慢性心力衰竭患者外周血中sCD14水平变化及临床意义(1)
 |
 |
[摘要] 目的 研究心力衰竭患者外周血sCD14水平的变化特点,探讨sCD14水平与慢性心力衰竭患者心功能及单核细胞的相关性。方法 选取慢性心力衰竭患者126例,入院次日清晨抽取静脉血,并以50例健康人作为对照。根据NYHA分级将慢性心力衰竭患者按心功能I、II、III、IV四个等级分为四组。ELISA法测定血清中的sCD14含量,并计算外周血中单核细胞的数量及百分比。结果 心功能I、II级慢性心力衰竭患者外周血清中sCD14水平、单核细胞数量及百分比与健康对照组相比无明显差异(P>0.05),心功能III、IV级慢性心力衰竭患者外周血中sCD14水平、单核细胞数量及百分比与健康对照组及心功能I、II级患者相比均显著增加(P<0.05);心衰患者sCD14水平与心衰分级、单核细胞数量及百分比均呈显著正相关(r=0.731,P=0.011;r=0.872,P=0.013;r=0.769,P=0.027)。结论 慢性心力衰竭患者外周血中的sCD14水平随着心功能加重而逐渐增高。
[关键词] 慢性心力衰竭; 细胞因子; 可溶性CD14(sCD14); 单核细胞
[中图分类号] R541.6 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-9701(2009)23-17-03
The Research of the Levels of Soulable-CD14 in Peripheral Blood in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure
WU Xiuping
The Department of Medicine Out-patient of Yanling Hospital ofGuangdong Province,Guangzhou,510507,China
[Abstract] ObjectiveTo investigate the levels of soulable-CD14(sCD14) in peripheral blood in patients with chronic heart failure and the correlation of the level of sCD14 with the quantities of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Methods126 patients with chronic heart failure were assigned four groups according to NYHA(NYHA I group,NYHA II group,NYHA III group and NYHA IV group),and 50 healthy volunteers were enrolled as control group. The levels of sCD14 in peripheral blood were measured by ELISA and calculated the the quantities of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. ResultsThere were no difference of the levels of sCD14 and the quantities of mononuclear cells in NYHA I group and NYHA II group compared with control group(P>0.05). The levels of sCD14 and the quantities of mononuclear cells in NYHA III group and NYHA IV group were significantly higher than those in NYHA I group,NYHA II group and control group(P<0.05). The levels of sCD14 were markedly positively correlated with heart function classification and the quantities of mononuclear cells respectively(r=0.731,P=0.011;r=0.872,P=0.013;r=0.769,P=0.027). ConclusionThe levels of sCD14 were significantly increased with the increasing of severity degree of heart function.
[Key Words]Chronic heart failure; Cytokine; Soulable-CD14; Mononuclear cells
可溶性CD14(sCD14)参与调控炎症因子的释放,大量的实验表明炎症因子在慢性心力衰竭的发生与发展过程中起着重要的作用[1],但慢性心力衰竭患者外周血中的sCD14水平如何尚未见报道。
本研究旨在研究慢性心力衰竭患者外周血中sCD14水平的变化特点,探讨sCD14水平与慢性心力衰竭患者临床症状严重程度的相关性。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
选取我院内科临床确诊无明显肺部感染的慢性心力衰竭患者126例,其中男性78例,女性48例;年龄33~81岁;排除血液病、肿瘤及严重肠道疾病等。
根据NYHA分级方案将慢性心力衰竭患者按心功能I、II、III、IV四个等级分为a、b、c、d四组,根据临床症状轻、中、重程度分为a、b、(c+d)三组,另选择健康体检者50例作为对照组,年龄40~79岁。
1.2 标本采集及处理
入院次日清晨静脉采血5mL,促凝,3000r/min 离心4min,取血清置于-20℃冰箱保存待测;EDTA-K2 抗凝管采静脉血2mL,用于血细胞分析。
1.3 方法
1.3.1 sCD14测定方法 采用莱德尔公司sCD14 Human ELISA Test Kit,按试剂盒说明书操作采用Bio Rad 公司Bench mark酶标仪制定标准曲线和样本检测。
1.3.2 单核细胞数量及比率的测定 采用日本东亚1800i五分类细胞仪,检测EDTA抗凝静脉血细胞,计算单核细胞数量及比率。
1.4 统计学处理
所有的数据采用均数±标准差(χ±s)表示,使用SPSS13.0统计软件处理数据,多组均数比较采用方差分析。相关性分析采用直线相关回归。P<0.05表示差异有显著性。
2 结果
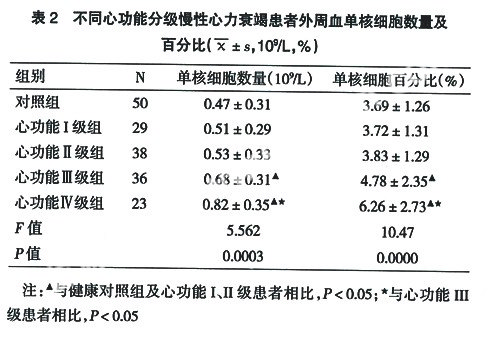
2.1 不同心功能分级慢性心力衰竭患者外周血中sCD14水平
心功能I、II级慢性心力衰竭患者外周血清中sCD14水平比健康对照组相比无明显差异(P=0.7610;P=0.3620),心功能III、IV级慢性心力衰竭患者外周血中sCD14水平与健康对照组及心功能I、II级患者相比均显著增加(P=0.0002,P=0.0269,P=0.0319;P=0.000,P=0.0001,P=0.0001)。见表1。, 百拇医药(伍秀萍)