PD-1/PD-L1相关免疫逃逸机制在头颈部鳞状细胞癌中的研究进展
季一鸣 孙乐刚 王岳 张凌楠 马向瑞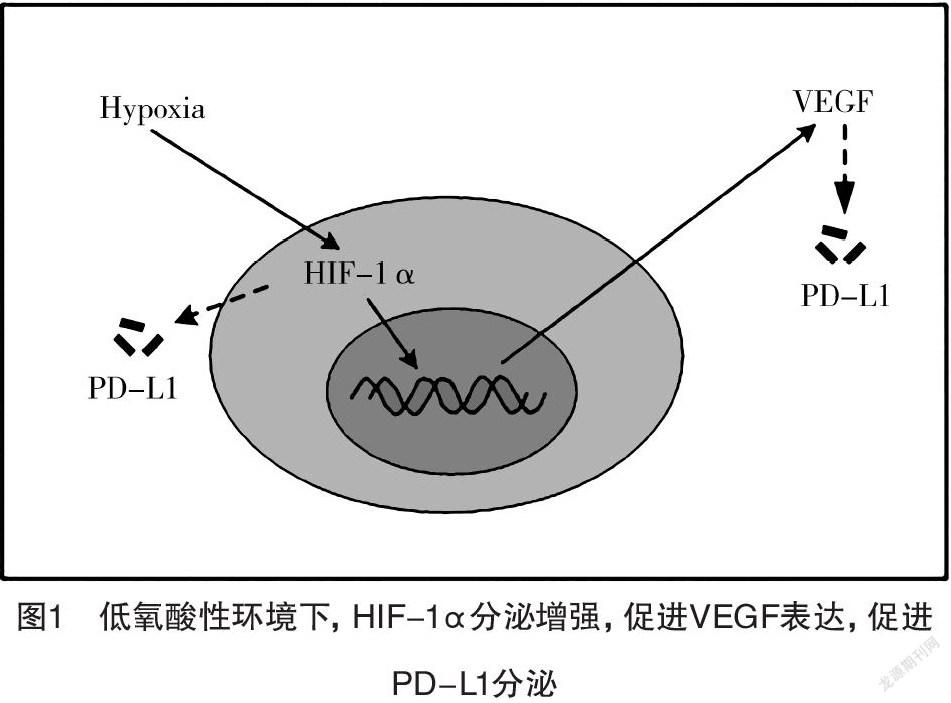
【摘要】 肿瘤细胞利用免疫检查点逃避免疫监视是肿瘤发生发展的重要步骤之一。程序性细胞死亡受体-1(programmed cell death protein 1, PD-1)/程序性细胞死亡配体-1(programmed cell death ligand 1, PD-L1)是参与肿瘤免疫逃逸过程重要的调节因子,与肿瘤的发生发展及预后密切相关。以PD-1/PD-L1为主要靶点的免疫疗法近年来在临床上取得了显著疗效。本文就PD-1/PD-L1参与肿瘤细胞免疫逃逸的机制及其在头颈部鳞状细胞癌(head and neck squamous cell carcinoma,HNSCC)免疫治疗中的应用现状及前景进行综述。
【关键词】 头颈部鳞状细胞癌 程序性细胞死亡受体-1 程序性细胞死亡配体-1 免疫逃逸 预后
[Abstract] Escape of immune surveillance using immune checkpoints by tumor cells is one of the important steps in tumorigenesis and development. Programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) and programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) are important regulators involved in tumor immune escape, and closely related to the occurrence, development and prognosis of tumors. Immunotherapy with PD-1 and PD-L1 as the main target has yielded significant therapeutic effects in recent years. This article reviews the PD-1 and PD-L1 mechanism involved in tumor cell immune escape and its current applications and prospects in immunotherapy of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. ......
您现在查看是摘要页,全文长 15449 字符。