颈动脉粥样硬化与血管性认知功能损害的相关性研究
 |
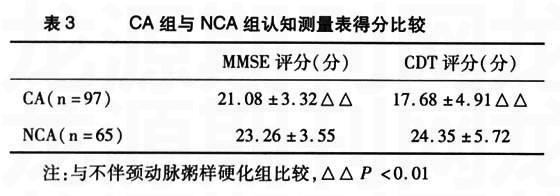 |
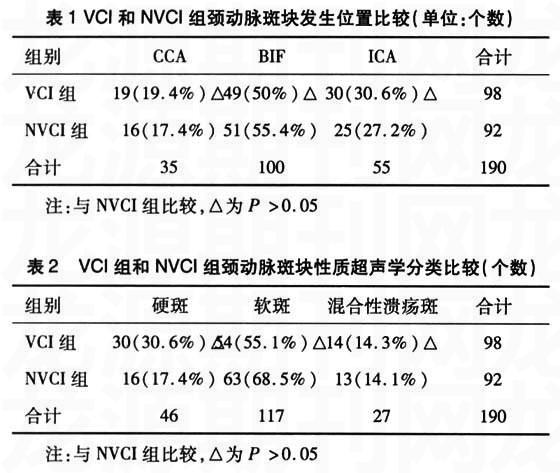
【摘要】目的:观察颈动脉粥样硬化对血管性认知功能损害的影响。 方法:选择162名腔隙性脑梗塞患者,进行神经心理检查和颈动脉超声检查,分为VCI组(研究组)67名和认知功能正常组(对照组)95名,并对二组的颈动脉粥样硬化情况进行分析。 结果:伴颈动脉粥样硬化患者VCI的发病率明显高于不伴颈动脉粥样硬化的腔隙性脑梗塞患者,腔隙性脑梗塞VCI者颈动脉粥样硬化的发病率明显高于认知功能正常的腔隙性脑梗塞患者,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。伴有颈动脉粥样硬化(CA)者在MMSE、CDT评分上表现出更差的得分,与NCA者比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。讨论:颈动脉粥样硬化与VCI的发生有密切关系。
【关键词】颈动脉粥样硬化;腔隙性脑梗塞;血管性认知功能损害
Relationship between carotid atherosclerosis and vascular cognitive impairment
XIAO Zhuyun,SHI Dan,BAO Xiao-min
(Shanghai Traditional Chinese Medicine University Affiliated Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Chinese
and Western Medicine,Shanghai,200437)
【Abstract】 Objective:To investigate the relationship between carotid atherosclerosis and vascular cognitive impairment. Methods:162 in-patients were selected.Neuropsychology examination and ultrasonic of the carotid artery were performed in all the patients and the patients were divided into two groups. Results The VCI incidence of infarction with AS was also higher than those NAS. The morbidity of carotid atherosclerosis in VCI group was remarkably higher than normal cognitive group, its difference was significance. The correlation between carotid atherosclerosis and MMSE and CDT were obviously inversed. Conclusions:There are close relationship between carotid atherosclerosis and vascular cognitive impairment. ......
您现在查看是摘要页,全文长 6423 字符。