不同认知水平条件下左右脑对左右视场信号的不对称反应特征
作者:魏金河 赵仑 任维 李大琛 严拱东 杨明浩
单位:魏金河.航天医学工程研究所,北京 100094
关键词:认知;视域;脑功能;选择注意;左脑;右脑
航天医学与医学工程000301Unsymmetrical Response Features of Left and Right Brain to Signals from Left and Right Visual Fields at Different Cognitive Levels
WEI Jin-he, ZHAO Lun,REN Wei,LI Da-chen,YAN Gong-dong,YANG Ming-hao
(Institute of Space Medico-Engineering, Beijing 100094)
, 百拇医药
Abstract:Objective To study the response characteristics of left and right brain to signals from left(LVF) and right(RVF) visual fields during cognitive activity. Method ERPs at 9 locations to LVF and RVF signals were compared in 23 normal subjects in 3 task conditions:looking forward only (VC); making switch response to target signals(T) only(SR); making switch response to T differentially(DR). Result (1)Significant difference in ERPs was found between that induced by LVF and RVF signals on left brain especially at frontal location(F5), which appeared as slow negative deflection induced by T and NT from RVF in SR and DR;(2) Condition-dependent unsymmetrical features between left and right brain were found: the slow potential at F5 was significantly more negative in T and contralateral spatial relation(i.e., left brain for RVF) but more positive in NT and ipsilateral relation than that at F6.Conclusion Signals with psychological meaning in RVF might cause more psychological load as suggested by the results obtained in this study.
, 百拇医药
Key words: cognition;visual field;brain function;selective attention;left brain;right brain
摘要: 目的 探讨在认知活动中左右脑对左右视场(LVF,RVF)信号的反应特性。 方法 对23名被试者在3种任务条件下9个部位的与LVF和RVF相应的事件关联电位(ERPs)进行了比较。刺激信号为位于LVF和RVF中的红、绿闪光,等概率随机出现,交叉地规定红或绿闪光为靶信号(T)。3种任务是:视对照(VC);简单选择反应(SR);选择区分反应(DR),对LVF和RVF的T分别向左和右拨开关。 结果 (1)除外源性的P1和N1成分外,与LVF和RVF相应的ERPs的差别突出地表现在左额区(F5),即在SR和DR条件下RVF的T-ERPs及NT-ERPs中出现显著的负慢波,而右脑对信号的方位不敏感;(2)左右脑对LVF和RVF信号反应的不对称性与认知状态有关:靶信号时与对侧视场相应的ERPs左脑比右脑显著偏负,而非靶信号则是与同侧视场相应的ERPs在左、右脑出现显著差别,且是右脑(F5,C5)偏负。 结论 左右脑对靶和非靶信号的反应不同提示二者在信号加工过程中的不同功能;左额区对RVF中靶和非靶信号的负慢电位反应提示右视场中具有心理意义的信号可能引起较大的心理负荷。
, 百拇医药
中图法分类号:B842.1 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1002-0837(2000)03-0157-05
The lateralization of brain response to signals from left and right visual field(LVF and RVF) has been revealed by divided visual field experiment, either by evoked potential[1] or by task related ERPs components[2]. The main characteristics of the task-related lateralization was that the amplitude became greater for negative and positive potentials induced by signals from contralateral and ipsilateral visual field, respectively.
, 百拇医药
In view of the response features of the two sides of brain, it is interesting to know further whether this kind of lateralization is symmetrical or not. Although findings for unsymmetrical lateralization have been reported[3~5],the lateral attention was involved in those studies.To see the effect of visual field or the response characteristics of left and fight brain per se, lateral attention should be avoided. Thus, in the present study, the same flashing signals from LVF and RVF were used in different cognitive tasks, and the effects of ipsilateral and contralateral spatial relationship on ERPs components at the two sides of brain were compared. The special concern was the slow potential response as it related to the brain function state change[6,7].
, 百拇医药
Method
Subjects and experiment condition The subjects were 23 paid healthy right-handed volunteers aged 23.4±2.9 years.The experiment was conducted in an electrical shielded and sound-damped room with moderate background lighting. The subjects were in supine position during experiment.
Stimulation and task The stimulation signals were red(R) and green(G) flashes provided by two double-color LEDs with moderate brightness which were positioned 3cm apart from the center yellow LED on the left and right, respectively. While the center LED was lighted weakly all the time, the red and green flashes appeared randomly in LVF or RVF with equal probability and intervals of 1.5 to 2.3s so that four types of input signal were produced, i.e., LVF-R, LVF-G, RVF-R and RVF-G. The number of flashes in one run was 120. The plastic board carrying the LEDs was positioned 30 cm in the front of subject eyes.
, http://www.100md.com
While the subjects were asked to look at the center LED, 3 task conditions were assigned as follows: 1) looking at only(VC); 2)making switching response simply(SR) to target signals(T) and ignoring the non-target ones(NT); 3) making switch response differentially(DR) to target signals, i.e., switching to left or right for Ts from LVF or RVF, respectively. Taking red or green flashes as Ts was cross-balanced among subjects.
Signal recording EEG signals were recorded at F5, F6, C5, C6, P5, P6, Fz, Cz and Pz according to the 10-10 EEG electrode system[8] referenced to the linked mastoids. EOG was recorded from left eye.The EEG, EOG and the event pulses representing the four types of signals were digitized on line at a rate of 256/s by a 12 bit A/D converter and stored on optical disk.
, 百拇医药
Procedures After the subjects practiced all the 3 task operations, recordings were made in VC, SR and DR conditions, intervened by 3 min.
Data analysis ERPs were derived by using the recorded 4 kinds of event pulses, representing red and green signals from LVF and RVF, respectively, as trigger signals. The resulted ERPs, with a time length of 2000 ms containing 500 ms before stimulus, in each subject were grouped into LT, RT(target from LVF and RVF respectively), and LN, RN(non-target from LVF and RVF respectively) according to the target assignment. Then it was digitally filtered(0~30 Hz) with no phase shift. The mean value of ERPs before stimulation(0.5 s) was used for baseline correction.
, 百拇医药
The ERPs were compared in terms of paired t-test between different conditions: LVF vs. RVF as well as left brain vs. right brain. Two-way ANOVA was used to evaluate the effect on ERPs of spatial relations and T and NT conditions.
Result
Features of ERPs induced by signals from LVF and RVF in VC, SR and DR conditions The ERPs induced by LVF and RVF signals in VC, SR and DR conditions were shown in Fig.1, Fig.2 and Fig.3, respectively. Two prominent points could be seen clearly in all the conditions. The P1(peaked around 160 ms) and N1(around 180 ms) components were evoked predominantly by the contralateral and ipsilateral signals, respectively; thereafter, significant difference appeared on left brain especially at F5 in a common way that the ERPs induced by contralateral signals were more negative than that induced by ipsilateral ones. The degree of this difference showed dependency upon mental condition, i.e., it became much more significant in SR and DR than in VC, and much more significant in T than in NT condition.
, http://www.100md.com
Fig.1 ERPs induced by signals from LVF and RVF respectively in VC condition
LVF-thin line, RVF-heavy line. The vertical line between the two ERP curves indicates the difference at given point was statistically significant(P<0.05). The presentation for target(A) and non-target(B) conditions in VC was only for the comparison with that in SR and DR as no selective attention was required in VC.
, 百拇医药
Fig.2 ERPs induced by signals from LVF and RVF respectively in SR condition
LVF-thin line, RVF-heavy line. The meaning of vertical line between the two ERP curves was as same as in Fig.1.A. T-ERPs; B. NT-ERPs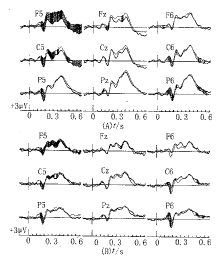
Fig.3 ERPs induced by signals from LVF and RVF respectively in DR condition.
LVF-thin line, RVF-heavy line. The meaning of vertical line between the two ERP curves was as same as in Fig.2
, http://www.100md.com
The results of ANOVA(Table 1) were in accordance with the points described above: the effect of spatial relation was dominant at frontal region and more significant in SR and DR conditions; significant effect of targetness appeared only in SR and DR conditions.
The differences of mean amplitude of T and NT ERPs in 4 time segments between left and right brain were shown in Table 2 for ipsilateral and contralateral spatial relations, respectively. It could be seen that in T condition, the potentials in 0.33~0.45s and 0.45~0.6 s post stimulus were significantly negative at left frontal and central locations both in SR and DR but only for contralateral conditions; in NT condition, however, significant difference appeared mainly in ipsilateral and SR condition such that the slow potential from 0.1 to 0.45 s were more positive on left brain, most prominently at frontal regions.Table 1 F values of two-way ANOVA showing the effect of ipsilateral and contralateral relations and targetness on the difference of ERPs amplitude between left and right brain in 4 time segments condition
, 百拇医药
location
F(ipsilateral vs. Contralateral)
F(T vs. NT)
Tsg1
Tsg2
Tsg3
Tsg4
Tsg1
Tsg2
Tsg3
Tsg4
VC
, http://www.100md.com
Frontal
0.9
4.4*
4.1*
4.0*
1.8
2.1
1.7
1.0
Central
0.2
1.5
, 百拇医药
0.0
1.3
0.3
0.0
0.3
0.0
Posterior
0.1
0.3
2.8
0.4
1.2
0.2
, http://www.100md.com
3.1
1.8
SR
Frontal
8.3**
17.6***
16.1***
5.4*
0.5
0.1
6.2*
1.2
, 百拇医药
Central
1.5
6.9*
2.6
0.1
0.0
4.2*
8.1**
2.5
Posterior
1.2
1.4
, http://www.100md.com
0.0
1.6
0.0
0.9
0.7
0.1
DR
Frontal
5.0*
5.3*
14.1***
3.3
, 百拇医药
0.3
0.2
2.3
0.1
Central
0.1
0.1
2.9
0.2
0.0
1.1
6.7*
1.8
, 百拇医药
Posterior
1.5
1.0
0.7
0.8
0.0
1.2
3.1
0.0
*P<0.05;**P<0.01;***P<0.001;Tsg1=0.1~0.2 s, Tsg2=0.2~0.33 s, Tsg3=0.33~0.45 s, Tsg4=0.45~0.6 s, post stimulusTable 2 Difference of ERPs amplitude(μV) between left and right brain in 4 time segments# condition
, 百拇医药
brain location
ipsilateral
contralateral
Tsg1
Tsg2
Tsg3
Tsg4
Tsg1
Tsg2
Tsg3
Tsg4
target
, http://www.100md.com
SR
frontal
0.9
1.0
0.1
0.6
-0.0
-1.4
-2.7**
-1.5*
central
0.2
, http://www.100md.com 0.2
-1.2
-0.7
0.4
-1.3
-2.3**
-1.2*
posterior
-0.6
-0.3
-0.9
-0.8
, 百拇医药 1.3
-0.2
-0.3
0.1
DR
frontal
1.4
1.8
1.3
0.9
-0.7
-2.1*
-3.2**
, http://www.100md.com
-1.9*
central
0.4
0.4
-1.0
-1.0
0.1
-0.9
-2.5**
-1.3*
posterior
-0.6
, 百拇医药
-0.3
-0.9
-0.8
0.3
-0.1
-1.1
-0.3
non-target
SR
frontal
1.0*
1.6**
, 百拇医药
1.9**
0.6
-0.9
-1.6*
-0.9
-0.6
central
1.2*
1.8**
1.0
-0.0
-0.5
, http://www.100md.com
-0.2
-0.2
0.2
posterior
0.5
1.3*
0.2
-0.8
-0.2
-0.0
-0.0
0.1
DR
, 百拇医药
frontal
0.3
0.4
1.0
-0.2
-0.3
0.0
-0.4
-0.4
central
0.2
0.1
0.7
, 百拇医药
-0.7
0.2
0.9
-0.3
0.2
posterior
-0.1
-0.0
0.6
-0.7
0.3
1.2
-0.2
, http://www.100md.com
-0.3
# left brain minus right brain;*P<0.05;**P<0.01;Tsg1=0.1~0.2s, Tsg2=0.2~0.33s, Tsg3=0.33~0.45s, Tsg4=0.45~0.6s, post stimulus Discussion
The most interesting point in the findings was the apparently different response property of the left and right frontal regions(F5 and F6).In a similar selective response study but the flashing signal only located at the center of the visual field, the amplitudes of P300 at F5 and F6 were close each other[9].
, http://www.100md.com
The difference in ERPs changes with respect to the visual field might be resulted from the function difference between left and right brain per se. The right brain was evidenced to be more involved in attention control[10,11], and the slow positive potential was supposed as an indication of the active inhibitory activity during attention and/or memory-related process[6,7,12], therefore, activation of the right brain by LVF signals was either less than the effect of attention or characterized by positive potential.Therefore, the unsymmetrical phenomenon revealed by DVF experiment was determined by the response property of the two sides of the brain. The possibility that competition among several brain processes such as, attention, general activation, movement and memory-related processes, might exist. If so, the more flexible response characteristics of left frontal region would probably suggest its importance in dealing with different requirements by cognition, this point was in accordance with the new findings in split-brain study[13].
, 百拇医药
Taking account of the points discussed above and the relation between ERPs amplitude and work load reported by Kramer et al[14],it might be hypothesized that the signals from RVF with psychological meaning put more mental load on the left brain.
The ERPs difference between left and right brain in NT condition was another interesting point which was probably resulted from an additional negative component appeared on the right brain induced by NT signals.As the right brain is more responsible for attention, the expected mode of target signal is probably stayed in the working memory in the right frontal lobe[15], thus, it responds to T with "yes" represented by slow poed at the center of the visual field, the amplitudes of P300 at F5 and F6 were close each other[9].
, http://www.100md.com
The difference in ERPs changes with respect to the visual field might be resulted from the function difference between left and right brain per se. The right brain was evidenced to be more involved in attention control[10,11], and the slow positive potential was supposed as an indication of the active inhibitory activity during attention and/or memory-related process[6,7,12], therefore, activation of the right brain by LVF signals was either less than the effect of attention or characterized by positive potential.Therefore, the unsymmetrical phenomenon revealed by DVF experiment was determined by the response property of the two sides of the brain. The possibility that competition among several brain processes such as, attention, general activation, movement and memory-related processes, might exist. If so, the more flexible response characteristics of left frontal region would probably suggest its importance in dealing with different requirements by cognition, this point was in accordance with the new findings in split-brain study[13].
, http://www.100md.com
Taking account of the points discussed above and the relation between ERPs amplitude and work load reported by Kramer et al[14],it might be hypothesized that the signals from RVF with psychological meanain potential
[1]Barrett G,Blumhardt LD,Halliday AM et al.A paradox in the lateralization of the visral response[J].Nature(London),1976,261:253-255
[2]Kok A,Rooyakers JAJ.ERPsto laterally presented [J].Psychophysiology,1986,23:672-683
, 百拇医药
[3]Heinze HJ,Mangun GR,Burchert W et al,Combined spatial and tmmporal imaging of brain activity during visual selective attention in humans[J].Nature(London),1994,372:543-546
[4]Verleger R,Heide W,Butt C et al On-line brain potential correlates of right periatal patiens' attentional deficit[J].Electroenceph Clin Neurophysiol,1996,99: 444~457
[5] Eimer M.ERP modulations indicate the selective processing of visual stimuli as a result of transient and sustained spatial attention[J].Psychophysiology,1996,33: 13~21
, 百拇医药
[6] Wei J,Yan G,Zhao L et al.A new component of brain potentials clearly related to number recall[J].Space Medicine & Medical Engineering,1997,10: 84~87
[7] Wei J,Zhao L,Yan G et al.Temporal and spatial features of slow positive potential related to visual selective response during head-down tilt[J].Space Medicine and Medical Engineering,1998,11:157~161
[8] Chatrian GE,Lettich E,Nelson PL.Improved nomenclature for the “10%" electrode system[J].Am J EEG Technol,1988,28: 161~163
, http://www.100md.com
[9] Lu Y,Wei J,Yan G et al.Study on P300 of selective response to visual signals with half to half probability[J].Space Medicine & Medical Engineering,1996,9:397~402
[10] Mesulam M~M.A cortical network for directed attention and unilateral neglect[J].Annals of Neurology,1981,10: 309~325
[11] Posner MI,Inhoff AW,Friedrich FJ et al.Isolating attentional systems: A cognitive anatomical analysis[J].Psychophysiology,1987,15: 107~121
, http://www.100md.com
[12] Elbert T.A theoretical approach to tate components of the event-related potential[C].In: A.Artsen and V.Braitenberg(Eds.),Information Processing in The Cortex Experiments and Theory.Berlin:Spring-Verlag,1992:225~245
[13] Gazzaniga MS.Groundbreaking work that began more than a quater of a century ago has led to ongoing insights about brain organization and consciousness[J].Scientific American,1998,7: 51~55
[14] Kramer AF,Sirevaag EJ,Braune R.A psychophysiological assesment of operator work load during simulated flight mission[J].Human Factor,1987,29(2): 145~160
[15] Smith EE,Jonides J.Storage and executive processes in the frontal lobes[J].Science,1999,283:1657~1661
Recieved date:1999-09-23, http://www.100md.com
单位:魏金河.航天医学工程研究所,北京 100094
关键词:认知;视域;脑功能;选择注意;左脑;右脑
航天医学与医学工程000301Unsymmetrical Response Features of Left and Right Brain to Signals from Left and Right Visual Fields at Different Cognitive Levels
WEI Jin-he, ZHAO Lun,REN Wei,LI Da-chen,YAN Gong-dong,YANG Ming-hao
(Institute of Space Medico-Engineering, Beijing 100094)
, 百拇医药
Abstract:Objective To study the response characteristics of left and right brain to signals from left(LVF) and right(RVF) visual fields during cognitive activity. Method ERPs at 9 locations to LVF and RVF signals were compared in 23 normal subjects in 3 task conditions:looking forward only (VC); making switch response to target signals(T) only(SR); making switch response to T differentially(DR). Result (1)Significant difference in ERPs was found between that induced by LVF and RVF signals on left brain especially at frontal location(F5), which appeared as slow negative deflection induced by T and NT from RVF in SR and DR;(2) Condition-dependent unsymmetrical features between left and right brain were found: the slow potential at F5 was significantly more negative in T and contralateral spatial relation(i.e., left brain for RVF) but more positive in NT and ipsilateral relation than that at F6.Conclusion Signals with psychological meaning in RVF might cause more psychological load as suggested by the results obtained in this study.
, 百拇医药
Key words: cognition;visual field;brain function;selective attention;left brain;right brain
摘要: 目的 探讨在认知活动中左右脑对左右视场(LVF,RVF)信号的反应特性。 方法 对23名被试者在3种任务条件下9个部位的与LVF和RVF相应的事件关联电位(ERPs)进行了比较。刺激信号为位于LVF和RVF中的红、绿闪光,等概率随机出现,交叉地规定红或绿闪光为靶信号(T)。3种任务是:视对照(VC);简单选择反应(SR);选择区分反应(DR),对LVF和RVF的T分别向左和右拨开关。 结果 (1)除外源性的P1和N1成分外,与LVF和RVF相应的ERPs的差别突出地表现在左额区(F5),即在SR和DR条件下RVF的T-ERPs及NT-ERPs中出现显著的负慢波,而右脑对信号的方位不敏感;(2)左右脑对LVF和RVF信号反应的不对称性与认知状态有关:靶信号时与对侧视场相应的ERPs左脑比右脑显著偏负,而非靶信号则是与同侧视场相应的ERPs在左、右脑出现显著差别,且是右脑(F5,C5)偏负。 结论 左右脑对靶和非靶信号的反应不同提示二者在信号加工过程中的不同功能;左额区对RVF中靶和非靶信号的负慢电位反应提示右视场中具有心理意义的信号可能引起较大的心理负荷。
, 百拇医药
中图法分类号:B842.1 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1002-0837(2000)03-0157-05
The lateralization of brain response to signals from left and right visual field(LVF and RVF) has been revealed by divided visual field experiment, either by evoked potential[1] or by task related ERPs components[2]. The main characteristics of the task-related lateralization was that the amplitude became greater for negative and positive potentials induced by signals from contralateral and ipsilateral visual field, respectively.
, 百拇医药
In view of the response features of the two sides of brain, it is interesting to know further whether this kind of lateralization is symmetrical or not. Although findings for unsymmetrical lateralization have been reported[3~5],the lateral attention was involved in those studies.To see the effect of visual field or the response characteristics of left and fight brain per se, lateral attention should be avoided. Thus, in the present study, the same flashing signals from LVF and RVF were used in different cognitive tasks, and the effects of ipsilateral and contralateral spatial relationship on ERPs components at the two sides of brain were compared. The special concern was the slow potential response as it related to the brain function state change[6,7].
, 百拇医药
Method
Subjects and experiment condition The subjects were 23 paid healthy right-handed volunteers aged 23.4±2.9 years.The experiment was conducted in an electrical shielded and sound-damped room with moderate background lighting. The subjects were in supine position during experiment.
Stimulation and task The stimulation signals were red(R) and green(G) flashes provided by two double-color LEDs with moderate brightness which were positioned 3cm apart from the center yellow LED on the left and right, respectively. While the center LED was lighted weakly all the time, the red and green flashes appeared randomly in LVF or RVF with equal probability and intervals of 1.5 to 2.3s so that four types of input signal were produced, i.e., LVF-R, LVF-G, RVF-R and RVF-G. The number of flashes in one run was 120. The plastic board carrying the LEDs was positioned 30 cm in the front of subject eyes.
, http://www.100md.com
While the subjects were asked to look at the center LED, 3 task conditions were assigned as follows: 1) looking at only(VC); 2)making switching response simply(SR) to target signals(T) and ignoring the non-target ones(NT); 3) making switch response differentially(DR) to target signals, i.e., switching to left or right for Ts from LVF or RVF, respectively. Taking red or green flashes as Ts was cross-balanced among subjects.
Signal recording EEG signals were recorded at F5, F6, C5, C6, P5, P6, Fz, Cz and Pz according to the 10-10 EEG electrode system[8] referenced to the linked mastoids. EOG was recorded from left eye.The EEG, EOG and the event pulses representing the four types of signals were digitized on line at a rate of 256/s by a 12 bit A/D converter and stored on optical disk.
, 百拇医药
Procedures After the subjects practiced all the 3 task operations, recordings were made in VC, SR and DR conditions, intervened by 3 min.
Data analysis ERPs were derived by using the recorded 4 kinds of event pulses, representing red and green signals from LVF and RVF, respectively, as trigger signals. The resulted ERPs, with a time length of 2000 ms containing 500 ms before stimulus, in each subject were grouped into LT, RT(target from LVF and RVF respectively), and LN, RN(non-target from LVF and RVF respectively) according to the target assignment. Then it was digitally filtered(0~30 Hz) with no phase shift. The mean value of ERPs before stimulation(0.5 s) was used for baseline correction.
, 百拇医药
The ERPs were compared in terms of paired t-test between different conditions: LVF vs. RVF as well as left brain vs. right brain. Two-way ANOVA was used to evaluate the effect on ERPs of spatial relations and T and NT conditions.
Result
Features of ERPs induced by signals from LVF and RVF in VC, SR and DR conditions The ERPs induced by LVF and RVF signals in VC, SR and DR conditions were shown in Fig.1, Fig.2 and Fig.3, respectively. Two prominent points could be seen clearly in all the conditions. The P1(peaked around 160 ms) and N1(around 180 ms) components were evoked predominantly by the contralateral and ipsilateral signals, respectively; thereafter, significant difference appeared on left brain especially at F5 in a common way that the ERPs induced by contralateral signals were more negative than that induced by ipsilateral ones. The degree of this difference showed dependency upon mental condition, i.e., it became much more significant in SR and DR than in VC, and much more significant in T than in NT condition.

, http://www.100md.com
Fig.1 ERPs induced by signals from LVF and RVF respectively in VC condition
LVF-thin line, RVF-heavy line. The vertical line between the two ERP curves indicates the difference at given point was statistically significant(P<0.05). The presentation for target(A) and non-target(B) conditions in VC was only for the comparison with that in SR and DR as no selective attention was required in VC.

, 百拇医药
Fig.2 ERPs induced by signals from LVF and RVF respectively in SR condition
LVF-thin line, RVF-heavy line. The meaning of vertical line between the two ERP curves was as same as in Fig.1.A. T-ERPs; B. NT-ERPs

Fig.3 ERPs induced by signals from LVF and RVF respectively in DR condition.
LVF-thin line, RVF-heavy line. The meaning of vertical line between the two ERP curves was as same as in Fig.2
, http://www.100md.com
The results of ANOVA(Table 1) were in accordance with the points described above: the effect of spatial relation was dominant at frontal region and more significant in SR and DR conditions; significant effect of targetness appeared only in SR and DR conditions.
The differences of mean amplitude of T and NT ERPs in 4 time segments between left and right brain were shown in Table 2 for ipsilateral and contralateral spatial relations, respectively. It could be seen that in T condition, the potentials in 0.33~0.45s and 0.45~0.6 s post stimulus were significantly negative at left frontal and central locations both in SR and DR but only for contralateral conditions; in NT condition, however, significant difference appeared mainly in ipsilateral and SR condition such that the slow potential from 0.1 to 0.45 s were more positive on left brain, most prominently at frontal regions.Table 1 F values of two-way ANOVA showing the effect of ipsilateral and contralateral relations and targetness on the difference of ERPs amplitude between left and right brain in 4 time segments condition
, 百拇医药
location
F(ipsilateral vs. Contralateral)
F(T vs. NT)
Tsg1
Tsg2
Tsg3
Tsg4
Tsg1
Tsg2
Tsg3
Tsg4
VC
, http://www.100md.com
Frontal
0.9
4.4*
4.1*
4.0*
1.8
2.1
1.7
1.0
Central
0.2
1.5
, 百拇医药
0.0
1.3
0.3
0.0
0.3
0.0
Posterior
0.1
0.3
2.8
0.4
1.2
0.2
, http://www.100md.com
3.1
1.8
SR
Frontal
8.3**
17.6***
16.1***
5.4*
0.5
0.1
6.2*
1.2
, 百拇医药
Central
1.5
6.9*
2.6
0.1
0.0
4.2*
8.1**
2.5
Posterior
1.2
1.4
, http://www.100md.com
0.0
1.6
0.0
0.9
0.7
0.1
DR
Frontal
5.0*
5.3*
14.1***
3.3
, 百拇医药
0.3
0.2
2.3
0.1
Central
0.1
0.1
2.9
0.2
0.0
1.1
6.7*
1.8
, 百拇医药
Posterior
1.5
1.0
0.7
0.8
0.0
1.2
3.1
0.0
*P<0.05;**P<0.01;***P<0.001;Tsg1=0.1~0.2 s, Tsg2=0.2~0.33 s, Tsg3=0.33~0.45 s, Tsg4=0.45~0.6 s, post stimulusTable 2 Difference of ERPs amplitude(μV) between left and right brain in 4 time segments# condition
, 百拇医药
brain location
ipsilateral
contralateral
Tsg1
Tsg2
Tsg3
Tsg4
Tsg1
Tsg2
Tsg3
Tsg4
target
, http://www.100md.com
SR
frontal
0.9
1.0
0.1
0.6
-0.0
-1.4
-2.7**
-1.5*
central
0.2
, http://www.100md.com 0.2
-1.2
-0.7
0.4
-1.3
-2.3**
-1.2*
posterior
-0.6
-0.3
-0.9
-0.8
, 百拇医药 1.3
-0.2
-0.3
0.1
DR
frontal
1.4
1.8
1.3
0.9
-0.7
-2.1*
-3.2**
, http://www.100md.com
-1.9*
central
0.4
0.4
-1.0
-1.0
0.1
-0.9
-2.5**
-1.3*
posterior
-0.6
, 百拇医药
-0.3
-0.9
-0.8
0.3
-0.1
-1.1
-0.3
non-target
SR
frontal
1.0*
1.6**
, 百拇医药
1.9**
0.6
-0.9
-1.6*
-0.9
-0.6
central
1.2*
1.8**
1.0
-0.0
-0.5
, http://www.100md.com
-0.2
-0.2
0.2
posterior
0.5
1.3*
0.2
-0.8
-0.2
-0.0
-0.0
0.1
DR
, 百拇医药
frontal
0.3
0.4
1.0
-0.2
-0.3
0.0
-0.4
-0.4
central
0.2
0.1
0.7
, 百拇医药
-0.7
0.2
0.9
-0.3
0.2
posterior
-0.1
-0.0
0.6
-0.7
0.3
1.2
-0.2
, http://www.100md.com
-0.3
# left brain minus right brain;*P<0.05;**P<0.01;Tsg1=0.1~0.2s, Tsg2=0.2~0.33s, Tsg3=0.33~0.45s, Tsg4=0.45~0.6s, post stimulus Discussion
The most interesting point in the findings was the apparently different response property of the left and right frontal regions(F5 and F6).In a similar selective response study but the flashing signal only located at the center of the visual field, the amplitudes of P300 at F5 and F6 were close each other[9].
, http://www.100md.com
The difference in ERPs changes with respect to the visual field might be resulted from the function difference between left and right brain per se. The right brain was evidenced to be more involved in attention control[10,11], and the slow positive potential was supposed as an indication of the active inhibitory activity during attention and/or memory-related process[6,7,12], therefore, activation of the right brain by LVF signals was either less than the effect of attention or characterized by positive potential.Therefore, the unsymmetrical phenomenon revealed by DVF experiment was determined by the response property of the two sides of the brain. The possibility that competition among several brain processes such as, attention, general activation, movement and memory-related processes, might exist. If so, the more flexible response characteristics of left frontal region would probably suggest its importance in dealing with different requirements by cognition, this point was in accordance with the new findings in split-brain study[13].
, 百拇医药
Taking account of the points discussed above and the relation between ERPs amplitude and work load reported by Kramer et al[14],it might be hypothesized that the signals from RVF with psychological meaning put more mental load on the left brain.
The ERPs difference between left and right brain in NT condition was another interesting point which was probably resulted from an additional negative component appeared on the right brain induced by NT signals.As the right brain is more responsible for attention, the expected mode of target signal is probably stayed in the working memory in the right frontal lobe[15], thus, it responds to T with "yes" represented by slow poed at the center of the visual field, the amplitudes of P300 at F5 and F6 were close each other[9].
, http://www.100md.com
The difference in ERPs changes with respect to the visual field might be resulted from the function difference between left and right brain per se. The right brain was evidenced to be more involved in attention control[10,11], and the slow positive potential was supposed as an indication of the active inhibitory activity during attention and/or memory-related process[6,7,12], therefore, activation of the right brain by LVF signals was either less than the effect of attention or characterized by positive potential.Therefore, the unsymmetrical phenomenon revealed by DVF experiment was determined by the response property of the two sides of the brain. The possibility that competition among several brain processes such as, attention, general activation, movement and memory-related processes, might exist. If so, the more flexible response characteristics of left frontal region would probably suggest its importance in dealing with different requirements by cognition, this point was in accordance with the new findings in split-brain study[13].
, http://www.100md.com
Taking account of the points discussed above and the relation between ERPs amplitude and work load reported by Kramer et al[14],it might be hypothesized that the signals from RVF with psychological meanain potential
[1]Barrett G,Blumhardt LD,Halliday AM et al.A paradox in the lateralization of the visral response[J].Nature(London),1976,261:253-255
[2]Kok A,Rooyakers JAJ.ERPsto laterally presented [J].Psychophysiology,1986,23:672-683
, 百拇医药
[3]Heinze HJ,Mangun GR,Burchert W et al,Combined spatial and tmmporal imaging of brain activity during visual selective attention in humans[J].Nature(London),1994,372:543-546
[4]Verleger R,Heide W,Butt C et al On-line brain potential correlates of right periatal patiens' attentional deficit[J].Electroenceph Clin Neurophysiol,1996,99: 444~457
[5] Eimer M.ERP modulations indicate the selective processing of visual stimuli as a result of transient and sustained spatial attention[J].Psychophysiology,1996,33: 13~21
, 百拇医药
[6] Wei J,Yan G,Zhao L et al.A new component of brain potentials clearly related to number recall[J].Space Medicine & Medical Engineering,1997,10: 84~87
[7] Wei J,Zhao L,Yan G et al.Temporal and spatial features of slow positive potential related to visual selective response during head-down tilt[J].Space Medicine and Medical Engineering,1998,11:157~161
[8] Chatrian GE,Lettich E,Nelson PL.Improved nomenclature for the “10%" electrode system[J].Am J EEG Technol,1988,28: 161~163
, http://www.100md.com
[9] Lu Y,Wei J,Yan G et al.Study on P300 of selective response to visual signals with half to half probability[J].Space Medicine & Medical Engineering,1996,9:397~402
[10] Mesulam M~M.A cortical network for directed attention and unilateral neglect[J].Annals of Neurology,1981,10: 309~325
[11] Posner MI,Inhoff AW,Friedrich FJ et al.Isolating attentional systems: A cognitive anatomical analysis[J].Psychophysiology,1987,15: 107~121
, http://www.100md.com
[12] Elbert T.A theoretical approach to tate components of the event-related potential[C].In: A.Artsen and V.Braitenberg(Eds.),Information Processing in The Cortex Experiments and Theory.Berlin:Spring-Verlag,1992:225~245
[13] Gazzaniga MS.Groundbreaking work that began more than a quater of a century ago has led to ongoing insights about brain organization and consciousness[J].Scientific American,1998,7: 51~55
[14] Kramer AF,Sirevaag EJ,Braune R.A psychophysiological assesment of operator work load during simulated flight mission[J].Human Factor,1987,29(2): 145~160
[15] Smith EE,Jonides J.Storage and executive processes in the frontal lobes[J].Science,1999,283:1657~1661
Recieved date:1999-09-23, http://www.100md.com