血管紧张素Ⅱ刺激Ras-磷酯肌醇-3激酶-蛋白激酶C-ζ复合物形成
细胞受AngⅡ和 PDGF刺激后,可观察到PI3K向Ras转位并与之结合的现象, 在抗Ras抗体沉淀的蛋白中有PI3K存在。图3A(Figure 3A)中可见抗Ras抗体沉淀的蛋白电泳分离转膜后再用抗PI3K抗体杂交可显示p85条带, wortmannin 10 nmol可阻断Ras-PI3K相互结合。图4B和图4C(Figure 4B and 4C)中可见不但抗Ras抗体可将PKC-ζ混合沉淀(B); 而且抗PI3K抗体也可将PKC-ζ沉淀下来, PI3K、PKC-ζ之间的相互作用亦可被wortmannin和pseudo Z阻断(C)。由此,我们可以推断细胞受AngⅡ和 PDGF刺激后, Ras、PI3K、PKC-ζ三种蛋白结合在一起形成一个功能复合体。Wortmannin和pseudo Z可阻断这个功能复合体的形成, 说明PI3K-PKC-ζ在这个功能复合体中起重要作用。

, 百拇医药
图2 血管紧张素Ⅱ对血管平滑肌细胞p70核蛋白体S6激酶活性的影响
Figure 2 The effects of AngⅡ on p70S6K activity of VSMC A: Time-course of AngⅡ on p70S6K activity. B: Concentration-response of AngⅡ on p70S6K activity.

图3 p70核蛋白体S6激酶抑制剂rapamycin、磷酯肌醇-3激酶抑制剂wortmannin和蛋白激酶C-ζ抑制剂pseudo Z对血管紧张素Ⅱ活化血管平滑肌细胞p70核蛋白体S6激酶的影响
Figure 3 The effects of p70S6K inhibitor rapamycin,PI3K inhibitor wortmannin and PKC-ζ inhibitor pseudo Z on AngⅡ activation of p70S6K in VSMC a: P<0.01 compared with control grpip, b: P<0.01 compared with AngⅡ group, c: P<0.01 compared with PDGF group.

, 百拇医药
图4 p85磷酯肌醇-3激酶和蛋白激酶C与Ras的联系
Figure 4 Ras association with p85PI3K and PKC-ζ A and B. p85PI3K and PKC-ζ were immuno-precipitated (IP) with Ras antibody. C. PKC-ζ was immuno-precipitated (IP) by p85PI3K antibody.
2.4 Wortmannin和chelerythrine阻断血管紧张素Ⅱ诱导血管平滑肌细胞增殖
台盼蓝染色细胞计数和3 H-TdR掺入法分析显示AngⅡ(100 nmol)和PDGF (10 μg/L)均有较强的刺激VSMC增殖的作用,AngⅡ和PDGF处理组细胞计数明显高于对照组,3 H-TdR掺入量显著增加。Wortmannin 和chelerythrine 均可阻断AngⅡ和PDGF的作用(表1, Table 1)。
, http://www.100md.com
表1 血管紧张素Ⅱ、血小板源生长因子、Wortmannin和chelerythrine对血管平滑肌细胞增殖的影响
Table 1 Effects of Ang Ⅱ, PDGF, wortmannin and chelerythrine on VSMC proliferation (n=6,
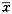 ±s) Groups
±s) GroupsCell number
(×104)
3 H-TdR incorporation
(dpm)
Control
, 百拇医药
2.26±0.14
503±51
AngⅡ
3.32±0.29a
740±75a
PDGF
3.51±0.46a
754±95a
Wortmannin
2.25±0.21
512±41
, 百拇医药
AngⅡ+Wortmannin
2.32±0.12b
540±34b
PDGF+Wortmannin
2.31±0.23c
542±60c
Chelerythrine
2.42±0.43
493±75
AngⅡ+Chelerythrine
, 百拇医药
2.47±0.43b
550±84b
PDGF+Chelerythrine
2.42±0.36c
560±71c
a:P<0.01 vs control; b: P<0.01 vs Ang Ⅱ; c: P<0.01 vs PDGF
3 讨 论
本文的主要发现是PKC-ζ和PI3K联合调节AngⅡ激活血管平滑肌细胞核蛋白体激酶p70S6激酶。有如下两点支持这一结论:①AngⅡ与VSMC作用5 min 即开始激活p70S6激酶, 20 min达高峰, 并呈剂量依赖性。P70S6K抑制剂rapamycin、 PI3K抑制剂wortmannin和PKC-ζ抑制剂(PKC假性底物) Pseudo Z均可明显阻断AngⅡ诱导的p70S6激酶激活; ② 细胞受AngⅡ和 PDGF刺激后,形成Ras-PI3K-PKC-ζ功能复合体,wortmannin和chelerythrine可抑制这个功能复合体的形成。以前认为AngⅡ主要引起VSMC肥大, 近年发现AngⅡ也具有生长因子的特性,可引起细胞增殖[1,13]。已知生长因子通过其细胞膜上的蛋白酪氨酸受体,将信号传给Ras, Ras发生膜转位并激活丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶Raf, 后者是蛋白酪氨酸激酶受体信号传导的中心,Raf通过MEK激活ERK1/2进行信号联级放大,ERK1/2 (又称丝裂素激活的激酶, mitogen-activated protein kinases, MAPK)将信号传至细胞核,启动DNA合成和相关蛋白合成, 促进VSMC增殖。然而,AngⅡ 并不作用于蛋白酪氨酸受体, 而是作用于7-TM受体(seven transmembrane receptors, 7-TM)。7-TM受体是一种G-蛋白受体, 并不具有酪氨酸激酶活性。那么,AngⅡ是怎样促进细胞增殖的呢? 不少文献报道提示蛋白酪氨酸受体与7-TM受体之间存在相互"对话"(cross talk)[19~21]。AngⅡ可借道生长因子信号传递通路。文献[21,22]报道AngⅡ可激活细胞内多种蛋白激酶及其信号通道,如Raf、PKC、PI3K、PLC等等。一般认为AngⅡ可通过两条途径激活p70S6激酶: 一条可能通过Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK1/2途径。作者以前的研究发现Raf在AngⅡ激活ERK1/2中并不起主要作用,而由PKC-ζ 取而代之[11,12]。另一条可能通过Ras-PI3K途径[8~10,12],然而,其详细通路并不清楚。 文献[14~16]报道PKC-ζ参与p70S6激酶的调节并介导其上游PI3K的效应,PKC-ζ的活性依赖于PI3K的产物PIP3。我们推测PKC-ζ和PI3K联合参与AngⅡ激活p70S6激酶的调节。本实验观察到VSMC优势表达p85PI3K和PKC-ζ, AngⅡ剂量依赖性地激活p70S6激酶。 Rapamycin、wortmannin和Pseudo Z均可阻断AngⅡ的作用。有趣的是,我们发现细胞受AngⅡ和 PDGF刺激后,形成Ras-PI3K-PKC-ζ功能复合体,抗Ras抗体和抗PI3K抗体可混合沉淀PKC-ζ, wortmannin和pseudo Z均可阻断此复合体的形成。此外,我们用VSMC增殖作为终点指标分析了PI3K和PKC-ζ的作用, 观察到PI3K抑制剂wortmannin和非特异性PKC抑制剂chelerythrine均可明显抑制AngⅡ诱导的VSMC增殖。结合以前的工作,我们提出AngⅡ激活血管平滑肌细胞p70S6激酶可能包含如下信号传导途径:AngⅡ 作用于VSMC AT1受体,激活PI3K, 活化的PI3K诱导PKC-ζ一同与Ras结合形成功能复合体, 并激活PKC-ζ, 最终激活p70S6激酶, 导致VSMC增殖(图5, Figure 5)。

, 百拇医药
图5 血管紧张素Ⅱ经由Ras-磷酶肌醇-3激酶-蛋白激酶C-ζ激活p70核蛋白体S6激酶的途径
Figure 5 AngⅡ activates p70S6K via the Ras-PI3K-PKC-ζ pathway.
[致谢] 本文部分工作在美国华盛顿大学Dr. Berk实验室和加拿大哥伦比亚大学Dr. Pelech实验室完成。
[基金项目] 国家自然科学基金资助课题(39970847)
[作者简介] 廖端芳,男,湖南省沅江市人,1959年出生,博士研究生。关永源,男,广东省人,中山医科大学药理学教授,博士研究生导师,国务院学位委员会药学科评议组成员,《中国药理学通报》常务编委,中国药理学会心血管专业委员会常务委员。
参考文献
, http://www.100md.com
[1] Berk BC. Angiotensin Ⅱ signal transduction in vascular smooth muscle: pathways activated by specific tyrosine kinases [J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 1999, 10: S62-S68
[2] Taubman MB, Berk BC, Izumo S, et al. Angiotensin Ⅱ induces c-fos mRNA in aortic smooth muscle cells: role of Ca2+ mobilization and protein kinase C activation [J]. J Biol Chem, 1989, 264: 526-530
[3] Molloy CJ, Taylor DS, Weber H. Angiotensin Ⅱ stimulation of rapid protein tyrosine phosphorylation and protein kinase activation in rat aortic smooth muscle cells [J]. J Biol Chem, 1993, 268 (10): 7 338-345
, 百拇医药
[4] Duff JL, Berk BC, Corson MA. Angiotensin Ⅱ stimulates the pp44 and pp42 mitogen-activated protein kinases in cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells [J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 1992, 188: 257-264
[5] Griendling KK, Ushio-Fukai M, Lassegue B, et al. Angiotensin Ⅱ signaling in vascular smooth muscle. New concepts [J]. Hypertension, 1997, 29 (1 Pt 2): 366-373
[6] Pullen N, Thomas G. The modular phosphorylation and activation of p70S6k [J]. FEBS Lett, 1997, 410 (1): 78-82
, 百拇医药
[7] Avruch J. Insulin signal transduction through protein kinase cascades [J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 1998, 182 (1-2): 31-48
[8] Chung J, Grammer TC, Lemon KP, et al. PDGF- and insulin-dependent pp70S6k activation mediated by phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase [J]. Nature, 1994, 370 (6484): 71-75
[9] Giasson E, Meloche S. Role of p70S6 protein kinase in angiotensin Ⅱ-induced protein synthesis in vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. J Biol Chem, 1995, 270 (10): 5 225-231
, 百拇医药
[10] Sadoshima J, Izumo S. Rapamycin selectively inhibits angiotensin Ⅱ-induced increase in protein synthesis in cardiac myocytes in vitro. Potential role of 70-kD S6 kinase in angiotensin Ⅱ-induced cardiac hypertrophy [J]. Circ Res, 1995, 77 (6): 1 040-052
[11] Liao DF, Duff JL, Daum G, et al. Angiotension Ⅱ stimulates MAP kinase kinase kinase activity in vascular smooth muscle cell. Role of Raf [J]. Circ Res, 1996, 79 (5): 1 007-014
, 百拇医药
[12] Liao DF, Monia B, Dean N, et al. Protein kinase C-ζ mediates angiotensin Ⅱ activation of ERK1/2 in vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. J Biol Chem, 1997, 272: 6 146-150
[13] Saward L, Zahradka P. Angiotensin Ⅱ activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. Circ Res, 1997, 81 (2): 249-257
[14] Chou MM, Hou W, Johnson J, et al. Regulation of protein kinase C zeta by PI3-kinase and PDK-1 [J]. Curr Biol, 1998, 8 (19): 1 069-077
, 百拇医药
[15] Le Good JA, Ziegler WH, Parekh DB, et al. Protein kinase C isotypes controlled by phosphoinositide 3-kinase through the protein kinase PDK1 [J]. Science, 1998, 281 (5385): 2 042-045
[16] Romanelli A, Martin KA, Toker A, et al. p70S6 kinase is regulated by protein kinase C zeta and participates in a phosphoinositide 3-kinase-regulated signalling complex [J]. Mol Cell Biol, 1999, 19 (4): 2 921-928
[17] Liao DF, Jin ZG, Baas AS, et al. Purification and identification of secreted oxidative stress-induced factors from vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275 (1): 189-196
, 百拇医药
[18] Xu YJ, Ouk Kim S, Liao DF, et al. Stimulation of 90- and 70-kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinases by arginine vasopressin and lysophosphatidic acid in rat cardiomyocytes [J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2000, 59 (9): 1 163-171
[19] Velloso LA, Folli F, Sun XJ, et al. Cross-talk between the insulin and angiotensin signaling systems [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1996, 93 (22): 12 490-495
[20] Eguchi S, Numaguchi K, Iwasaki H, et al. Calcium-dependent epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation mediates the angiotensin Ⅱ-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. J Biol Chem, 1998, 273 (15): 8 890-896
, 百拇医药
[21] Berk BC, Corson MA. Angiotensin Ⅱ signal transduction in vascular smooth muscle: role of tyrosine kinases [J]. Circ Res, 1997, 80 (5): 607-616
[22] Eguchi S, Iwasaki H, Ueno H, et al. Intracellular signaling of angiotensin Ⅱ-induced p70S6 kinase phosphorylation at Ser(411) in vascular smooth muscle cells. Possible requirement of epidermal growth factor receptor, Ras, extracellular signal-regulated kinase, and Akt [J]. J Biol Chem, 1999, 274 (52): 36 843-851
(此文2000-07-11收到, 2000-09-05修回), http://www.100md.com