电针对全脑缺血大鼠学习记忆能力和海马神经元超微结构的影响
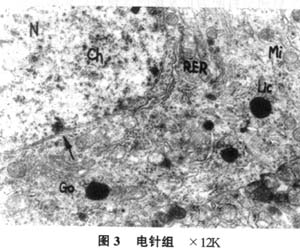 |
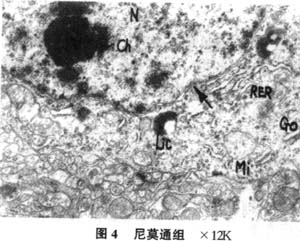 |
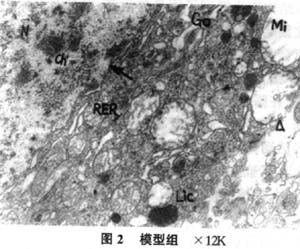 |
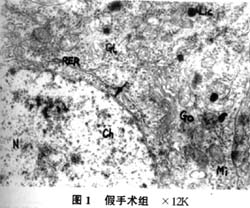 |
 |
(广州中医药大学,广东510407)
[摘 要] 目的:探讨电针治疗血管性痴呆(VD)的疗效及可能机制。
方法:实验用4血管阻断模型,用Morris水迷宫测定大鼠学习记忆能力,并用电镜观察鼠脑海马神经元的超微结构变化。
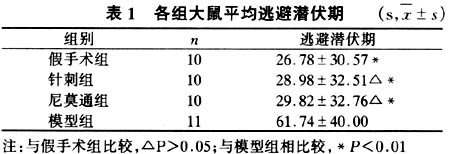
结果:模型大鼠表现明显的学习记忆障碍,逃避潜伏期显著延长;在原平台象限跨越平台次数未明显高于其余3个象限;海马神经元超微结构发生明显改变,神经元损害严重。电针及尼莫通组能显著缩短定位航行试验的逃避潜伏期;在原平台象限跨越平台次数显著多于其余3个象限,与假手术组比无显著差异;海马神经元超微结构变化相对较轻,神经元受损程度明显轻于模型组。
[主题词] 电针;海马/超微结构;学习/针灸效应;记忆/针灸效应;脑缺血/针灸疗法
EffectsofElectroacupunctureonLearningandMemoryAbilityandUltrastruct
uresofHippocampusNeuronsinRatsofWholeCerebralIschemiaWangLi,LaiXinsheng,LeiWeiwei(GuangzhouUniversityofTCM,Guangdong5104
07,China)[Abstract] Purpose
Toobserveeffectsofelectroacupuncture(EA)
onlearningandmemoryabilityandneuronsofhip
pocampusintheratofvasculardementia(VD).Methods
Infourvesselsocclusion(4vo)modelrats,Morriswatermazetestswereusedforbehaviouralstudy.
Ultrastructuralchangesofneuronsinhippocampuswereobservedwithtransmi
ssionelectronmicroscope.Results
Themodelanimalsneededmoreescapetime(latency)
thanthecontrolanimalsinplacenavigationtest,andtheydidnotswimmoretimesinplatformquadrantthanintheothersinspatia ......
您现在查看是摘要页,全文长 9374 字符。