急性脑血管病卒中后抑郁相关因素的临床分析
 |
 |
 |
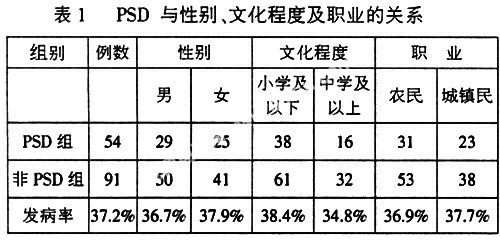 |
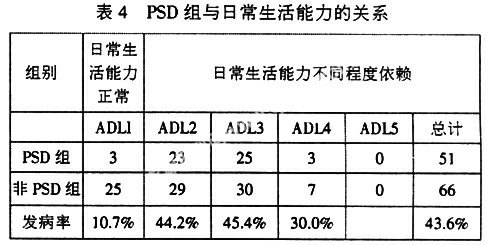
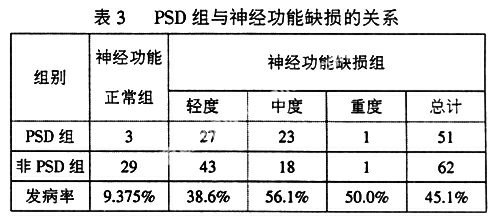
摘 要目的:探讨脑卒中后急性期抑郁的发生率及相关因素。方法:因脑血管病住院或门诊治疗急性期145例患者用自制的一般情况调查表、汉密尔顿抑郁量表、改良的爱丁堡斯堪的那维亚神经功能缺损评分表及日常生活能力量表进行调查、评分。结果:脑卒中后抑郁的发生率为37.2%。抑郁的发生与性别、职业、文化程度及病灶部位没有关系。与神经功能缺损及日常生活能力依赖有密切关系。结论:脑卒中后抑郁是脑卒中的常见并发症。与神经功能缺损、日常生活能力依赖等有密切关系。为早期预防脑卒中后抑郁的发生提供依据。
关键词脑卒中;抑郁状态;神经功能
AbstractObjective:To explore the incidence and relative factors of Post Stroke Depression (PSD). Methods:145 patients with acute stroke were evaluated and investigated by Hamilton depression rating scales (HAMD),neurologic deficit scale and self-designed personality questionnaire. Results:The incidence rate of PSD was 37.2%. PSD had positively relation to neurologic deficits and activities of daily living. PSD was not related to age, occupation, level of education and the location of focus. Conclusion:PSD was a common complication of stroke. It was positively related to neurological deficits and activities of daily living.The factors above provided basis for PSD prevention.
Key words stroke;depression state;neurologic function
脑卒中具有高死亡率和高致残率的特点 ......
您现在查看是摘要页,全文长 4881 字符。