茶多酚对重复+Gz暴露大鼠脑脂质过氧化反应和肝肾功能的影响
作者:詹 皓 陈立敏 辛益妹 唐桂香 温 静
单位:詹 皓.空军航空医学研究所,北京 100036
关键词:加速度应激;脂质过氧化作用;肝功能;肾功能;抗氧化剂;茶多酚;大鼠
航天医学与医学工程990101Effects of Tea Polyphenols on Cerebral Lipid Peroxidation,Liver and Renal Functions in Rats after Repeated +Gz Stress*
ZHAN Hao XIN Yi-mei TANG Gui-xiang
(Institute of Aviation Medicine,Beijing 100036,China)
, http://www.100md.com
CHEN Li-ming WEN Jing
(General Hospital of Air Force,PLA,Beijing 100036,China)
Abstract:Objective To observe the effects of repeated +10 Gz stress on cerebral lipid peroxidation,liver and renal function in rats and the prophylactic effects of antioxidant tea polyphenols(TP).Method Twenty-four male Wistar rats were randomly divided into three groups(n=8 each):group A(control),group B(+10 Gz),and group C(TP).Group B and C were exposed to repeated +10 Gz stress(each for 30s,onset rate about 0.5 G/s,3 times/d with +1 Gz 1 min intervals,3 d/wk,4 weeks in total),but group A was only submitted to +1 Gz.TP(200 mg/kg) was given orally in group C about 1 h prior to the +Gz experiment,while distilled water was given in group A and B.Lipid peroxidation in the brain,liver and renal functions and serum lipids were determined.Results As compared with the control,lipid peroxidation in rat cerebral homogenate,mitochondria and cytoplasm was significantly increased( P<0.05),and serum creatinine concentration was markedly elevated after repeated +10 Gz stress(P<0.01).But,TP had significant inhibitory effect on +10 Gz stress induced peroxidative injury in rat brain and reduced the serum creatinine level.There were no differences of serum triglyceride and total cholesterol concentrations and glutamic-pyruvic transaminase activity among the three groups.Conclusion These results indicated that repeated high +Gz stress could bring about peroxidative injury in brain and harmful effect on renal function,and natural antioxidant TP had signficant protective effects.
, 百拇医药
Key words:acceleration stress;lipid peroxidation;liver function;renal function;antioxidant;tea polyphenols;rat
摘要:目的 观察重复+10 Gz暴露对大鼠脑脂质过氧化反应和肝肾功能的影响以及天然抗氧化剂茶多酚(TP)的防护作用。方法 24只雄性Wistar大鼠随机等分为三组(n=8):A组(对照组),B组(+10 Gz组)和C组(TP组)。B、C组重复+10 Gz暴露(每次30 s,G增长率约为0.5 G/s,3次/d,间隔+1 Gz 1min,3 d/wk,共4 wk),而A组仅受+1 Gz作用。C组于+Gz实验前约1 h灌胃给予TP(200 mg/kg),另外两组给予等量蒸馏水。测定脑脂质过氧化反应、肝肾功能和血脂水平。结果 与对照组相比,B组大脑皮层匀浆、线粒体和胞浆脂质过氧化反应明显增强(P<0.05),血浆肌酐水平明显升高(P<0.01);而TP对此过氧化反应具有显著抑制作用并明显降低血浆肌酐水平。各组间血清谷丙转氨酶活性、甘油三酯和总胆固醇水平无统计学差异。结论 重复高+Gz作用可引起脑自由基损伤并损害肾功能,而天然抗氧化剂茶多酚具有明显的保护作用。
, 百拇医药
中图法分类号:R852.21 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1002-0837(1999)01-0001-05
Many studies have shown the occurrence of free radical generation and lipid peroxidation in ischemic or injuried brain tissue,and the protective effects of antioxidants and free radical scavengers provide further evidence for the involvement of oxygen free radicals and lipid peroxidation in case of brain ischemia or trauma[1,2].It has been found that repeated +Gz exposure could bring about effects on brain tissue similar to ischemia and reperfusion or hypoxia and reoxygenetion[3],and induced brain injury[4].But,in aviation medicine,the role of free radical metabolism in +Gz exposure induced brain injury hasn't been systematically studied.In our previous study,it was shown that +10 Gz stress(3 times each for 3 min with 40 min intervals) could induce peroxidative injury in rat brain.Malondialdehyde(MDA) content in cerebral mitochondria was significantly increased after +10 Gz exposure,but in cytoplasm,there was no such difference in MDA concentration between the control and +10 Gz stressed rats[5].After pretreatment with antioxidant tea polyphenols(TP) at dose of 30 and 100 mg.kg-1.d-1(ip),for three consecutive days,the mitochondrial lipid peroxidation was significantly inhibited.In addition,TP had remarkable protective effect on blood brain barrier injury induced by +10 Gz stress,as indicated by measuring the leakage of Evan's blue,and could substantially elevate mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase(ATPase) activity[6].In this study,we further observed the changes of cerebral lipid peroxidation,liver and renal functions in rats after long-term,repeated +10 Gz stress and the prophylactic effects of antioxidant TP.
, 百拇医药
Materials and Methods
Experimental animal and drug administration Male Wistar rats(193.1±14.2 g,n=24) from the Experimental Animal Center,Chinese Academy of Military Medical Sciences served as test subjects.These animals were randomly divided into three groups(n=8 each):group A(control),group B(+10 Gz) and group C(+10 Gz TP).TP (200 mg/kg) was given orally in group C about 1 h prior to the +Gz experiment,while distilled water was given in group A and B.TP with concentration >97% was produced by Hangzhou Dongya Tea Polyphenol Factory and provided by Professor YANG Xian-qiang of Zhejiang Agriculture University.
, http://www.100md.com
+Gz stress profile Centrifuge for small animals(radius of 2 m) in our institute was used .Rats(without anesthethia) were restrained in a special frame(3 cm in diameter,10 cm in length).The rate of +Gz onset was about 0.5 G/s.Both group B and C were exposed to repeated +Gz stress(each for 30 s,3 times/d with +1 Gz 1 min intervals,3 d/wk,4 weeks in total);the rats in group A were handled in the same way but only submitted to +1 Gz.
Determination of MDA concentration in rat brain The rats were decapitated in the next day after the last centrifuge run,and the brains and serum were collected.Cerebral cortices were homogenized with 1/15 M phosphate buffer(pH 7.4,1∶10,W/V).The homogenate was centrifuged at 2000 g for 5 min,then the supernatant was further centrifuged at 12500g for 20 min.The resulting supernatant and pellet of this centrifugation were the cytosolic and crude mitochondrial function,respectively[7].Malondialdehyde(MDA) contents in cerebral homogenate,mitochondria and cytoplasm were determined by thiobarbituric acid(TBA) reaction[8].Tissue sample was mixed with sodium dodecylsulfate,acetate buffer(pH 3.5) and aqueous solution of TBA.After heating at 95 ℃ for 60 min,the produced red pigment was estimated by the absorbance at 532 nm.1,1,3,3-tetraethoxy-propane(Fluka chemie AG) was used as an MDA standard.MDA content was expressed as nmol/mg protein.
, http://www.100md.com
Assay of superoxide dismutase(SOD) activity Above mentioned cerebral homogenate,mitochondria and cytoplasm were used.Assaying of SOD activity was indirect and based on this enzymatic ability to scavenge superoxide radical( ) from the autoxidation of pyrogallol[9],but slight modification was made.Reaction system contained 4.5 ml of 50 mmol/L K2HPO4-KH2PO4 buffer(pH 8.3) and 10 μl of 50 mmol/L pyrogallol.The rate of autoxidation was taken from the increase in A325 per min.SOD activity was expressed as U/mg protein.
) from the autoxidation of pyrogallol[9],but slight modification was made.Reaction system contained 4.5 ml of 50 mmol/L K2HPO4-KH2PO4 buffer(pH 8.3) and 10 μl of 50 mmol/L pyrogallol.The rate of autoxidation was taken from the increase in A325 per min.SOD activity was expressed as U/mg protein.
, 百拇医药
Measurment of liver and renal functions and serum lipid level BUN(blood urea nitrogen) and serum creatinine levels,serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase(GPT) activity,and serum triglyceride and total cholesterol concentration were analyzed by using ALCYON 300 full automatic biochemical analyzer.Reagent kits were purchased from Chinese High Technical Company(BUN) and Ausio Bioengineering limited Company(creatinine,GPT,triglyceride and total cholesterol) .Serum GPT activity is an indicator of liver function; BUN and serum creatinine levels are commonly used as the parameters of renal functions.
, 百拇医药
Results
Effects of TP on lipid peroxidation in rat brain after repeated + 10 Gz stress The results were presented in table l.It was observed that MDA concentrations in brain homogenate,mitochondria and cytoplasm were significantly increased after repeated +10 Gz stress (compared with the control,P<0.05),but TP inhibited significantly the lipid peroxidation .Compared with group A,mitochondrial and cytoplasmic SOD activities were significantly reduced after repeated +10 Gz stress(P<0.01),but the enzymatic activity in the animals treated with TP increased.
, 百拇医药
Effects of TP on liver and renal functions and serum lipids in rats after repeated +10 Gz stress After repeated +10 Gz stress,serum creatinine concentration was significantly increased(compared with the control,P<0.01).But,compared with group B,TP remarkably decreased serum creatinine level(P<0.05 ).However,there were no differences of liver function and serum lipids among the three groups.These results were shown in table 2.
Table 1 Effects of TP on lipid peroxidation in rat brain after repeated +10Gz stress(n=8,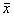 ±s) indices
±s) indices
, 百拇医药
group A
group B
group C
MDA concent(nmol/mg prot)
homogenate
0.382±0.039
0.468±0.117*
0.343±0.069△△
mitochondria
0.572±0.078
0.615±0.072*
, http://www.100md.com
0.553±0.026△
cytoplasm
1.130±0.25
1.360±0.18*
1.150±1.18△
SOD activity(U/mg prot)
mitochondria
2.610±0.88
1.110±0.30**
1.700±0.42*△
, 百拇医药
cytoplasm
19.410±5.55
10.890±1.86**
13.860±5.33*
Note:*P<0.05,**P<0.01,as compared with group A;△P<0.05,△△P<0.01,as compared with group B
Table 2 Effects of TP on liver and renal functions and serum lipids in rats after repeated ±10 Gz stress(n=8,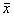 ±s) indices
±s) indices
, 百拇医药
group A
group B
group C
BUN(mmol/L)
9.20±1.55
8.40±0.64
8.75±0.82
creatinine(μmol/L)
83.00±10.7
101.60±6.4**
94.60±6.1**△△
, 百拇医药
GPT activity(U/L)
58.30±11.7
58.30±9.4
54.50±9.8
triglyceride(mmol/L)
1.20±0.25
1.12±0.30
0.99±0.38
total cholesterol(mmol/l)
1.65±0.21
1.74±0.20
, http://www.100md.com
1.71±0.25
Note:**P<0.01,as compared with group A;△△P<0.01,as compared with group B
Discussion
In this study,+Gz stress profile was different from that used in our previous work[5]:each +10 Gz peak acting time was shorter,but repetitions were significantly more.Therefore,+Gz induced peroxidative injury in rat brain in this study (or long-term +Gz experiment) was quite different from that of our previous investigation(or acute +Gz experiment)[5].In general,cells of various types contain several enzymes to scavenger superoxide radical( ) coordinately.SOD exists in two major forms,as a copper-zinc containing enzyme in cytoplasm and a manganese containing enzyme in mitochondria.SOD c atalyzes the dismutation of
) coordinately.SOD exists in two major forms,as a copper-zinc containing enzyme in cytoplasm and a manganese containing enzyme in mitochondria.SOD c atalyzes the dismutation of  to yield H2O2 and
to yield H2O2 and  .Although the central nervous system contains very little catalase,it has more glutathione peroxidase (GSHpx) for decomposition of H2O2 and organic peroxides.In normal rat cerebral cortex,CuZn-SOD(located mainly in cytoplasm) content was(93.2±8.2)μg/g tissue and (1.02±0.05)μg/mg protein;and Mn-SOD(located mainly in mitochondrial) content was(62.0±5.4)μg/g tissue and (0.69±0.06)μg/mg protein,respectively[10].In acute +Gz experiment,it was observed that only mitochondrial MDA formation in cerebral cortex was significantly increased after +10 Gz stress,while in cytoplasm,there was no such increase.Cytoplasmic SOD and GSHpx activities were significantly increased after acute +10 Gz stress; but there was no significant change of these enzymatic activities in mitochondria among the control and +10 Gz stressed rats[5,6].Therefore,acute +10 Gz exposure induced mitochondrial peroxidative injury might be related to the differences of antioxidase contents and compensative responses in subcellular fractions after +Gz stress.Long-term,repeated +Gz exposure induced lipid peroxidation in rat brain became more serious,indicating the cumulative effects of free radical injury caused by +Gz stress.
.Although the central nervous system contains very little catalase,it has more glutathione peroxidase (GSHpx) for decomposition of H2O2 and organic peroxides.In normal rat cerebral cortex,CuZn-SOD(located mainly in cytoplasm) content was(93.2±8.2)μg/g tissue and (1.02±0.05)μg/mg protein;and Mn-SOD(located mainly in mitochondrial) content was(62.0±5.4)μg/g tissue and (0.69±0.06)μg/mg protein,respectively[10].In acute +Gz experiment,it was observed that only mitochondrial MDA formation in cerebral cortex was significantly increased after +10 Gz stress,while in cytoplasm,there was no such increase.Cytoplasmic SOD and GSHpx activities were significantly increased after acute +10 Gz stress; but there was no significant change of these enzymatic activities in mitochondria among the control and +10 Gz stressed rats[5,6].Therefore,acute +10 Gz exposure induced mitochondrial peroxidative injury might be related to the differences of antioxidase contents and compensative responses in subcellular fractions after +Gz stress.Long-term,repeated +Gz exposure induced lipid peroxidation in rat brain became more serious,indicating the cumulative effects of free radical injury caused by +Gz stress.
, http://www.100md.com
In normal rats,BUN and serum creatinine concentrations were 1.78~10.35 mmol/l and 17.68~70.73 μmol/L,respectively[ 11].Our experimental results indicated that BUN and serum creatinine levels in the control (group A) were in normal range,but repeated +10 Gz stress had detrimental effects on renal function.DAI et al[12] also reported the harmful effect of +Gz on renal function and structure in rats.Compared with +Gz group,BUN level in +10 Gz stressed rats(3 times each for 3 min ,with 40 min intervals) was elevated by 20.3%(P<0.01).After +10 Gz exposure,vasoconstriction was observed by optical microscopic examination,and pathological changes of ultrastructure and mitochondria of glomeruli and renal tubules were found by electron microscopic examination.WU et al[13] observed G-induced changes in urine properties of pilots.The specific gravity of urine were significantly higher post riding(high G training) than pre-riding.Proteinuria was noted in post riding urine samples of twenty-five pilots(58%) who had not had proteinuria before exposed to high G environment .These results were in accordance with our experiment and indicated that the effects of repeated +Gz stress on the renal function were profound.
, 百拇医药
Scaveging effects of natural antioxidant TP on and OH· were proved by the electron spin trapping and chemiluminescence methods.In isolated rat cerebral mitochondria and rat's incomplete cerebral ischemic/reperfusion injury models,lipid peroxidation was significantly inhibited by TP,while the mitochondrial ATPase acti-vity was remarkably increased after administration of this antioxidant[14].Protective effects of TP on acute + 10 Gz exposure induced brain mitochondrial peroxidation and blood brain barrier injury were observed[6].In addition,short-term(100 mg.kg-1.d-1,3 d,ip) and long-term(300 mg.kg-1.d-1,6 d/wk,4 wk,po) administration of TP had significantly inhibitory effect on different +Gz[(+3~18) Gz]induced lipid peroxidation in mouse brain[15].The present experiment further demonstrated the protective effect of TP on long-term,repeated +10 Gz stress induced peroxidative injury in rat brain.At the same time,primary clinical investigation showed that a close relationship existed between the change of renal function and serum antioxidase activities in 42 patients with renal diseases[16],and that TP could significantly improve the renal function and decreased plasma lipid peroxide level in 26 patients with chronic renal insufficiency.Our study showed that TP had protective effect on + Gz induced renal injury.However,the change of free radical metabolism in kidney after repeated +10 Gz stress and the influences of TP remains to be further studied.
and OH· were proved by the electron spin trapping and chemiluminescence methods.In isolated rat cerebral mitochondria and rat's incomplete cerebral ischemic/reperfusion injury models,lipid peroxidation was significantly inhibited by TP,while the mitochondrial ATPase acti-vity was remarkably increased after administration of this antioxidant[14].Protective effects of TP on acute + 10 Gz exposure induced brain mitochondrial peroxidation and blood brain barrier injury were observed[6].In addition,short-term(100 mg.kg-1.d-1,3 d,ip) and long-term(300 mg.kg-1.d-1,6 d/wk,4 wk,po) administration of TP had significantly inhibitory effect on different +Gz[(+3~18) Gz]induced lipid peroxidation in mouse brain[15].The present experiment further demonstrated the protective effect of TP on long-term,repeated +10 Gz stress induced peroxidative injury in rat brain.At the same time,primary clinical investigation showed that a close relationship existed between the change of renal function and serum antioxidase activities in 42 patients with renal diseases[16],and that TP could significantly improve the renal function and decreased plasma lipid peroxide level in 26 patients with chronic renal insufficiency.Our study showed that TP had protective effect on + Gz induced renal injury.However,the change of free radical metabolism in kidney after repeated +10 Gz stress and the influences of TP remains to be further studied.
, 百拇医药
*Foundation item:supported by the Medical Research Foundation of PLA(9115908),China
[References]
[1] Traystman RJ,Kirsch JR,Koehler RC.Oxygen radical mechanisms of brain injury following ischemia and reperfusion[J].J Appl Physiol,1991,71 :1185~1195
[2] Sweeney MI,Yager JY,Walz W et al.Cellular mechanisms involved in brain ischemia[J].Can J Physiol Pharmacol,1995,73:1525~1535
, http://www.100md.com
[3] Glaster DH,Jobsis-Vander Vliet FF.A near-infrared spectrophotometric method for studying brain O2 sufficiency in man during +Gz acceleration[J].Aviat Space Environ Med,1988,59:199~207
[4] Shahed AR,Barber JA,Werchan PM.Multiple +Gz exposures cause brain edema in rats[J].Aviat Space Environ Med,1994,65:522~526
[5] 詹 皓,辛益妹,刘人富.+Gz作用下鼠脑线粒体和胞浆脂质过氧化作用的比较[J].中华航空医学杂志,1992,3(4):193~195
, 百拇医药 [6] Zhan H,Xin YM,Tang GX et al.Effect of tea polyphenols on +Gz induced brain injury[J].Chin J Aviat Med,1995,6(2):69~74
[7] Vitorica J,Machado A,Satrustegui J.Age-dependent variations in peroxide-utilizing enzyme from rat brain mitochondria and cytoplasm[J].J Neurochem,1984,42:351~356
[8] Ohkawa H,Ohishi N,Yagi K.Assay for lipid peroxide in animal tissue by thiobarbituric acid reaction[J].Anal Biochem,1979,95:351~358
, 百拇医药
[9] Marklund S,Marklund G.Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase[J].Eur J Biochem,1974,47:469~474
[10] Asayama K,Burr IM.Rat superoxide dismutase.Purification,labeling,immunoassay,and tissue concentration[J].J Biol Chem,1985,260(4):2212~2217
[11] 徐叔云,卞如濂,陈修.药理实验方法学[M].第2版.北京:人民卫生出版社,1991:1065
[12] 戴 雨,纪桂英,王 喆等.正加速度对大鼠肾功能和组织结构的影响[J].中华航空航天医学杂志,1997,8(1):35~37
, 百拇医药
[13] Wu JC,Wu YC,Leu LC.G-induced changes in urine properties of pilots[J].Aviat Space Environ Med,1997,86(7):642
[14] 詹 皓,辛益妹,唐桂香等.茶多酚和人参茎叶皂甙对鼠脑线粒体过氧化反应和脂质ATP酶活性的影响[J].中华航空医学杂志,1993,4(4):196~200
[15] Zhan H,Xin YM,Lu JY et al.Inhibitory effect of short and long-term administration of tea polyphenols on +Gz induced lipid peroxidation in mouse brain[J].Chin J Aerospace Med,1997,8(3):133~137
[16] 姜素芝,张秀玉,田亚平等.自由基损伤与肾脏疾病关系的研究[C].见:方允中,郑荣梁,沈文梅.自由基生命科学进展(第4集).北京:原子能出版社,1996:111~114
Recieved date:April 28,1998, 百拇医药
单位:詹 皓.空军航空医学研究所,北京 100036
关键词:加速度应激;脂质过氧化作用;肝功能;肾功能;抗氧化剂;茶多酚;大鼠
航天医学与医学工程990101Effects of Tea Polyphenols on Cerebral Lipid Peroxidation,Liver and Renal Functions in Rats after Repeated +Gz Stress*
ZHAN Hao XIN Yi-mei TANG Gui-xiang
(Institute of Aviation Medicine,Beijing 100036,China)
, http://www.100md.com
CHEN Li-ming WEN Jing
(General Hospital of Air Force,PLA,Beijing 100036,China)
Abstract:Objective To observe the effects of repeated +10 Gz stress on cerebral lipid peroxidation,liver and renal function in rats and the prophylactic effects of antioxidant tea polyphenols(TP).Method Twenty-four male Wistar rats were randomly divided into three groups(n=8 each):group A(control),group B(+10 Gz),and group C(TP).Group B and C were exposed to repeated +10 Gz stress(each for 30s,onset rate about 0.5 G/s,3 times/d with +1 Gz 1 min intervals,3 d/wk,4 weeks in total),but group A was only submitted to +1 Gz.TP(200 mg/kg) was given orally in group C about 1 h prior to the +Gz experiment,while distilled water was given in group A and B.Lipid peroxidation in the brain,liver and renal functions and serum lipids were determined.Results As compared with the control,lipid peroxidation in rat cerebral homogenate,mitochondria and cytoplasm was significantly increased( P<0.05),and serum creatinine concentration was markedly elevated after repeated +10 Gz stress(P<0.01).But,TP had significant inhibitory effect on +10 Gz stress induced peroxidative injury in rat brain and reduced the serum creatinine level.There were no differences of serum triglyceride and total cholesterol concentrations and glutamic-pyruvic transaminase activity among the three groups.Conclusion These results indicated that repeated high +Gz stress could bring about peroxidative injury in brain and harmful effect on renal function,and natural antioxidant TP had signficant protective effects.
, 百拇医药
Key words:acceleration stress;lipid peroxidation;liver function;renal function;antioxidant;tea polyphenols;rat
摘要:目的 观察重复+10 Gz暴露对大鼠脑脂质过氧化反应和肝肾功能的影响以及天然抗氧化剂茶多酚(TP)的防护作用。方法 24只雄性Wistar大鼠随机等分为三组(n=8):A组(对照组),B组(+10 Gz组)和C组(TP组)。B、C组重复+10 Gz暴露(每次30 s,G增长率约为0.5 G/s,3次/d,间隔+1 Gz 1min,3 d/wk,共4 wk),而A组仅受+1 Gz作用。C组于+Gz实验前约1 h灌胃给予TP(200 mg/kg),另外两组给予等量蒸馏水。测定脑脂质过氧化反应、肝肾功能和血脂水平。结果 与对照组相比,B组大脑皮层匀浆、线粒体和胞浆脂质过氧化反应明显增强(P<0.05),血浆肌酐水平明显升高(P<0.01);而TP对此过氧化反应具有显著抑制作用并明显降低血浆肌酐水平。各组间血清谷丙转氨酶活性、甘油三酯和总胆固醇水平无统计学差异。结论 重复高+Gz作用可引起脑自由基损伤并损害肾功能,而天然抗氧化剂茶多酚具有明显的保护作用。
, 百拇医药
中图法分类号:R852.21 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1002-0837(1999)01-0001-05
Many studies have shown the occurrence of free radical generation and lipid peroxidation in ischemic or injuried brain tissue,and the protective effects of antioxidants and free radical scavengers provide further evidence for the involvement of oxygen free radicals and lipid peroxidation in case of brain ischemia or trauma[1,2].It has been found that repeated +Gz exposure could bring about effects on brain tissue similar to ischemia and reperfusion or hypoxia and reoxygenetion[3],and induced brain injury[4].But,in aviation medicine,the role of free radical metabolism in +Gz exposure induced brain injury hasn't been systematically studied.In our previous study,it was shown that +10 Gz stress(3 times each for 3 min with 40 min intervals) could induce peroxidative injury in rat brain.Malondialdehyde(MDA) content in cerebral mitochondria was significantly increased after +10 Gz exposure,but in cytoplasm,there was no such difference in MDA concentration between the control and +10 Gz stressed rats[5].After pretreatment with antioxidant tea polyphenols(TP) at dose of 30 and 100 mg.kg-1.d-1(ip),for three consecutive days,the mitochondrial lipid peroxidation was significantly inhibited.In addition,TP had remarkable protective effect on blood brain barrier injury induced by +10 Gz stress,as indicated by measuring the leakage of Evan's blue,and could substantially elevate mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase(ATPase) activity[6].In this study,we further observed the changes of cerebral lipid peroxidation,liver and renal functions in rats after long-term,repeated +10 Gz stress and the prophylactic effects of antioxidant TP.
, 百拇医药
Materials and Methods
Experimental animal and drug administration Male Wistar rats(193.1±14.2 g,n=24) from the Experimental Animal Center,Chinese Academy of Military Medical Sciences served as test subjects.These animals were randomly divided into three groups(n=8 each):group A(control),group B(+10 Gz) and group C(+10 Gz TP).TP (200 mg/kg) was given orally in group C about 1 h prior to the +Gz experiment,while distilled water was given in group A and B.TP with concentration >97% was produced by Hangzhou Dongya Tea Polyphenol Factory and provided by Professor YANG Xian-qiang of Zhejiang Agriculture University.
, http://www.100md.com
+Gz stress profile Centrifuge for small animals(radius of 2 m) in our institute was used .Rats(without anesthethia) were restrained in a special frame(3 cm in diameter,10 cm in length).The rate of +Gz onset was about 0.5 G/s.Both group B and C were exposed to repeated +Gz stress(each for 30 s,3 times/d with +1 Gz 1 min intervals,3 d/wk,4 weeks in total);the rats in group A were handled in the same way but only submitted to +1 Gz.
Determination of MDA concentration in rat brain The rats were decapitated in the next day after the last centrifuge run,and the brains and serum were collected.Cerebral cortices were homogenized with 1/15 M phosphate buffer(pH 7.4,1∶10,W/V).The homogenate was centrifuged at 2000 g for 5 min,then the supernatant was further centrifuged at 12500g for 20 min.The resulting supernatant and pellet of this centrifugation were the cytosolic and crude mitochondrial function,respectively[7].Malondialdehyde(MDA) contents in cerebral homogenate,mitochondria and cytoplasm were determined by thiobarbituric acid(TBA) reaction[8].Tissue sample was mixed with sodium dodecylsulfate,acetate buffer(pH 3.5) and aqueous solution of TBA.After heating at 95 ℃ for 60 min,the produced red pigment was estimated by the absorbance at 532 nm.1,1,3,3-tetraethoxy-propane(Fluka chemie AG) was used as an MDA standard.MDA content was expressed as nmol/mg protein.
, http://www.100md.com
Assay of superoxide dismutase(SOD) activity Above mentioned cerebral homogenate,mitochondria and cytoplasm were used.Assaying of SOD activity was indirect and based on this enzymatic ability to scavenge superoxide radical(
 ) from the autoxidation of pyrogallol[9],but slight modification was made.Reaction system contained 4.5 ml of 50 mmol/L K2HPO4-KH2PO4 buffer(pH 8.3) and 10 μl of 50 mmol/L pyrogallol.The rate of autoxidation was taken from the increase in A325 per min.SOD activity was expressed as U/mg protein.
) from the autoxidation of pyrogallol[9],but slight modification was made.Reaction system contained 4.5 ml of 50 mmol/L K2HPO4-KH2PO4 buffer(pH 8.3) and 10 μl of 50 mmol/L pyrogallol.The rate of autoxidation was taken from the increase in A325 per min.SOD activity was expressed as U/mg protein., 百拇医药
Measurment of liver and renal functions and serum lipid level BUN(blood urea nitrogen) and serum creatinine levels,serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase(GPT) activity,and serum triglyceride and total cholesterol concentration were analyzed by using ALCYON 300 full automatic biochemical analyzer.Reagent kits were purchased from Chinese High Technical Company(BUN) and Ausio Bioengineering limited Company(creatinine,GPT,triglyceride and total cholesterol) .Serum GPT activity is an indicator of liver function; BUN and serum creatinine levels are commonly used as the parameters of renal functions.
, 百拇医药
Results
Effects of TP on lipid peroxidation in rat brain after repeated + 10 Gz stress The results were presented in table l.It was observed that MDA concentrations in brain homogenate,mitochondria and cytoplasm were significantly increased after repeated +10 Gz stress (compared with the control,P<0.05),but TP inhibited significantly the lipid peroxidation .Compared with group A,mitochondrial and cytoplasmic SOD activities were significantly reduced after repeated +10 Gz stress(P<0.01),but the enzymatic activity in the animals treated with TP increased.
, 百拇医药
Effects of TP on liver and renal functions and serum lipids in rats after repeated +10 Gz stress After repeated +10 Gz stress,serum creatinine concentration was significantly increased(compared with the control,P<0.01).But,compared with group B,TP remarkably decreased serum creatinine level(P<0.05 ).However,there were no differences of liver function and serum lipids among the three groups.These results were shown in table 2.
Table 1 Effects of TP on lipid peroxidation in rat brain after repeated +10Gz stress(n=8,
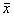 ±s) indices
±s) indices, 百拇医药
group A
group B
group C
MDA concent(nmol/mg prot)
homogenate
0.382±0.039
0.468±0.117*
0.343±0.069△△
mitochondria
0.572±0.078
0.615±0.072*
, http://www.100md.com
0.553±0.026△
cytoplasm
1.130±0.25
1.360±0.18*
1.150±1.18△
SOD activity(U/mg prot)
mitochondria
2.610±0.88
1.110±0.30**
1.700±0.42*△
, 百拇医药
cytoplasm
19.410±5.55
10.890±1.86**
13.860±5.33*
Note:*P<0.05,**P<0.01,as compared with group A;△P<0.05,△△P<0.01,as compared with group B
Table 2 Effects of TP on liver and renal functions and serum lipids in rats after repeated ±10 Gz stress(n=8,
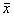 ±s) indices
±s) indices, 百拇医药
group A
group B
group C
BUN(mmol/L)
9.20±1.55
8.40±0.64
8.75±0.82
creatinine(μmol/L)
83.00±10.7
101.60±6.4**
94.60±6.1**△△
, 百拇医药
GPT activity(U/L)
58.30±11.7
58.30±9.4
54.50±9.8
triglyceride(mmol/L)
1.20±0.25
1.12±0.30
0.99±0.38
total cholesterol(mmol/l)
1.65±0.21
1.74±0.20
, http://www.100md.com
1.71±0.25
Note:**P<0.01,as compared with group A;△△P<0.01,as compared with group B
Discussion
In this study,+Gz stress profile was different from that used in our previous work[5]:each +10 Gz peak acting time was shorter,but repetitions were significantly more.Therefore,+Gz induced peroxidative injury in rat brain in this study (or long-term +Gz experiment) was quite different from that of our previous investigation(or acute +Gz experiment)[5].In general,cells of various types contain several enzymes to scavenger superoxide radical(
 ) coordinately.SOD exists in two major forms,as a copper-zinc containing enzyme in cytoplasm and a manganese containing enzyme in mitochondria.SOD c atalyzes the dismutation of
) coordinately.SOD exists in two major forms,as a copper-zinc containing enzyme in cytoplasm and a manganese containing enzyme in mitochondria.SOD c atalyzes the dismutation of  to yield H2O2 and
to yield H2O2 and  .Although the central nervous system contains very little catalase,it has more glutathione peroxidase (GSHpx) for decomposition of H2O2 and organic peroxides.In normal rat cerebral cortex,CuZn-SOD(located mainly in cytoplasm) content was(93.2±8.2)μg/g tissue and (1.02±0.05)μg/mg protein;and Mn-SOD(located mainly in mitochondrial) content was(62.0±5.4)μg/g tissue and (0.69±0.06)μg/mg protein,respectively[10].In acute +Gz experiment,it was observed that only mitochondrial MDA formation in cerebral cortex was significantly increased after +10 Gz stress,while in cytoplasm,there was no such increase.Cytoplasmic SOD and GSHpx activities were significantly increased after acute +10 Gz stress; but there was no significant change of these enzymatic activities in mitochondria among the control and +10 Gz stressed rats[5,6].Therefore,acute +10 Gz exposure induced mitochondrial peroxidative injury might be related to the differences of antioxidase contents and compensative responses in subcellular fractions after +Gz stress.Long-term,repeated +Gz exposure induced lipid peroxidation in rat brain became more serious,indicating the cumulative effects of free radical injury caused by +Gz stress.
.Although the central nervous system contains very little catalase,it has more glutathione peroxidase (GSHpx) for decomposition of H2O2 and organic peroxides.In normal rat cerebral cortex,CuZn-SOD(located mainly in cytoplasm) content was(93.2±8.2)μg/g tissue and (1.02±0.05)μg/mg protein;and Mn-SOD(located mainly in mitochondrial) content was(62.0±5.4)μg/g tissue and (0.69±0.06)μg/mg protein,respectively[10].In acute +Gz experiment,it was observed that only mitochondrial MDA formation in cerebral cortex was significantly increased after +10 Gz stress,while in cytoplasm,there was no such increase.Cytoplasmic SOD and GSHpx activities were significantly increased after acute +10 Gz stress; but there was no significant change of these enzymatic activities in mitochondria among the control and +10 Gz stressed rats[5,6].Therefore,acute +10 Gz exposure induced mitochondrial peroxidative injury might be related to the differences of antioxidase contents and compensative responses in subcellular fractions after +Gz stress.Long-term,repeated +Gz exposure induced lipid peroxidation in rat brain became more serious,indicating the cumulative effects of free radical injury caused by +Gz stress., http://www.100md.com
In normal rats,BUN and serum creatinine concentrations were 1.78~10.35 mmol/l and 17.68~70.73 μmol/L,respectively[ 11].Our experimental results indicated that BUN and serum creatinine levels in the control (group A) were in normal range,but repeated +10 Gz stress had detrimental effects on renal function.DAI et al[12] also reported the harmful effect of +Gz on renal function and structure in rats.Compared with +Gz group,BUN level in +10 Gz stressed rats(3 times each for 3 min ,with 40 min intervals) was elevated by 20.3%(P<0.01).After +10 Gz exposure,vasoconstriction was observed by optical microscopic examination,and pathological changes of ultrastructure and mitochondria of glomeruli and renal tubules were found by electron microscopic examination.WU et al[13] observed G-induced changes in urine properties of pilots.The specific gravity of urine were significantly higher post riding(high G training) than pre-riding.Proteinuria was noted in post riding urine samples of twenty-five pilots(58%) who had not had proteinuria before exposed to high G environment .These results were in accordance with our experiment and indicated that the effects of repeated +Gz stress on the renal function were profound.
, 百拇医药
Scaveging effects of natural antioxidant TP on
 and OH· were proved by the electron spin trapping and chemiluminescence methods.In isolated rat cerebral mitochondria and rat's incomplete cerebral ischemic/reperfusion injury models,lipid peroxidation was significantly inhibited by TP,while the mitochondrial ATPase acti-vity was remarkably increased after administration of this antioxidant[14].Protective effects of TP on acute + 10 Gz exposure induced brain mitochondrial peroxidation and blood brain barrier injury were observed[6].In addition,short-term(100 mg.kg-1.d-1,3 d,ip) and long-term(300 mg.kg-1.d-1,6 d/wk,4 wk,po) administration of TP had significantly inhibitory effect on different +Gz[(+3~18) Gz]induced lipid peroxidation in mouse brain[15].The present experiment further demonstrated the protective effect of TP on long-term,repeated +10 Gz stress induced peroxidative injury in rat brain.At the same time,primary clinical investigation showed that a close relationship existed between the change of renal function and serum antioxidase activities in 42 patients with renal diseases[16],and that TP could significantly improve the renal function and decreased plasma lipid peroxide level in 26 patients with chronic renal insufficiency.Our study showed that TP had protective effect on + Gz induced renal injury.However,the change of free radical metabolism in kidney after repeated +10 Gz stress and the influences of TP remains to be further studied.
and OH· were proved by the electron spin trapping and chemiluminescence methods.In isolated rat cerebral mitochondria and rat's incomplete cerebral ischemic/reperfusion injury models,lipid peroxidation was significantly inhibited by TP,while the mitochondrial ATPase acti-vity was remarkably increased after administration of this antioxidant[14].Protective effects of TP on acute + 10 Gz exposure induced brain mitochondrial peroxidation and blood brain barrier injury were observed[6].In addition,short-term(100 mg.kg-1.d-1,3 d,ip) and long-term(300 mg.kg-1.d-1,6 d/wk,4 wk,po) administration of TP had significantly inhibitory effect on different +Gz[(+3~18) Gz]induced lipid peroxidation in mouse brain[15].The present experiment further demonstrated the protective effect of TP on long-term,repeated +10 Gz stress induced peroxidative injury in rat brain.At the same time,primary clinical investigation showed that a close relationship existed between the change of renal function and serum antioxidase activities in 42 patients with renal diseases[16],and that TP could significantly improve the renal function and decreased plasma lipid peroxide level in 26 patients with chronic renal insufficiency.Our study showed that TP had protective effect on + Gz induced renal injury.However,the change of free radical metabolism in kidney after repeated +10 Gz stress and the influences of TP remains to be further studied., 百拇医药
*Foundation item:supported by the Medical Research Foundation of PLA(9115908),China
[References]
[1] Traystman RJ,Kirsch JR,Koehler RC.Oxygen radical mechanisms of brain injury following ischemia and reperfusion[J].J Appl Physiol,1991,71 :1185~1195
[2] Sweeney MI,Yager JY,Walz W et al.Cellular mechanisms involved in brain ischemia[J].Can J Physiol Pharmacol,1995,73:1525~1535
, http://www.100md.com
[3] Glaster DH,Jobsis-Vander Vliet FF.A near-infrared spectrophotometric method for studying brain O2 sufficiency in man during +Gz acceleration[J].Aviat Space Environ Med,1988,59:199~207
[4] Shahed AR,Barber JA,Werchan PM.Multiple +Gz exposures cause brain edema in rats[J].Aviat Space Environ Med,1994,65:522~526
[5] 詹 皓,辛益妹,刘人富.+Gz作用下鼠脑线粒体和胞浆脂质过氧化作用的比较[J].中华航空医学杂志,1992,3(4):193~195
, 百拇医药 [6] Zhan H,Xin YM,Tang GX et al.Effect of tea polyphenols on +Gz induced brain injury[J].Chin J Aviat Med,1995,6(2):69~74
[7] Vitorica J,Machado A,Satrustegui J.Age-dependent variations in peroxide-utilizing enzyme from rat brain mitochondria and cytoplasm[J].J Neurochem,1984,42:351~356
[8] Ohkawa H,Ohishi N,Yagi K.Assay for lipid peroxide in animal tissue by thiobarbituric acid reaction[J].Anal Biochem,1979,95:351~358
, 百拇医药
[9] Marklund S,Marklund G.Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase[J].Eur J Biochem,1974,47:469~474
[10] Asayama K,Burr IM.Rat superoxide dismutase.Purification,labeling,immunoassay,and tissue concentration[J].J Biol Chem,1985,260(4):2212~2217
[11] 徐叔云,卞如濂,陈修.药理实验方法学[M].第2版.北京:人民卫生出版社,1991:1065
[12] 戴 雨,纪桂英,王 喆等.正加速度对大鼠肾功能和组织结构的影响[J].中华航空航天医学杂志,1997,8(1):35~37
, 百拇医药
[13] Wu JC,Wu YC,Leu LC.G-induced changes in urine properties of pilots[J].Aviat Space Environ Med,1997,86(7):642
[14] 詹 皓,辛益妹,唐桂香等.茶多酚和人参茎叶皂甙对鼠脑线粒体过氧化反应和脂质ATP酶活性的影响[J].中华航空医学杂志,1993,4(4):196~200
[15] Zhan H,Xin YM,Lu JY et al.Inhibitory effect of short and long-term administration of tea polyphenols on +Gz induced lipid peroxidation in mouse brain[J].Chin J Aerospace Med,1997,8(3):133~137
[16] 姜素芝,张秀玉,田亚平等.自由基损伤与肾脏疾病关系的研究[C].见:方允中,郑荣梁,沈文梅.自由基生命科学进展(第4集).北京:原子能出版社,1996:111~114
Recieved date:April 28,1998, 百拇医药