反复喘息幼儿外周血CD4+CD25+Foxp3+调节性T淋巴细胞、IL-10及IgE水平的研究
颉雅苹?童志杰?樊慧峰?卢秉泰?陈容珊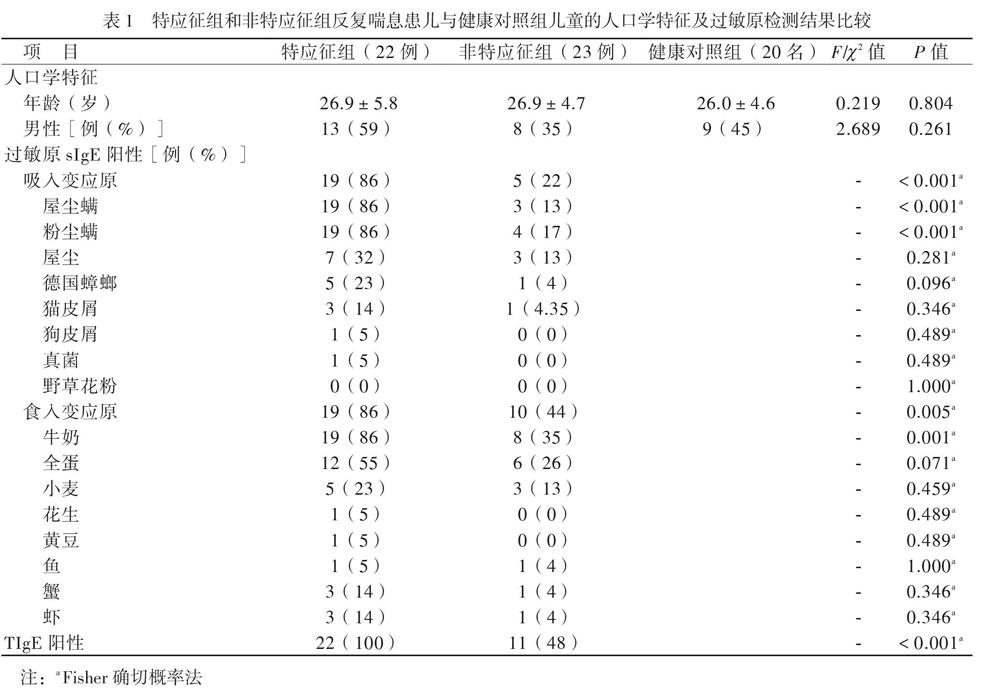
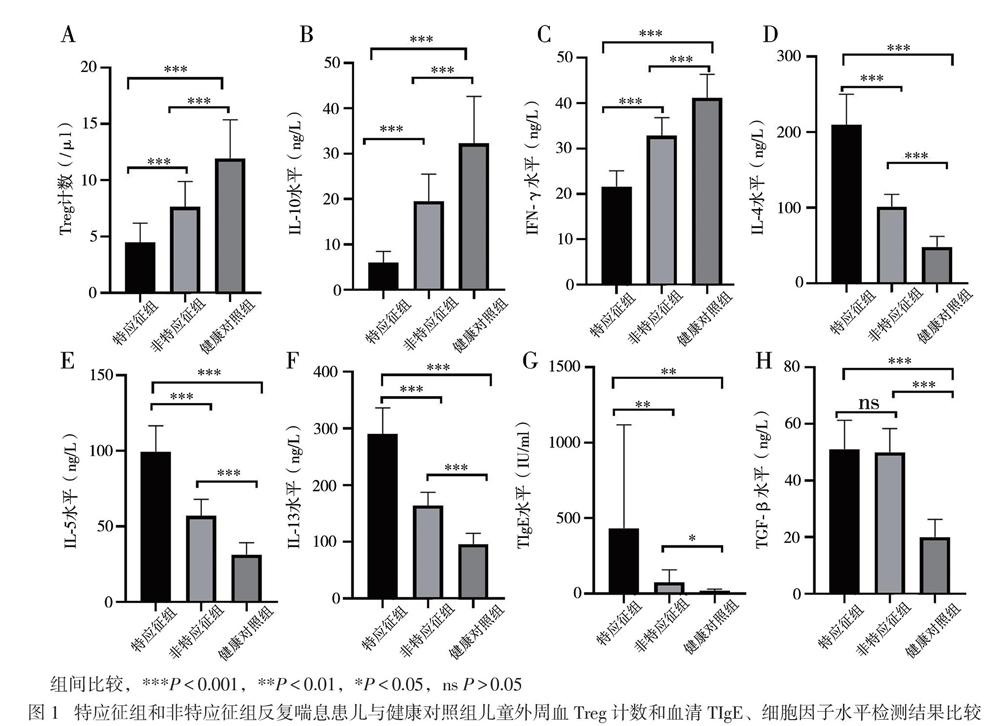
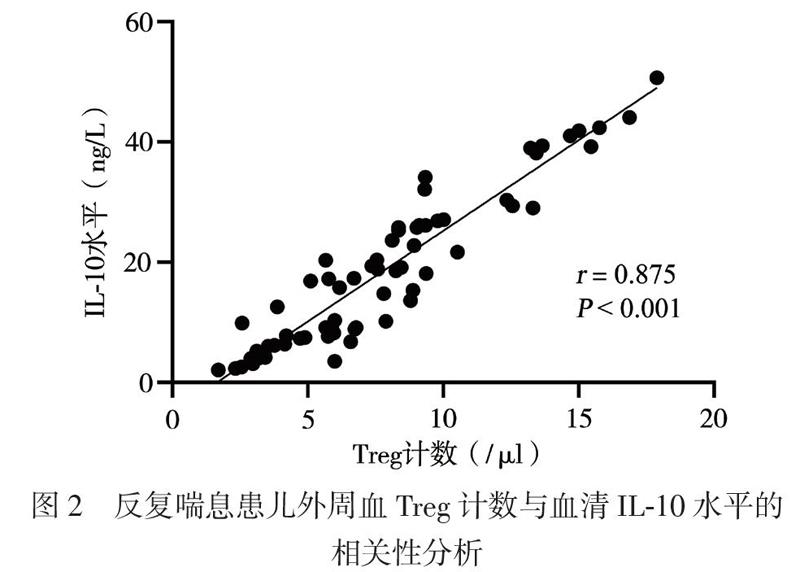
【摘要】目的 研究CD4+CD25+叉頭样转录因子3阳性(Foxp3+)调节性T淋巴细胞(Treg)及相关细胞因子、总IgE(TIgE)、特异性IgE(sIgE)在有或无特应征反复喘息幼儿外周血介导的免疫应答差异,为幼儿喘息性疾病的发展预测及治疗提供新思路。方法 选择反复喘息幼儿45例,分为特应征组22例和非特应征组23例,另选20名健康幼儿作为健康对照组,分别检测3组幼儿外周静脉血Treg计数和血清IL-10、IL-4、IL-5、IL-13、IFN-γ、TGF-β及TIgE、sIgE水平。结果 特应征组吸入及食入变应原sIgE阳性率高于非特应征组(P均 0.05),均高于对照组(P均 0.05), which were significantly higher than that in the control group (both P < 0.05). In children with repeated wheezing, the proportion of peripheral blood Treg cells was positively correlated with serum IL-10 levels (r = 0.875, P < 0.001). Conclusions Peripheral blood Treg cells, IL-10, IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, TGF-β and IFN-γ may be involved with the infantile wheezing, and play an immunomodulatory role in allergic diseases. The counts of peripheral blood Treg cells is positively correlated with the serum IL-10 levels in infants with repeated wheezing. Treg and IL-10 may serve as novel targets for early prediction and treatment of repeated wheezing in the future. ......
您现在查看是摘要页,全文长 9516 字符。