IL-1β诱导类风湿性关节炎滑膜细胞MAPKs通路的活化
作者:孙铁铮 药立波 吕厚山 王吉村 杨敏 张育军
单位:孙铁铮(北京医科大学人民医院骨关节病诊疗研究中心);药立波(第四军医大学生物化学与分子生物学教研室,陕西西安710032);吕厚山(北京医科大学人民医院骨关节病诊疗研究中心);王吉村(第四军医大学生物化学与分子生物学教研室,陕西西安710032);杨敏(第四军医大学生物化学与分子生物学教研室,陕西西安710032);张育军(妇产科,北京100044)
关键词:关节炎;滑膜;成纤维细胞;信号转导;IL-1beta;MAPK
细胞与分子免疫学杂志000201
摘要:目的研究类风湿性关节炎(rheumatoidarthritis,RA)成纤维样滑膜细胞(fibroblast-like
synoviocyte,FLS)信号转导中,IL-1β介导的丝裂原活化的蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated-proteinkinaseMAPKs)的激活情况。方法原代培养RFFLS;应用Westernblot检测IL-1β对于RAFLS蛋白质酪氨酸磷酸化状态的影响,及其对MAPKs家族成员活化的浓度效应和时相特点。结果IL-1β可以瞬时增加RAFLS蛋白质酪氨酸磷酸化的程度,并在短时间内激活MAPKs通路(以ERK2,JNK2和P38为主)。不同浓度的IL-1β对MAPKs的活化无明显差异,但ERK2,JNK2和P38的活化分别在IL-1β作用后5min,15min和1min最明显。结论IL-1β在RAFLS信号转导中,可以瞬时导致蛋白质酪氨酸化的程度增加,并同时激活MAPKs3条通路;但
, 百拇医药
MAPKs3个亚家族成员的活化具有异质性。
Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinae induced by IL-1β in fibroblast- like synoviocytes of rheumatoid arthritis
SUN Tie- zheng,YAO Li- bo,LU Hou- shan
Abstract:Aim To study activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase(MAPKs)in fibroblast-like synoviocytes(FLS)of rheumatoid arthritis(RA)under the stimulation of IL- 1β . Methods RA FLS wereprimarily cultured. Western blots were used to examine transient change of protein tyrosine phosphorylation status andMAPKs activation in RA FLS stimulated with various doses and periods of IL- 1β . Results IL- 1β transiently increasedprotein tyrosine phosphorylation, and activated MAPKs cascades (mainly ERK2, JNK2 and P38) in RA FLS. There was noobvious difference of MAPKs' activation among different doses of IL- 1β (1× 103 IU/L,1× 104 IU/L and 1× 105IU/L), but the peak activations of ERK2,JNK2 and P38 took place at 5 min,15 min and 1 min, respectively after stimulationwith IL- 1β . Conclusion During signal transduction of IL- 1β in RA FLS, tyrosine phoshorylation was increasedtransiently, MAPKs cascades were activated in a few minutes, and there was heterogenicity of activation among threesubfamily members.
, 百拇医药
Keywords: arthritis; synovial membrane; fibroblasts; signal transduction; IL- 1beta; MAPK
Rheumatoid arthritis(RA) is a chronic inflammatory cytokine-mediated disease, characterized by uncontrolled proliferation of synoviocytes, infiltration of abundant inflammatory cells and progressive joint erosion. In the pathogenesis of RA , the cytokine network mainly including IL-1,TNF-α and other cytokines contributs to activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes(FLS)and further leads to erosion of cartilage and bone. IL-1β can increase production of collagenase,stinulate secretion of prostaglandin E2 and secondary cytokines such as IL- 6 and IL- 8; induce expression of adhesion moleculars such as ICAM-1 and VCAM-1,etc〔1〕. IL-1β receptors don't contain any intrinsic kinase domain.However, IL-1β activates a kinase which phosphorylates protein substrates such as the EGF receptor,the heat shock protein of relative molecule mass(Mr)27 000,L- plastin and IL-1β receptor of Mr 80 000. Although cAMP,diacylglycerol, PKC and the arachidonic acid metabolites have been reported to participate in IL- 1β signal transduction, the status of their involvement in different cell lines remains uncertain and controversial[2]. So signal transduction pathway of IL-1 is still not very clear. The mitogen-activated protein kinase(MAPK) family is a group of evolutionary conservative proline- directed serine/threonine kinase, converting extracellular stimuli to intracellular signals and controlling the expression of genes essential for many cellular processes including cell growth and differentiation[3]. The purpose of our study is to investigate MAPKs cascade activation in RA FLS stimulated with IL-1β.
, 百拇医药
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Synoviocytes culture Synovial tissue was collected at the time of total knee replacement(TKR) or synovectomy from patients with RA. The diagnosis of RA conformed to the 1987 revised American College of Rheumatology Criteria〔4〕 .Fibroblast-like synoviocytes were isolated by enzymatic dispersion of synovial tissue. Briefly, the synovial membrane was minced aseptically and then incubated with 1.0 mg/L collagenase I(Gibco-BRL) in serum-free DMEM for 4 hour at 37℃, filtered through a nylon mesh, extensively washed, and cultured in DMEM suplemented with 200 g/L fetal bovine serum(FBS), penicillin,streptomycin and L-glutamine in a humidified 50 mL/L CO2 atmosphere. After overnight culture, nonadherent cells were removed, and adherent cells were cultured in DMEM plus 200 mL/L FBS. At 85% confluence, cells were trypsinized, split at 1∶3 ratio and recultured in medium. Synoviocytes from passage 3-5 were used in theseexperiments.
, 百拇医药
Preparation and quantitative of protein exstracts and action of cytokines 5× 105 synovial cells were grown to subconflunce for 24 hour. After starvation with 10 ml/L FBS or 3 g/L BSA, synovial cells were stimulated with IL-1β in different doses(1,10,1× 104 IU/L) for 5 min,or 1× 104 IU/L in different periods (1, 2, 5 and 15 min). Serum-free DMEM was used as the control. Cells were washed with cold PBS and lysed by the addition of 100 μ L lysis buffer[20 mmol Tris/Cl (pH∶ 8.0), 1% (v/v)NP- 40, 150 mmol/L NaCl, 1 g/L(v/w)NaN3,5 mg/L aprotinin, 1 mmol/L PMSF, 1 mmol/L EDTA, 1mmol/L Na3VO4, 25 μ mol/L PNP',1 μ mol/L pepstatin A, 1 μ mol/L leupeptin], then scraped off and kept on ice for 20min. Insoluble material was removed by centrifugation at 15 000× g for 15 min at 4℃ . The supernatant was saved and protein concentration was determined using Bio-Rad DC protein assay kit.
, http://www.100md.com
SDS-PAGE and Western Blot An identical amount of protein(30 μ g) for each lysate was subjected to 100 g/L SDS-PAGE. Protein were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. The membranes were blocked overnight with 50 g/L non-fat milk in PBS at 4℃ , washed in PBS-T and incubated at room temperature for 3 hour in a 1∶2 000 dilution of mouse anti- phospho-rylated monoclonal antibody(4G10), or a 1∶ 2 000 dilution of rabbit anti-active ERK antibody, 1∶2000 dilution of mouse anti-active JNK antibody, or 1∶ 2 000 dilution of mouse anti-active P38 antibody(Promega). The membranes were then washed in PBS-T and were incubated with 1∶2 000 goat anti-mouse or rabbit IgG antibodies coupled with horseradish peroxidase. The enhanced chemiluminecence(ECL)system (Amersha-m) was used to detection.The membranes were sequentially exposed to X-Kodak film for 15 seconds and the latter was processed. Then the membranes were probed with antinon-active ERK, -JNK and -P38 antibodies to ensure that the identical amount of protein were loaded.
, 百拇医药
RESULTS
Synoviocytes of passage 3 were homogenous population of fibroblast-like synoviocytes. We analyzed the early biological events of RA FLS stimulated with IL-1β . As shown in figure 1 , stimulation with IL-1β resulted in tyrosine phosphorylation of several bands [including (Mr× 103)110,75,65,54,46,42 and 38].Among these bands,bands of Mr 42 000 and 38 000 increased to the peak activation in 1-2 min. The bands of Mr× 103 110,75,65 and 54increased gradually in 15 min.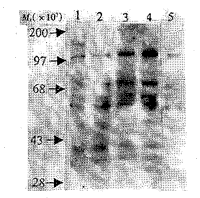
, 百拇医药
Fig 1 Transient effect of IL-1β (10 kU/L) on protein tyrosine
phosphorylation in RA FLS
1: 1 min; 2: 2 min; 3: 5 min; 4:15 min; 5: 0 min.
Because the activation of three subfamily members of MAPKs was all induced by biphosphorylation on the sites of Tyr-Xaa-Thr, we deduced that the bands of P54, P46, P42 and P38 in the above figure 1 might be JNK2,JNK1, ERK2 and P38 of MAPKs family.Then with anti-active ERK/JNK/P38 antibodies in Western blot, MAPKs activation was investigated in RA FLS induced by IL-1β in different concentrations and in periods. ERK/JNK/P38 was able to be simultaneously activated by IL-1β in a short time, mainly ERK2, JNK2 and P38. However, the activation of ERK1(P44), JNK1(P46) and other subfamilly members were relatively weak. There was no obvious difference in activation of MAPKs among different concentrations of IL- 1β (1 kU/L, 10 kU/L, 100 kU /L)(figure 2a, 3a and 4a), in accordance with efficiency of IL-1R. The peak activation of ERK2 was obtained at 2 min(figure 2b); the activation of JNK2 increased grandually in 1-15 min(figure 3 b); the maxial activation of P38 was got at 1 min(figure 4 b) and then decreased with time going by. The above results were repeated 3 times. The figures are only one representative.
, 百拇医药
Fig 2 The effects of different induction time(min) and concen-trations
of IL-1β on RA FLK ERK activation
(a): IL- 1β with defferent concentrations: 1:0 kU/L;
2:1kU/L; 3:10 kU/L; 4:100 kU/L.
(b): Times induced by IL-1β : 1: 0 min; 2: 1 min; 3: 5 min; 4:15 min.
Fig 3 The effects of different induction time(min) and
, http://www.100md.com
concen-trations of IL-1β on RA FLS JNK activation
(a)Different concentration of IL-1β :I:100 kU/L;2:10 kU/L; 3: 1 kU/L; 4: 0 kU/L.
(b)Timed induced by IL-1β : 1:15 min; 2:5 min; 3:1 min; 4: 0 min/L.
Fig 4 The effects of different induction times and concentra-tions
of IL-1β on RA FLS P38 activation
, http://www.100md.com
(a) Different concentration of IL-1β : 1:100 kU/L; 2: 10 kU/L; 3:1 kU/L; 4:0 kU/L.
(b) Times induced by IL-1β : 1:0 min; 2: 1 min; 3: 5 min; 4: 15 min.
After the filters were stripped off, and rehybrided with non- active anti- MAPKs antibody, the bands had no obvious difference(figure 5), which showed that the same amount of protein was loaded again.
, 百拇医药
Fig 5 Non-activated MAPKs
(a)Non-activated ERK; (b)Non-activated JNK;(c)Non-activated p38.
DISCUSSION:
Interleukin 1 (IL-1) was the first cytokine derived from synovial membrane and fluids shown to promote cartilage degradation in vitro. Although the initiator of RA is difficult to quantify, there has been little disagreement about the fact that cytokine networks play an essential role in the perpetuation of the disease[5]. Moreover, the side effect and /or poor efficiency of traditional pharmacological therapies (NSAIDS and DMARDS) in treatment of RA, has led to the development of anti-cytokine strategies. Now, gene therapy with IL-1rα in RA FLS has been permitted by FDA, followed by clinic phase II trial[6]. However, the signal transduction of IL-1β in RA FLS is still to be elucidated.
, 百拇医药
Disappointingly, IL-1R′ s structure gave no clues to a possible signal transduction pathway. IL-1R did not pocess any intrinsic protein kinase activity and so far there has been no single pathway confined post receptor binding events; instead,different pathways of IL-1β signal transduction have been proposed[7]. Most recently, it has been shown that IL-1β activates protein kinases leading to activation pathways which are often cell specific. IL-1β can activate different signal transducers and induce various biological effects in different cell lines.The IL-1R signal transduction system is also amazingly efficient in that fewer than 10 ligand-occupied receptors are required per cell in order to induce a strong response. This is compared with a 10 to 100 fold higher occupancy required for most other system[8]. A likely explanation is that the receptor activates multiple pathways that are all induced in parallel and can synergize to result in a strong response. The hypothesis is proved by our experiments that IL-1β could activate three MAPKs subfamily members simultaneously, mainly P42MAPK/ERK2, P54JNK2 and P38. There was no obvious difference in activation of every member from 1 kU/L to 100 kU/L, which was another example of high efficiency of IL-1R. However, the peak of activation of ERK and P38 by IL-1β was obtained at 1-5 mins, but that of JNK kinase was at 20 min.
, 百拇医药
It has been illustrated that MAPKs is a convergence point of many signal pathways (PKC,RPTK, JAK- STAT and ion-channle,etc). It can transduce extracellular stimuli to nucleus, regulate transcription factors, and drive expression of the relative genes. The classic activation pathway of ERK is RPTK-ras-raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2-MAPKPK to initiate cellular process, such as proliferation,differentiation, transformation and cell cycle[3]. Our
recent reports showed that IL-1β in a defined concentration could stimulate RA FLS proliferation, acting as mitogens. It is possible that the mitogenic role of IL-1β in RA FLS is mediated by MAPK/ERK. In contrast, JNK and P38 kinase are activated by inflammatory cytokines and cellular stresses such as heat shock, osmotic stress or ultraviolet (UV) light[9]. Just as described above, MAPKs may be stimulated by different factors, to construct three independent pathways and to govern a large number of cellular proceses. However, MAPKs act in concert with other signaling systems. Therefore, the cross-talk between the above pathways is crucial to the coordinated response of cells. MAPKs may act antagonistically in cells undergoing apoptosis; or may cooperate with or antagonize each other in supporting cell proliferation.
, 百拇医药
Altogether, IL-1β can activate three MAPKs subfamily members in RA FLS independently and coordinantly, and can lead to a serial of proteins tyrosine phosphorylated transiently in RA FLS , which may induce the complicate biological response leading to cartilage and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis.
Biography: The study is granted by the Important Item of National Natural Science fundation of China, No. 39730430
Author: Sun TZ, male, twenty- six- year- old,undergraduate MD
, http://www.100md.com
No.42,Bei- Li- Shi Road, Beijing 100044, China
Tel.(010)68314422- 5936, E- mail. Suntz@public3. bta.net.cn
REFERENCES
〔1〕 Lafyatis R,Remmers EF,Roberts AB,et al.Anchorage-independent growth of synoviocytes from arthritic and normal joints.Stimulation by exogenous platelet-derived growth factor and inhibition by transforming growth factor-beta and retinoids〔J〕.J Clin Invest,1989;83:1267-1276.
, http://www.100md.com
〔2〕 Guy GR,Chua SP,Wong NS,et al.Interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor activate common multiple protein kinases in human fibroblast〔J〕.J Biol Chem,1991;266:14343-14352.
〔3〕 Seger R,Krebs E.The MAPK signaling cascade〔J〕.FASEB J,1995;9:726-735.
〔4〕 Arnet FC,Edworthy SM,Bloch DA,et al.The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis〔J〕.Arthritis Rheum,1988;31:315-324.
, 百拇医药
〔5〕 Breecheld F.New tumor necrosis factor-alpha biologic therapies for rheumatoid arthritis〔J〕.Eur Cytokine Netw,1998;9:233-238.
〔6〕 Evans CH,Ghivizzani SC,Kang R,et al.Gene therapy for rheumatic diseases〔J〕.Arthritis Rheumatism,1999;42:1-16.
〔7〕 Dinarello CA.The interleukin-1 family:10 years of discovery〔J〕.FASEB J,1994;8:1314-1325.
〔8〕 Auron PE.The interleukin 1 receptor:ligand interaction and signal transduction〔J〕.Cyto Grow Fact Rev,1998;314:221-237.
〔9〕 Kyriakis JM,Banerjee P,Niklokaki E,et al.The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-jun kinases〔J〕.Nature,1994;369:156-160.
Received date:1999-10-09
revised date:1999-11-13, 百拇医药
单位:孙铁铮(北京医科大学人民医院骨关节病诊疗研究中心);药立波(第四军医大学生物化学与分子生物学教研室,陕西西安710032);吕厚山(北京医科大学人民医院骨关节病诊疗研究中心);王吉村(第四军医大学生物化学与分子生物学教研室,陕西西安710032);杨敏(第四军医大学生物化学与分子生物学教研室,陕西西安710032);张育军(妇产科,北京100044)
关键词:关节炎;滑膜;成纤维细胞;信号转导;IL-1beta;MAPK
细胞与分子免疫学杂志000201
摘要:目的研究类风湿性关节炎(rheumatoidarthritis,RA)成纤维样滑膜细胞(fibroblast-like
synoviocyte,FLS)信号转导中,IL-1β介导的丝裂原活化的蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated-proteinkinaseMAPKs)的激活情况。方法原代培养RFFLS;应用Westernblot检测IL-1β对于RAFLS蛋白质酪氨酸磷酸化状态的影响,及其对MAPKs家族成员活化的浓度效应和时相特点。结果IL-1β可以瞬时增加RAFLS蛋白质酪氨酸磷酸化的程度,并在短时间内激活MAPKs通路(以ERK2,JNK2和P38为主)。不同浓度的IL-1β对MAPKs的活化无明显差异,但ERK2,JNK2和P38的活化分别在IL-1β作用后5min,15min和1min最明显。结论IL-1β在RAFLS信号转导中,可以瞬时导致蛋白质酪氨酸化的程度增加,并同时激活MAPKs3条通路;但
, 百拇医药
MAPKs3个亚家族成员的活化具有异质性。
Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinae induced by IL-1β in fibroblast- like synoviocytes of rheumatoid arthritis
SUN Tie- zheng,YAO Li- bo,LU Hou- shan
Abstract:Aim To study activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase(MAPKs)in fibroblast-like synoviocytes(FLS)of rheumatoid arthritis(RA)under the stimulation of IL- 1β . Methods RA FLS wereprimarily cultured. Western blots were used to examine transient change of protein tyrosine phosphorylation status andMAPKs activation in RA FLS stimulated with various doses and periods of IL- 1β . Results IL- 1β transiently increasedprotein tyrosine phosphorylation, and activated MAPKs cascades (mainly ERK2, JNK2 and P38) in RA FLS. There was noobvious difference of MAPKs' activation among different doses of IL- 1β (1× 103 IU/L,1× 104 IU/L and 1× 105IU/L), but the peak activations of ERK2,JNK2 and P38 took place at 5 min,15 min and 1 min, respectively after stimulationwith IL- 1β . Conclusion During signal transduction of IL- 1β in RA FLS, tyrosine phoshorylation was increasedtransiently, MAPKs cascades were activated in a few minutes, and there was heterogenicity of activation among threesubfamily members.
, 百拇医药
Keywords: arthritis; synovial membrane; fibroblasts; signal transduction; IL- 1beta; MAPK
Rheumatoid arthritis(RA) is a chronic inflammatory cytokine-mediated disease, characterized by uncontrolled proliferation of synoviocytes, infiltration of abundant inflammatory cells and progressive joint erosion. In the pathogenesis of RA , the cytokine network mainly including IL-1,TNF-α and other cytokines contributs to activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes(FLS)and further leads to erosion of cartilage and bone. IL-1β can increase production of collagenase,stinulate secretion of prostaglandin E2 and secondary cytokines such as IL- 6 and IL- 8; induce expression of adhesion moleculars such as ICAM-1 and VCAM-1,etc〔1〕. IL-1β receptors don't contain any intrinsic kinase domain.However, IL-1β activates a kinase which phosphorylates protein substrates such as the EGF receptor,the heat shock protein of relative molecule mass(Mr)27 000,L- plastin and IL-1β receptor of Mr 80 000. Although cAMP,diacylglycerol, PKC and the arachidonic acid metabolites have been reported to participate in IL- 1β signal transduction, the status of their involvement in different cell lines remains uncertain and controversial[2]. So signal transduction pathway of IL-1 is still not very clear. The mitogen-activated protein kinase(MAPK) family is a group of evolutionary conservative proline- directed serine/threonine kinase, converting extracellular stimuli to intracellular signals and controlling the expression of genes essential for many cellular processes including cell growth and differentiation[3]. The purpose of our study is to investigate MAPKs cascade activation in RA FLS stimulated with IL-1β.
, 百拇医药
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Synoviocytes culture Synovial tissue was collected at the time of total knee replacement(TKR) or synovectomy from patients with RA. The diagnosis of RA conformed to the 1987 revised American College of Rheumatology Criteria〔4〕 .Fibroblast-like synoviocytes were isolated by enzymatic dispersion of synovial tissue. Briefly, the synovial membrane was minced aseptically and then incubated with 1.0 mg/L collagenase I(Gibco-BRL) in serum-free DMEM for 4 hour at 37℃, filtered through a nylon mesh, extensively washed, and cultured in DMEM suplemented with 200 g/L fetal bovine serum(FBS), penicillin,streptomycin and L-glutamine in a humidified 50 mL/L CO2 atmosphere. After overnight culture, nonadherent cells were removed, and adherent cells were cultured in DMEM plus 200 mL/L FBS. At 85% confluence, cells were trypsinized, split at 1∶3 ratio and recultured in medium. Synoviocytes from passage 3-5 were used in theseexperiments.
, 百拇医药
Preparation and quantitative of protein exstracts and action of cytokines 5× 105 synovial cells were grown to subconflunce for 24 hour. After starvation with 10 ml/L FBS or 3 g/L BSA, synovial cells were stimulated with IL-1β in different doses(1,10,1× 104 IU/L) for 5 min,or 1× 104 IU/L in different periods (1, 2, 5 and 15 min). Serum-free DMEM was used as the control. Cells were washed with cold PBS and lysed by the addition of 100 μ L lysis buffer[20 mmol Tris/Cl (pH∶ 8.0), 1% (v/v)NP- 40, 150 mmol/L NaCl, 1 g/L(v/w)NaN3,5 mg/L aprotinin, 1 mmol/L PMSF, 1 mmol/L EDTA, 1mmol/L Na3VO4, 25 μ mol/L PNP',1 μ mol/L pepstatin A, 1 μ mol/L leupeptin], then scraped off and kept on ice for 20min. Insoluble material was removed by centrifugation at 15 000× g for 15 min at 4℃ . The supernatant was saved and protein concentration was determined using Bio-Rad DC protein assay kit.
, http://www.100md.com
SDS-PAGE and Western Blot An identical amount of protein(30 μ g) for each lysate was subjected to 100 g/L SDS-PAGE. Protein were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. The membranes were blocked overnight with 50 g/L non-fat milk in PBS at 4℃ , washed in PBS-T and incubated at room temperature for 3 hour in a 1∶2 000 dilution of mouse anti- phospho-rylated monoclonal antibody(4G10), or a 1∶ 2 000 dilution of rabbit anti-active ERK antibody, 1∶2000 dilution of mouse anti-active JNK antibody, or 1∶ 2 000 dilution of mouse anti-active P38 antibody(Promega). The membranes were then washed in PBS-T and were incubated with 1∶2 000 goat anti-mouse or rabbit IgG antibodies coupled with horseradish peroxidase. The enhanced chemiluminecence(ECL)system (Amersha-m) was used to detection.The membranes were sequentially exposed to X-Kodak film for 15 seconds and the latter was processed. Then the membranes were probed with antinon-active ERK, -JNK and -P38 antibodies to ensure that the identical amount of protein were loaded.
, 百拇医药
RESULTS
Synoviocytes of passage 3 were homogenous population of fibroblast-like synoviocytes. We analyzed the early biological events of RA FLS stimulated with IL-1β . As shown in figure 1 , stimulation with IL-1β resulted in tyrosine phosphorylation of several bands [including (Mr× 103)110,75,65,54,46,42 and 38].Among these bands,bands of Mr 42 000 and 38 000 increased to the peak activation in 1-2 min. The bands of Mr× 103 110,75,65 and 54increased gradually in 15 min.

, 百拇医药
Fig 1 Transient effect of IL-1β (10 kU/L) on protein tyrosine
phosphorylation in RA FLS
1: 1 min; 2: 2 min; 3: 5 min; 4:15 min; 5: 0 min.
Because the activation of three subfamily members of MAPKs was all induced by biphosphorylation on the sites of Tyr-Xaa-Thr, we deduced that the bands of P54, P46, P42 and P38 in the above figure 1 might be JNK2,JNK1, ERK2 and P38 of MAPKs family.Then with anti-active ERK/JNK/P38 antibodies in Western blot, MAPKs activation was investigated in RA FLS induced by IL-1β in different concentrations and in periods. ERK/JNK/P38 was able to be simultaneously activated by IL-1β in a short time, mainly ERK2, JNK2 and P38. However, the activation of ERK1(P44), JNK1(P46) and other subfamilly members were relatively weak. There was no obvious difference in activation of MAPKs among different concentrations of IL- 1β (1 kU/L, 10 kU/L, 100 kU /L)(figure 2a, 3a and 4a), in accordance with efficiency of IL-1R. The peak activation of ERK2 was obtained at 2 min(figure 2b); the activation of JNK2 increased grandually in 1-15 min(figure 3 b); the maxial activation of P38 was got at 1 min(figure 4 b) and then decreased with time going by. The above results were repeated 3 times. The figures are only one representative.

, 百拇医药
Fig 2 The effects of different induction time(min) and concen-trations
of IL-1β on RA FLK ERK activation
(a): IL- 1β with defferent concentrations: 1:0 kU/L;
2:1kU/L; 3:10 kU/L; 4:100 kU/L.
(b): Times induced by IL-1β : 1: 0 min; 2: 1 min; 3: 5 min; 4:15 min.

Fig 3 The effects of different induction time(min) and
, http://www.100md.com
concen-trations of IL-1β on RA FLS JNK activation
(a)Different concentration of IL-1β :I:100 kU/L;2:10 kU/L; 3: 1 kU/L; 4: 0 kU/L.
(b)Timed induced by IL-1β : 1:15 min; 2:5 min; 3:1 min; 4: 0 min/L.

Fig 4 The effects of different induction times and concentra-tions
of IL-1β on RA FLS P38 activation
, http://www.100md.com
(a) Different concentration of IL-1β : 1:100 kU/L; 2: 10 kU/L; 3:1 kU/L; 4:0 kU/L.
(b) Times induced by IL-1β : 1:0 min; 2: 1 min; 3: 5 min; 4: 15 min.
After the filters were stripped off, and rehybrided with non- active anti- MAPKs antibody, the bands had no obvious difference(figure 5), which showed that the same amount of protein was loaded again.

, 百拇医药
Fig 5 Non-activated MAPKs
(a)Non-activated ERK; (b)Non-activated JNK;(c)Non-activated p38.
DISCUSSION:
Interleukin 1 (IL-1) was the first cytokine derived from synovial membrane and fluids shown to promote cartilage degradation in vitro. Although the initiator of RA is difficult to quantify, there has been little disagreement about the fact that cytokine networks play an essential role in the perpetuation of the disease[5]. Moreover, the side effect and /or poor efficiency of traditional pharmacological therapies (NSAIDS and DMARDS) in treatment of RA, has led to the development of anti-cytokine strategies. Now, gene therapy with IL-1rα in RA FLS has been permitted by FDA, followed by clinic phase II trial[6]. However, the signal transduction of IL-1β in RA FLS is still to be elucidated.
, 百拇医药
Disappointingly, IL-1R′ s structure gave no clues to a possible signal transduction pathway. IL-1R did not pocess any intrinsic protein kinase activity and so far there has been no single pathway confined post receptor binding events; instead,different pathways of IL-1β signal transduction have been proposed[7]. Most recently, it has been shown that IL-1β activates protein kinases leading to activation pathways which are often cell specific. IL-1β can activate different signal transducers and induce various biological effects in different cell lines.The IL-1R signal transduction system is also amazingly efficient in that fewer than 10 ligand-occupied receptors are required per cell in order to induce a strong response. This is compared with a 10 to 100 fold higher occupancy required for most other system[8]. A likely explanation is that the receptor activates multiple pathways that are all induced in parallel and can synergize to result in a strong response. The hypothesis is proved by our experiments that IL-1β could activate three MAPKs subfamily members simultaneously, mainly P42MAPK/ERK2, P54JNK2 and P38. There was no obvious difference in activation of every member from 1 kU/L to 100 kU/L, which was another example of high efficiency of IL-1R. However, the peak of activation of ERK and P38 by IL-1β was obtained at 1-5 mins, but that of JNK kinase was at 20 min.
, 百拇医药
It has been illustrated that MAPKs is a convergence point of many signal pathways (PKC,RPTK, JAK- STAT and ion-channle,etc). It can transduce extracellular stimuli to nucleus, regulate transcription factors, and drive expression of the relative genes. The classic activation pathway of ERK is RPTK-ras-raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2-MAPKPK to initiate cellular process, such as proliferation,differentiation, transformation and cell cycle[3]. Our
recent reports showed that IL-1β in a defined concentration could stimulate RA FLS proliferation, acting as mitogens. It is possible that the mitogenic role of IL-1β in RA FLS is mediated by MAPK/ERK. In contrast, JNK and P38 kinase are activated by inflammatory cytokines and cellular stresses such as heat shock, osmotic stress or ultraviolet (UV) light[9]. Just as described above, MAPKs may be stimulated by different factors, to construct three independent pathways and to govern a large number of cellular proceses. However, MAPKs act in concert with other signaling systems. Therefore, the cross-talk between the above pathways is crucial to the coordinated response of cells. MAPKs may act antagonistically in cells undergoing apoptosis; or may cooperate with or antagonize each other in supporting cell proliferation.
, 百拇医药
Altogether, IL-1β can activate three MAPKs subfamily members in RA FLS independently and coordinantly, and can lead to a serial of proteins tyrosine phosphorylated transiently in RA FLS , which may induce the complicate biological response leading to cartilage and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis.
Biography: The study is granted by the Important Item of National Natural Science fundation of China, No. 39730430
Author: Sun TZ, male, twenty- six- year- old,undergraduate MD
, http://www.100md.com
No.42,Bei- Li- Shi Road, Beijing 100044, China
Tel.(010)68314422- 5936, E- mail. Suntz@public3. bta.net.cn
REFERENCES
〔1〕 Lafyatis R,Remmers EF,Roberts AB,et al.Anchorage-independent growth of synoviocytes from arthritic and normal joints.Stimulation by exogenous platelet-derived growth factor and inhibition by transforming growth factor-beta and retinoids〔J〕.J Clin Invest,1989;83:1267-1276.
, http://www.100md.com
〔2〕 Guy GR,Chua SP,Wong NS,et al.Interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor activate common multiple protein kinases in human fibroblast〔J〕.J Biol Chem,1991;266:14343-14352.
〔3〕 Seger R,Krebs E.The MAPK signaling cascade〔J〕.FASEB J,1995;9:726-735.
〔4〕 Arnet FC,Edworthy SM,Bloch DA,et al.The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis〔J〕.Arthritis Rheum,1988;31:315-324.
, 百拇医药
〔5〕 Breecheld F.New tumor necrosis factor-alpha biologic therapies for rheumatoid arthritis〔J〕.Eur Cytokine Netw,1998;9:233-238.
〔6〕 Evans CH,Ghivizzani SC,Kang R,et al.Gene therapy for rheumatic diseases〔J〕.Arthritis Rheumatism,1999;42:1-16.
〔7〕 Dinarello CA.The interleukin-1 family:10 years of discovery〔J〕.FASEB J,1994;8:1314-1325.
〔8〕 Auron PE.The interleukin 1 receptor:ligand interaction and signal transduction〔J〕.Cyto Grow Fact Rev,1998;314:221-237.
〔9〕 Kyriakis JM,Banerjee P,Niklokaki E,et al.The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-jun kinases〔J〕.Nature,1994;369:156-160.
Received date:1999-10-09
revised date:1999-11-13, 百拇医药